
Introduction
Overview of Firewalls
A firewall serves as the frontline defense in cybersecurity, acting as a barrier between an internal network and potential external threats. Imagine a medieval castle: the walls protect against invaders, just like firewalls shield sensitive data from cybercriminals. Firewalls monitor incoming and outgoing traffic, ensuring that only legitimate communications are allowed while blocking harmful activities.
There are various types of firewalls, each designed to cater to different security requirements. Whether it’s a simple packet filtering firewall or a sophisticated next-generation firewall, each serves a unique purpose in the cybersecurity landscape.
Importance of Firewalls in Cybersecurity
The importance of having a robust firewall cannot be underestimated in today’s digital world. Here are key reasons why firewalls are crucial for cybersecurity:
- Protection Against Cyber Attacks: They act as the first line of defense against malware and unauthorized access.
- Data Security: By controlling traffic, firewalls help safeguard sensitive information from breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many organizations are required to meet specific regulations regarding data protection; firewalls play a pivotal role in achieving compliance.
In short, understanding firewalls is crucial to establishing a secure network environment, making them indispensable in modern cybersecurity strategies.
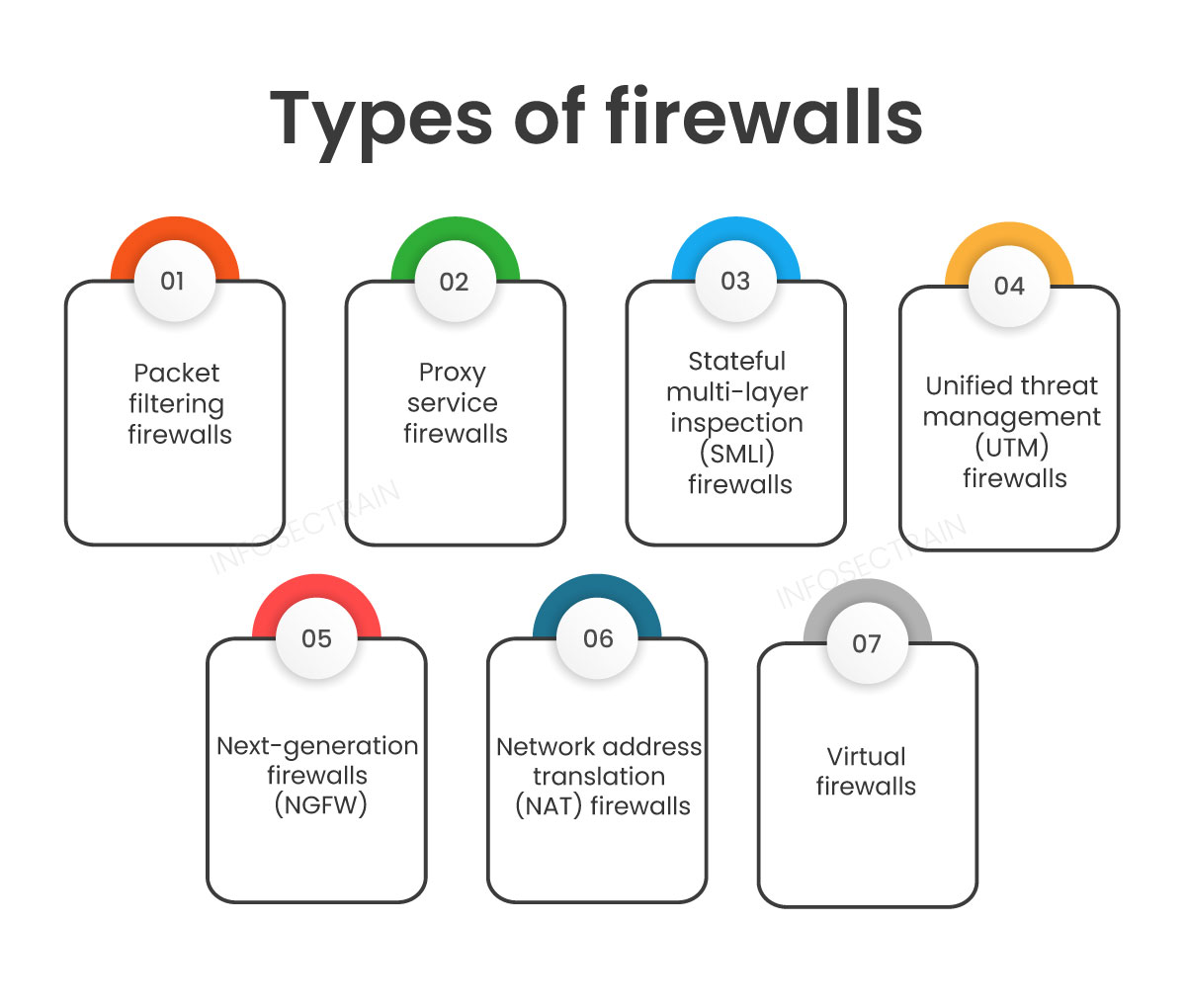
Types of Firewalls
Packet Filtering Firewalls
Among the simplest forms of firewalls, packet filtering firewalls examine data packets that enter or exit the network. They analyze the headers of packets, checking for specific attributes such as source/destination IP addresses and port numbers. If the configured rules permit the traffic, the packets pass through; otherwise, they get blocked.
- Key Features:
- Speedy processing as no deep analysis occurs
- Less resource-intensive
- Basic level of protection
However, they can be less effective in identifying sophisticated threats, making them insufficient for complex network environments.
Stateful Inspection Firewalls
Stateful inspection firewalls go a step further. They track the state of active connections and make decisions based on the context of traffic. This means they can recognize established connections and differentiate them from unsolicited requests.
- Advantages:
- Provides enhanced security than packet filtering
- Better at managing multiple connections
These firewalls enable more sophisticated traffic filtering while still maintaining optimal performance.
Proxy Firewalls
Proxy firewalls act as intermediaries between users and the internet. They intercept requests and responses, adding an additional layer of security by masking the user’s IP address online.
- Benefits:
- Content filtering and malware scanning
- Anonymity for users
These firewalls are particularly effective for organizations requiring stringent security measures.
Next-Generation Firewalls
Next-generation firewalls (NGFW) incorporate advanced features that previously required multiple standalone systems. They combine traditional firewall capabilities with features like intrusion detection and prevention, deep packet inspection, and application awareness.
- Why Choose NGFW:
- Protection against complex threats
- Ability to handle the demanding nature of modern traffic
In an era where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, investing in the right kind of firewall is essential for robust cybersecurity. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses, so understanding them is critical for making informed decisions tailored to specific network security needs.

How Firewalls Work
Filtering Traffic
At the heart of a firewall’s function is its ability to filter traffic. Think of it as a digital doorman who decides who gets in and who stays out. Firewalls utilize predefined rules to inspect packets of data and, based on these rules, either allow or block them.
- Common Criteria for Filtering:
- Source and destination IP addresses
- Port numbers
- Protocols (e.g., TCP, UDP)
This process ensures that only legitimate traffic reaches the internal network while blocking potentially harmful data.
Monitoring Network Connections
Beyond filtering, firewalls continuously monitor network connections, analyzing traffic patterns for any anomalies. This ongoing oversight helps organizations detect unusual activity that could indicate a security breach.
- Important Monitoring Aspects:
- Active connections
- Data flow frequency
- Source of incoming data
By maintaining vigilance, firewalls create an environment where threats can be promptly identified and addressed.
Setting Access Control Rules
Another critical feature of firewalls is their ability to set access control rules tailored to organizational needs. Administrators can define who or what can access specific resources on the network.
- Examples of Access Control:
- User authentication protocols
- Time-based access restrictions
- Role-based access control
These customizable rules ensure that sensitive information remains protected while allowing authorized users to maintain their productivity. Overall, understanding how firewalls work equips organizations to deploy them effectively, safeguarding their networks against emerging threats.

Importance of Firewalls
Protecting Against Cyber Attacks
In the digital age, cyber attacks are not just a possibility—they’re an inevitability. Firewalls are the first line of defense that protect networks from a myriad of threats, including viruses, spam, and unauthorized access. By filtering out potentially harmful traffic, firewalls help prevent attacks before they can penetrate the network.
- Key Benefits of Firewall Protection:
- Detects and blocks malicious traffic
- Prevents unauthorized access to internal resources
- Reduces the risk of data breaches
One personal experience comes to mind: at a previous workplace, a well-configured firewall thwarted a DDoS attack, preventing what could have been catastrophic downtime.
Securing Sensitive Data
With increasing amounts of sensitive data being generated—be it customer information, financial records, or proprietary business intelligence—firewalls play a crucial role in keeping this data safe. They monitor and control the flow of information, guarding against data leaks and theft.
- Protection Methods:
- Encryption of sensitive data
- Comprehensive auditing of data access
Organizations that prioritize firewall security are better equipped to safeguard their valuable information assets.
Compliance with Regulations
Many industries are governed by stringent regulations regarding data security, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Firewalls help organizations comply with such standards by ensuring that unauthorized access is minimized and that sensitive information is properly secured.
- Key Compliance Aspects:
- Documentation of access controls
- Regular monitoring and reporting of security incidents
In conclusion, firewalls are not merely optional security components; they are vital in creating robust cyber defenses, ensuring data integrity, and maintaining compliance in an increasingly threatening digital landscape.

Choosing the Right Firewall
Assessing Security Needs
Selecting the appropriate firewall begins with a thorough assessment of your security needs. Every organization operates in a unique threat landscape, so understanding what you’re protecting is crucial. Start by identifying:
- Types of Data: Consider the sensitivity of the information handled, such as personal data, financial records, and intellectual property.
- Potential Threats: Analyze the most likely attack vectors suited to your industry.
- User Groups: Understand who will access the network and their security requirements.
For instance, when I transitioned to a new company, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of our data assets, which directly influenced our choice of firewall.
Considering Network Infrastructure
Next, evaluate your network infrastructure. The type of firewall needed can vary based on the complexity and scale of your network. Key points to consider include:
- Network Size: Larger networks may require more advanced firewalls capable of handling heightened traffic.
- Integration Needs: Ensure compatibility with existing security tools, routers, and switches.
- Cloud vs. On-Premise: Decide if you need a cloud-based firewall or a traditional on-premise solution based on your remote/work-from-home policies.
Budget Considerations
Finally, budget constraints will play a significant role in your firewall decision. Firewalls come in a wide range of prices, from basic options to high-end ones with advanced features.
- Cost vs. Benefit: Consider not only the purchase price but also ongoing costs like subscriptions, updates, and maintenance.
- Long-Term Value: Investing in a robust firewall can save money in the long run by preventing breaches and downtime.
By thoughtfully assessing these factors, organizations can choose the right firewall tailored to their specific needs, ultimately reinforcing their cybersecurity posture.

Implementing and Managing Firewalls
Installation Process
Once you’ve chosen the right firewall, the installation process is the next critical step. Depending on the type of firewall—hardware or software—the installation may vary. For instance, hardware firewalls can be plugged in between your network’s modem and router, while software firewalls are typically installed directly on devices.
- Basic Steps to Follow:
- Assess the network layout and identify optimal installation points.
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for physical setup or installation.
- Confirm connectivity with network devices after installation.
I remember the excitement of deploying our first hardware firewall, as it felt like a significant leap forward in enhancing our cyber defenses.
Configuring Firewall Settings
Configuring firewall settings is where the real magic happens. This step involves creating rules that dictate what traffic is allowed and what should be blocked.
- Key Configurations to Consider:
- Define access control lists (ACLs)
- Set permission levels for different user groups
- Enable logging features for tracking and analysis
By taking the time to customize settings, businesses can ensure their firewall meets their specific security posture.
Monitoring Firewall Activity
The final stage in managing firewalls is continuous monitoring of activity. This step is crucial for detecting and responding to potential threats.
- Monitoring Techniques:
- Regularly review logs for unusual patterns
- Utilize alerts for suspicious activities
- Periodically conduct health checks and audit reviews
Incorporating a monitoring strategy not only enhances security but also helps organizations adapt to changing threat landscapes. Overall, effective implementation and management of firewalls lay the groundwork for a more secure network environment.

Best Practices for Firewall Security
Regularly Updating Firewall Software
One of the cornerstone best practices for firewall security is to regularly update firewall software. Cyber threats are ever-evolving, and keeping your firewall software updated ensures you are protected against the latest vulnerabilities.
- Update Frequency Recommendations:
- Monthly checks for updates
- Immediate application of critical patches
In my previous role, we encountered a near-breach incident simply because our firewall software wasn’t updated in time, showcasing the importance of staying current.
Monitoring Network Traffic
Monitoring network traffic is another vital practice that helps in identifying suspicious activities early. A firewall alone cannot guarantee protection; proactive oversight is essential.
- Effective Monitoring Techniques:
- Use analytics tools to visualize traffic patterns
- Set up alerts for unusual spikes in activity
- Analyze logs for unauthorized access attempts
By diligently monitoring network traffic, organizations can swiftly tackle potential threats before they escalate.
Conducting Firewall Audits
Conducting regular firewall audits is crucial for maintaining optimal security standards. These audits evaluate the effectiveness of the firewall rules and overall performance.
- Benefits of Audits:
- Identifying configuration errors or misconfigurations
- Ensuring compliance with internal and external security policies
- Gaining insights into necessary improvements
At my last company, a scheduled audit revealed outdated rules that no longer aligned with our security needs, resulting in immediate action and strengthened defenses. Together, these best practices for firewall security create a robust framework for safeguarding your network against emerging threats.

Conclusion
Recap of Firewall Types and Importance
As we wrap up our discussion on firewall security, it’s essential to recap the types of firewalls and their vital role in cybersecurity. From the simple packet filtering firewalls that act as the first line of defense to next-generation firewalls equipped with sophisticated features, each type serves its unique purpose. Firewalls protect against cyber attacks, secure sensitive data, and ensure compliance with industry regulations—making them indispensable in today’s digital landscape.
Just a few months ago, I witnessed first-hand how upgrading to a next-generation firewall significantly improved my organization’s security posture, highlighting the undeniable value of staying informed about firewall options.
Future Trends in Firewall Technology
Looking ahead, several trends will shape the future of firewall technology. With increasing reliance on cloud computing, cloud firewalls are becoming more prominent, offering flexibility and scalability. Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence will enable firewalls to predict and respond to threats more effectively.
- Key Trends to Watch:
- Increased automation in threat detection
- Enhanced cloud-based firewall solutions
- Focus on zero-trust architecture
By staying updated on these trends, organizations can better prepare for evolving cyber threats, ensuring their defenses remain robust and effective.

