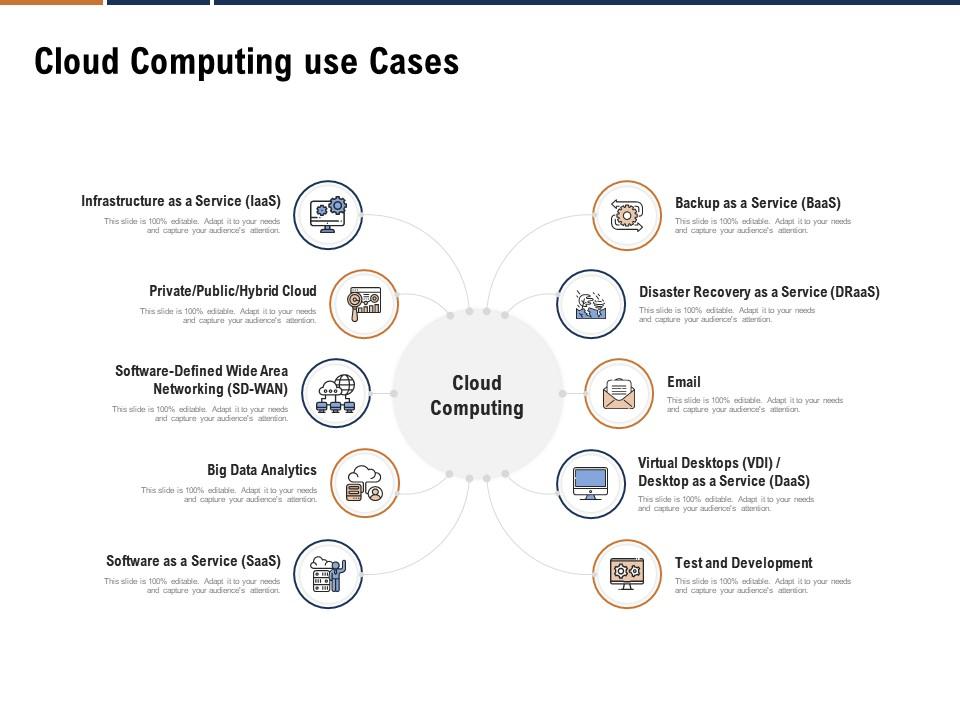
Introduction
Overview of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses operate, providing them with flexible resources accessible over the internet. Imagine being able to store vast amounts of data, run complex applications, or collaborate with your team from anywhere in the world, all without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure. This shift to a cloud-centric environment has enabled enterprises to enhance their operational efficiency significantly.
Importance of Cloud Computing in Enterprises
For businesses today, cloud computing is not just a trend; it’s essential. Here are a few reasons why:
- Cost Savings: Transitioning to the cloud can significantly reduce IT expenses.
- Flexibility: Companies can scale their resources based on demand.
- Collaboration: Teams can work seamlessly no matter where they are.
Personal experiences shared by organizations have highlighted how cloud solutions have led to increased productivity and improved decision-making processes. With these capabilities, it’s clear that embracing cloud technology is no longer optional for enterprises aiming to stay competitive in today’s digital landscape.
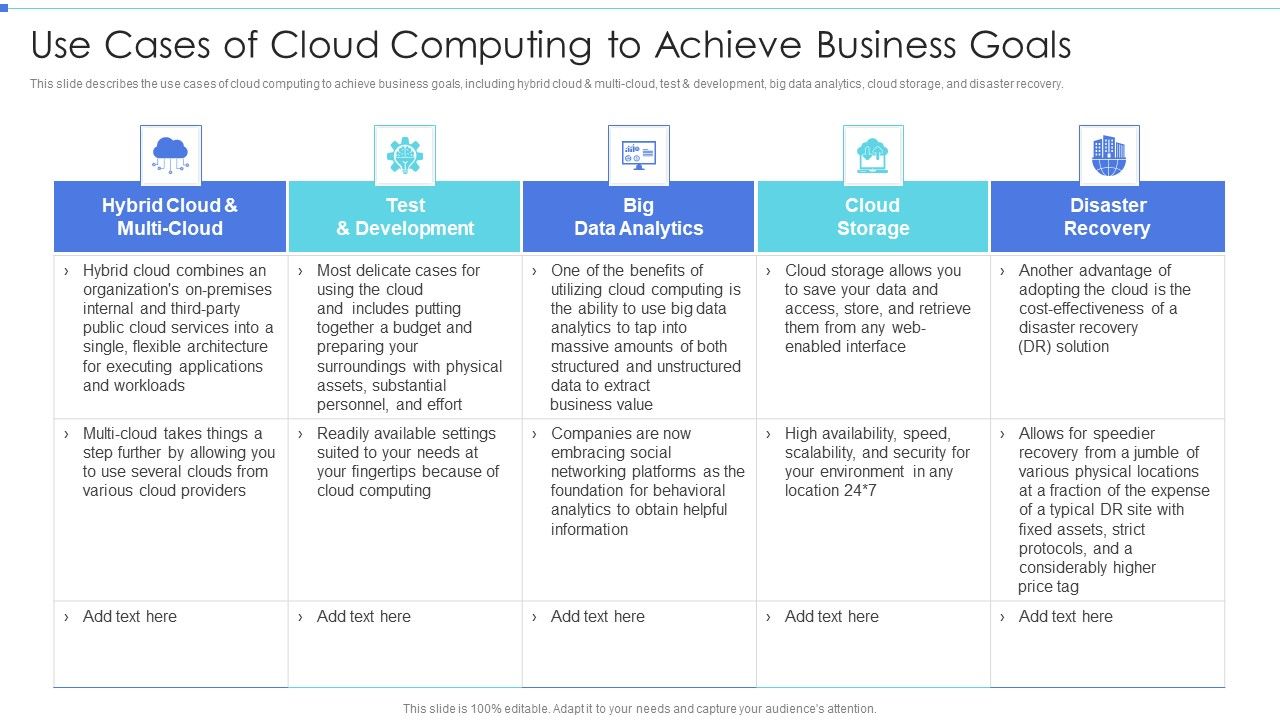
Cost Efficiency and Scalability
Cost Reduction with Cloud
One of the most appealing advantages of cloud computing is its potential for cost reduction. By moving to the cloud, businesses can minimize the need for expensive hardware and maintenance. Consider this: instead of investing capital in servers or data centers, companies can opt for a pay-as-you-go model. This shift means:
- Lower Initial Investment: No need for heavy upfront costs.
- Reduced Maintenance: Service providers handle hardware updates.
- Predictable Costs: Budgeting becomes easier with monthly subscriptions.
Many organizations have reported significant savings, allowing them to redirect resources toward growth initiatives.
Scalability Benefits of Cloud Computing
Scalability is where cloud computing truly shines. Gone are the days of over-provisioning resources. With the cloud:
- On-Demand Resources: Businesses can scale up or down as needed.
- Rapid Deployment: New applications or services can be launched quickly.
- Global Reach: Companies can easily expand to new markets without physical limitations.
For example, a startup can start small, experimenting with a few cloud services, then seamlessly grow to accommodate increased demand without the hassle of hardware constraints. This flexibility empowers businesses to innovate and adapt in the fast-paced digital landscape.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Cloud-Based Data Backup
With the increasing importance of data in today’s businesses, cloud-based data backup has become a lifesaver for many organizations. It provides a secure and reliable way to store critical information. Unlike traditional backup solutions, which can be cumbersome and costly, cloud backup offers:
- Automation: Regular backups happen seamlessly, reducing human error.
- Accessibility: Data can be accessed anytime, anywhere.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Only pay for the storage you use.
For instance, a small business can set up automatic backups to the cloud, easing the burden on IT staff and safeguarding vital information without the headaches of managing physical drives.
Disaster Recovery Solutions in the Cloud
Disaster recovery in the cloud takes protection a step further, offering businesses a structured plan to quickly recover data and restore normal operations after a disruptive event. The benefits include:
- Rapid Recovery: Minimize downtime with quick restoration processes.
- Geographical Redundancy: Data is continually replicated across multiple locations for enhanced security.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, disaster recovery plans can easily scale to meet new demands.
A real-world example is an e-commerce company that experienced a server failure. Thanks to its cloud disaster recovery solution, they were able to restore operations within hours, maintaining customer trust and minimizing financial loss. Embracing these cloud solutions ensures businesses can bounce back efficiently, protecting their future.
Flexibility and Mobility
Flexible Work Environments
As the modern workplace evolves, flexibility has become a key advantage of cloud computing. Organizations can create tailored work environments that cater to employee needs. By leveraging cloud technology, companies can offer:
- Remote Work Options: Employees can access files and applications from home or on the go.
- Collaborative Tools: Teams can work together in real-time using cloud-based platforms.
- Customizable Workspaces: Personalization enhances productivity and job satisfaction.
For example, a marketing agency found that allowing their team to work remotely increased creativity and collaboration, leading to better campaign outcomes.
Mobility Features in Cloud Computing
Mobility is another game-changer in the cloud ecosystem. With cloud-based solutions, employees are no longer tied to their desks. Benefits include:
- Access Anywhere: Employees can work from any location, on any device.
- Real-Time Updates: Changes are synced instantly, keeping teams aligned.
- Increased Responsiveness: Quick access to information enables faster decision-making.
Imagine a sales representative on a business trip who needs to pull up client data for a last-minute meeting. With the cloud, accessing this information is seamless. This flexibility and mobility not only enhance employee satisfaction but also boost overall efficiency within the organization.

Collaboration and Communication
Cloud-Based Collaboration Tools
In today’s fast-paced business environment, cloud-based collaboration tools are reshaping how teams work together. These platforms offer a blend of convenience and efficiency, making it easier than ever to connect and collaborate. Key advantages include:
- Centralized Document Sharing: Teams can store and access files in one place.
- Real-Time Editing: Collaborators can work on documents simultaneously, reducing turnaround time.
- Task Management Features: Assign tasks and set deadlines, all within the same platform.
For instance, a tech startup found that using a cloud-based project management tool significantly improved their workflow, allowing team members to work unified towards shared goals.
Enhanced Communication through Cloud Services
Cloud computing also enhances communication, bridging gaps that can hinder productivity. Here’s how:
- Integrated Messaging: Teams can chat, hold video calls, or send emails all in one system.
- Accessibility: Team members can communicate from anywhere, ensuring that critical information flows seamlessly.
- Application Integration: Link various services for smooth operations across platforms.
A sales team, for example, benefited from a cloud service that integrated communication and CRM tools, allowing for quicker responses to client inquiries. By enhancing collaboration and communication, businesses can drive better outcomes and foster a culture of teamwork and innovation.

Security and Compliance
Cloud Security Measures
As organizations embrace cloud computing, the focus on security becomes paramount. A robust cloud security strategy is essential to protect sensitive data and maintain trust. Effective security measures include:
- Data Encryption: Information is encrypted during transmission and storage, shielding it from unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): An extra layer of security ensures only authorized users gain access.
- Regular Security Audits: Frequent assessments help identify vulnerabilities and enhance security protocols.
For example, a financial services company enhanced its security posture by implementing these measures, leading to increased confidence among clients regarding data protection.
Compliance in Cloud Computing
Compliance regulations also play a significant role in cloud adoption. Different industries have specific requirements that must be met, including:
- Data Privacy Laws: Adhering to regulations such as GDPR for data handling practices.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Compliance with standards like HIPAA in the healthcare sector to protect patient information.
- Regular Reporting: Maintaining documentation to demonstrate compliance during audits.
One healthcare provider reported a smoother compliance process after moving to the cloud, thanks to the built-in features designed to meet regulatory requirements. By prioritizing security and compliance, organizations can safely harness the power of cloud technology while mitigating risks associated with data breaches and regulatory non-compliance.

Big Data Analytics
Utilizing Cloud for Big Data Analysis
The synergy between big data analytics and cloud computing is transforming how businesses operate today. Utilizing the cloud for big data analysis allows organizations to harness vast amounts of data without overwhelming their local infrastructure. The benefits are numerous:
- Scalable Resources: Easily adjust computing power based on the data volume.
- Advanced Tools: Access sophisticated analytics tools that may be costly on-premises.
- Data Integration: Seamlessly combine data from various sources for comprehensive analysis.
For example, a retail chain leveraged cloud resources to analyze customer purchasing patterns, allowing them to optimize inventory and improve sales strategies.
Benefits of Big Data Analytics in the Cloud
The advantages of conducting big data analytics in the cloud are compelling:
- Cost Savings: Reduced infrastructure costs, with payment models tailored to usage.
- Faster Insights: Real-time data processing enables immediate decision-making.
- Collaboration: Teams can share insights and findings instantly across locations.
A financial services provider, for instance, utilized cloud-based analytics to detect fraudulent transactions more swiftly, ultimately saving significant sums and enhancing customer trust. By embracing big data analytics in the cloud, organizations can unlock valuable insights and drive strategic initiatives, solidifying their competitive edge in the market.

Software Development and Testing
Cloud Environments for Development
The shift to cloud environments has revolutionized software development, offering developers the flexibility and resources they need. Working in the cloud allows teams to set up development environments quickly and efficiently, which can lead to increased productivity. Benefits include:
- Rapid Provisioning: Instantly create and configure development environments without the need for physical hardware.
- Collaboration Tools: Enhanced collaboration among team members, regardless of their geographical location.
- Resource Scalability: Easily adjust resources as project requirements evolve.
For instance, a startup utilized a cloud-based development environment that enabled their team to prototype new features in days rather than weeks.
Testing Applications on Cloud Platforms
Once the development phase is complete, testing on cloud platforms offers significant advantages. With the cloud, companies can:
- Access Diverse Testing Environments: Test applications across different operating systems and devices effortlessly.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Pay only for the resources used during testing, minimizing costs.
- Automated Testing: Utilize cloud-based tools for automated testing, ensuring quicker feedback cycles.
A notable example is a gaming company that was able to conduct extensive testing in the cloud, resulting in a smoother launch and enhanced user experience. By leveraging cloud environments for both development and testing, businesses can streamline processes and accelerate their software delivery timelines.
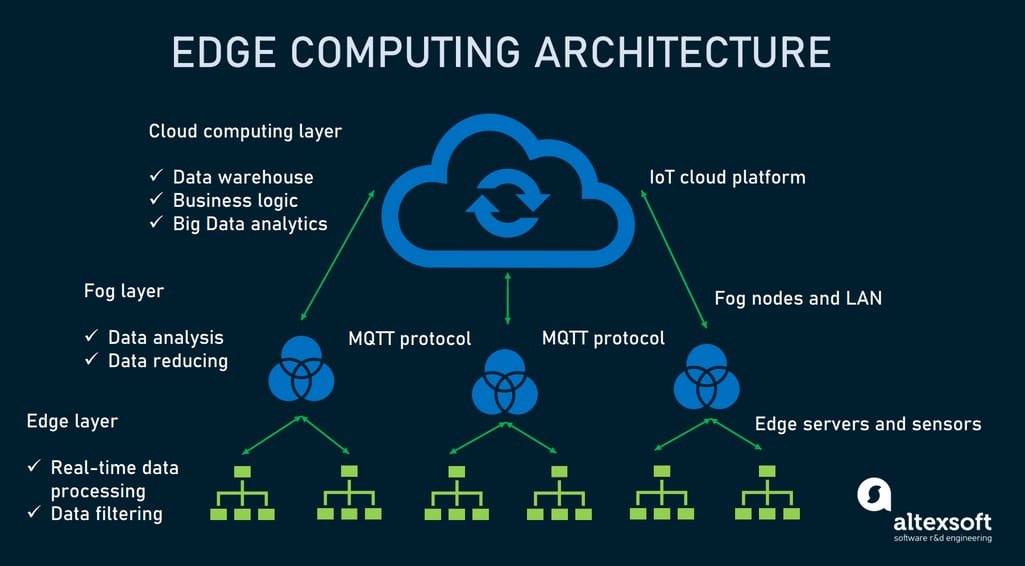
IoT and Edge Computing
Integration of IoT with Cloud
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with cloud computing is a game-changer for many industries. By utilizing the cloud, businesses can manage IoT data more effectively, leading to improved operational efficiency. Key benefits include:
- Centralized Data Management: Gather and analyze data from numerous IoT devices in one place.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources to accommodate the increasing influx of data from connected devices.
- Real-Time Insights: Generate actionable insights from data analysis in real-time.
For example, a smart city initiative used cloud integration to collect and process data from street sensors, optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion.
Edge Computing Capabilities in Cloud Systems
As IoT devices proliferate, edge computing enhances cloud systems by processing data closer to the source. This approach brings a range of advantages:
- Reduced Latency: Quick decision-making and response times for time-sensitive applications.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: Decrease the amount of data sent to the cloud by processing it at the edge, optimizing bandwidth usage.
- Reliability: Ensures functionality even when connectivity issues occur.
A manufacturing plant, for instance, deployed edge computing to analyze sensor data from machinery, enabling immediate adjustments to operations and minimizing downtime. This combination of cloud and edge computing empowers businesses to harness the full potential of IoT, driving innovation and efficiency across various sectors.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Cloud-Based CRM Solutions
In the realm of customer relationship management, cloud-based CRM solutions have transformed how businesses engage with customers. These systems offer flexibility and accessibility, allowing employees to interact with client data from anywhere. The key benefits include:
- Real-time Access: Teams can retrieve and update customer information instantly, improving responsiveness.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, cloud CRMs can easily scale to accommodate increasing data and user needs.
- Integrated Tools: Many cloud CRMs come with built-in marketing, sales, and customer service utilities, fostering a holistic approach to customer management.
For example, a growing e-commerce business adopted a cloud CRM and saw a notable improvement in their customer satisfaction scores.
Enhancing Customer Relationships through Cloud
Cloud CRM solutions also enhance customer relationships in several impactful ways:
- Personalized Experiences: Leverage data analytics to tailor interactions based on customer preferences.
- Collaboration Across Teams: Sales, marketing, and support teams can access the same customer insights, ensuring cohesive communication.
- Follow-Up Automation: Automatic reminders and follow-ups ensure timely engagement, keeping customers feeling valued.
One successful application involved a service organization that used their cloud CRM to automate customer feedback collection, leading to rapid response implementations. By utilizing cloud-based CRM systems, companies can build stronger, more meaningful connections with their customers, ultimately driving loyalty and satisfaction.

