
Understanding Cybersecurity Policy
Definition of Cybersecurity Policy
A cybersecurity policy serves as a formal document that outlines an organization’s stance on protecting its digital assets and sensitive information. This policy sets the framework for how cybersecurity threats are managed and mitigated across the organization. In essence, it’s like a detailed map guiding teams through the often-complex landscape of cybersecurity.
For instance, a cybersecurity policy might cover the following:
- Guidelines for secure password management.
- Procedures for reporting suspicious activity.
- Protocols for remote work and data access.
Role of Cybersecurity Policy in Organizations
The role of a cybersecurity policy in organizations cannot be overstated; it is foundational for building a strong security posture. Imagine you’re navigating through a dense forest without a compass—similarly, organizations without a cybersecurity policy may find themselves lost amid various threats.
Key roles include:
- Risk Mitigation: Establishing procedures that minimize the risk of data breaches.
- Employee Guidance: Providing clear instructions for employees to follow, enhancing overall security awareness.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring the organization meets industry standards and legal requirements, thus avoiding hefty fines.
In the end, a well-articulated cybersecurity policy not only safeguards digital assets but also fosters a culture of security consciousness within the organization.

Importance of Developing a Cybersecurity Policy
Risks of Not Having a Cybersecurity Policy
Failing to establish a cybersecurity policy is like leaving the front door wide open in a neighborhood known for break-ins. Without defined guidelines, organizations face numerous risks, including:
- Increased Vulnerability: Employees may unknowingly create security holes through poor practices.
- Data Breaches: Sensitive information can be compromised, leading to financial losses and reputation damage.
- Regulatory Penalties: Non-compliance with industry regulations can result in hefty fines and sanctions.
For example, imagine a small business with no policy in place; they may be blissfully unaware of the threats until a cyberattack hits, leading to devastating consequences.
Benefits of a Robust Cybersecurity Policy
On the flip side, a well-crafted cybersecurity policy brings a plethora of benefits. By committing to comprehensive policies, organizations can:
- Strengthen Defense Mechanisms: Robust policies enhance the overall security framework, making it hard for attackers to breach systems.
- Foster Employee Accountability: Clear guidelines empower employees to take ownership of cybersecurity, following best practices.
- Boost Customer Trust: Clients are more likely to engage with organizations that demonstrate a proactive approach to security.
In summary, developing a cybersecurity policy is not just a best practice—it’s a necessity. It protects an organization’s assets while cultivating a security-aware culture that benefits everyone involved.

Components of a Comprehensive Cybersecurity Policy
Access Control Policies
Access control policies are the gatekeepers of an organization’s data, determining who can view or interact with sensitive information. Think of it as a bouncer at an exclusive club—only authorized personnel can enter. Effective access control policies include:
- User Authentication: Methods like multi-factor authentication ensure that only the right people access sensitive data.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Employees are granted access based on their roles, minimizing unnecessary exposure to sensitive data.
Data Protection Guidelines
Data protection guidelines safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, loss, or corruption. Consider this as a trusted vault protecting valuable assets. Key elements of these guidelines encompass:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit prevents unauthorized users from making sense of it.
- Data Retention Policies: Establishing clear procedures on how long different types of data should be kept helps mitigate compliance risks.
Incident Response Plans
Incident response plans are essential for swiftly tackling cybersecurity incidents. When a cyber threat occurs, having a playbook can be the difference between chaos and control. Effective components include:
- Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Assigning specific team members to response actions ensures a well-coordinated effort.
- Communication Protocols: Clear guidelines on how to communicate during and after an incident help stakeholders stay informed and reduce panic.
These components work together to form a robust cybersecurity policy, ensuring organizations are prepared to defend against and respond to threats efficiently.

Creating and Implementing a Cybersecurity Policy
Assessment of Organizational Needs
The journey to crafting an effective cybersecurity policy begins with a thorough assessment of organizational needs. This phase is vital, as it helps identify vulnerabilities and specific areas where protection is required. Conducting a risk analysis might look something like this:
- Identify Critical Assets: Understand what data or systems are most valuable to your operations.
- Evaluate Current Security Measures: Review existing policies and technologies to spot gaps in protection.
For instance, during a recent audit, a medium-sized firm discovered their customer database was unencrypted—an alarming vulnerability they quickly addressed.
Drafting Policies and Procedures
Once the needs assessment is complete, it’s time to start drafting the policies and procedures. These documents should be clear, concise, and tailored to the organization’s specific requirements. Key elements to include are:
- Incident Reporting Procedures: How employees should report security incidents or suspicious activity.
- Acceptable Use Policies: Guidelines on how employees can properly use organizational technology.
A clear and accessible policy fosters compliance, making it easier for employees to adhere to security protocols.
Employee Training and Awareness
No cybersecurity policy can succeed without the active participation of its employees. Hence, training and awareness are crucial. Consider implementing:
- Regular Training Sessions: Schedule workshops to keep employees informed about the latest threats and best practices.
- Phishing Simulations: Test their responses to mock phishing attempts to gauge awareness and effectiveness of training.
As a personal anecdote, a friend of mine worked at a company that issued monthly cyber awareness newsletters, drastically decreasing the occurrence of phishing incidents.
By focusing on these steps, organizations not only create a robust cybersecurity policy but also cultivate a culture of security-mindedness, ensuring all members are part of the defense strategy.

Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Understanding Industry Standards
Compliance and regulatory considerations are paramount when developing a cybersecurity policy. Understanding industry standards is crucial to ensure that your policy is not only effective but also meets the required benchmarks. Different industries have various standards, such as:
- ISO 27001: Focuses on information security management.
- PCI-DSS: Mandatory for any organization handling credit card information.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Provides a flexible approach to managing cybersecurity risks.
For example, a healthcare provider must adhere to HIPAA regulations, ensuring patient information is safeguarded comprehensively.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Beyond industry standards, legal and regulatory compliance is a core component that organizations must navigate, often complicated by different jurisdictions. Key aspects to consider include:
- Data Protection Laws: Understanding laws such as GDPR and CCPA that govern how personal information is collected and processed.
- Breach Notification Requirements: Many jurisdictions require organizations to inform affected individuals within a certain timeframe after a data breach.
An interesting realization occurred when a local business faced a fine for not complying with data retention laws simply because they hadn’t kept themselves updated on regulatory changes. This highlights the need for ongoing diligence in these matters.
In summary, staying informed about industry standards and regulatory requirements is essential as they guide organizations in building a robust cybersecurity policy. Ignoring these elements could lead to both legal repercussions and reputational harm.

Monitoring, Review, and Continuous Improvement
Periodic Policy Reviews
As the cybersecurity landscape evolves, the importance of monitoring, reviewing, and continuously improving your cybersecurity policy becomes increasingly evident. Periodic policy reviews are essential to ensure that they remain relevant and effective. These reviews should be scheduled regularly—think of it like routine maintenance for your car to keep it running smoothly. Important steps include:
- Incorporating Feedback: Gather insights from employees on the policy’s effectiveness and areas needing improvement.
- Assessing Compliance: Check that the policy aligns with new regulations and industry standards.
For instance, a colleague in IT recalls how their organization saw a significant increase in employees reporting security incidents after updating the review process to include more frequent feedback loops.
Adapting to Emerging Threats
Cyber threats are continuously changing, making it essential to adapt your policies accordingly. Effective organizations remain vigilant about potential new threats by:
- Staying Informed: Regularly consult cybersecurity news sources to understand emerging trends and potential vulnerabilities.
- Conducting Threat Assessments: Assess potential impacts of new threats on existing policies, adjusting protocols to address these challenges.
Consider how numerous companies had to enhance their security measures in response to the rise of ransomware attacks. Being proactive helps prevent falling victim and demonstrates a commitment to safeguarding sensitive information.
In summary, effective monitoring, periodic reviews, and adaptation to new threats not only strengthen a cybersecurity policy but also foster a culture of awareness and responsiveness within an organization. This continual commitment to evolution reinforces trust among stakeholders.
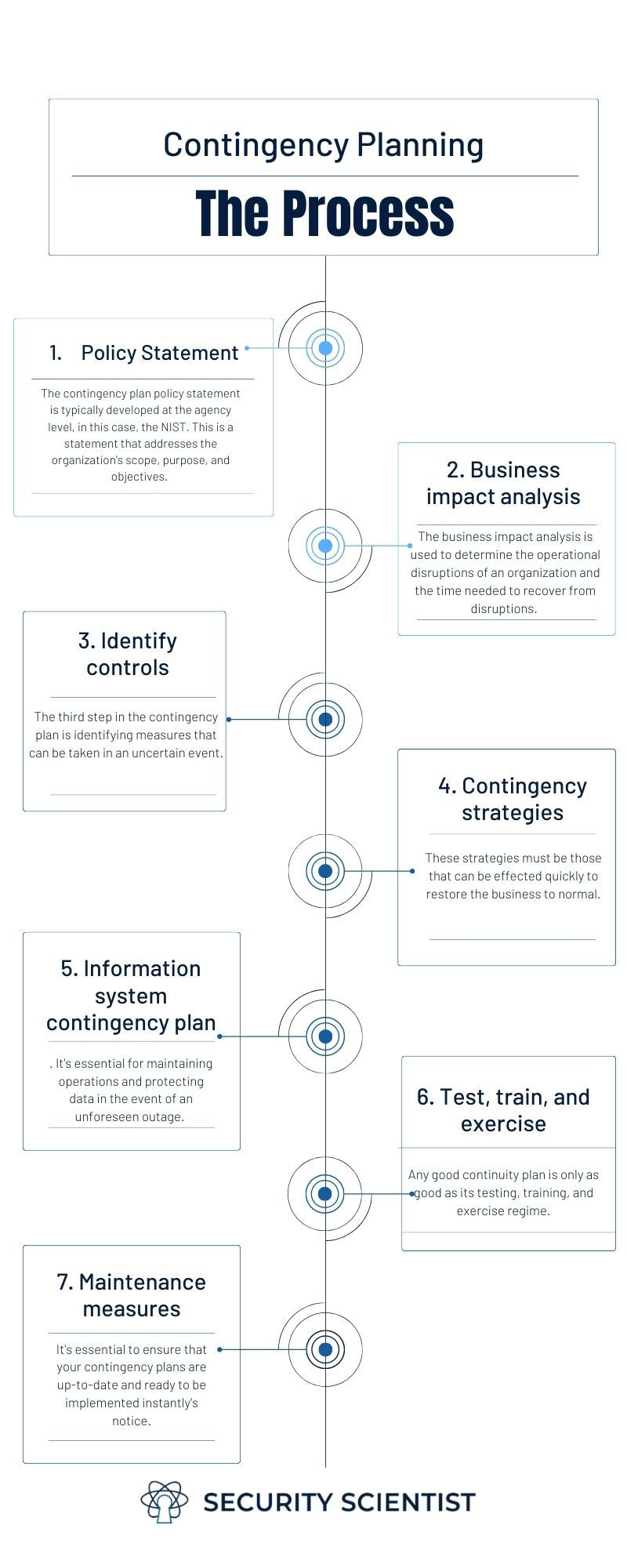
Incident Response and Contingency Planning
Establishing Incident Response Protocols
Having robust incident response protocols is crucial for mitigating the impact of cybersecurity incidents. These protocols act as a roadmap, guiding teams on how to effectively handle a crisis when it strikes. Effective protocols should include:
- Identification and Triage Procedures: Clearly define how incidents are detected and classified based on severity.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Assign specific tasks to team members, ensuring everyone knows their role during an incident.
A key memory for many is how a friend’s company successfully contained a data breach by swiftly activating their incident response plan, allowing them to minimize damage and inform affected customers promptly.
Creating Contingency Plans
Complementing incident response protocols, contingency plans prepare organizations for unexpected scenarios and ensure business continuity. These plans should outline:
- Backup Procedures: Regular data backups help restore systems quickly and reduce downtime.
- Communication Strategies: Define how information will be shared internally and with external stakeholders during an incident.
For example, a local business that experienced a ransomware attack had already established a comprehensive contingency plan, allowing them to recover operations seamlessly without extensive delays.
In essence, proactive incident response and effective contingency planning not only reduce the impact of threats but also strengthen an organization’s resilience, instilling confidence both internally and externally. By being prepared, organizations can move beyond merely reacting to threats and embrace a more strategic approach to cybersecurity.

Cross-functional Collaboration and Communication
Involving Different Departments
Cross-functional collaboration is vital for creating a well-rounded cybersecurity policy. When various departments—such as IT, HR, and legal—come together, the policy benefits from diverse perspectives and expertise. For example:
- IT Team: Provides insights on the technical aspects of security measures.
- HR Department: Ensures employee conduct and training align with cybersecurity best practices.
- Legal Team: Addresses compliance and regulatory requirements.
A memorable instance was when a company formed a cybersecurity task force comprising members from various departments to tailor the policy effectively. This collaborative effort enhanced the understanding of cybersecurity’s impact across the organization.
Communicating the Policy Across the Organization
Once developed, it’s crucial to communicate the cybersecurity policy effectively across the organization. Clear communication ensures that everyone understands their responsibilities. Strategies can include:
- Interactive Training Sessions: Engage employees with real-life scenarios to illustrate the importance of security.
- Regular Updates: Keep staff informed about any changes to the policy and emerging threats.
For instance, a company that used newsletters and internal webinars to disseminate cybersecurity updates noticed a marked increase in employee awareness and engagement.
In conclusion, fostering cross-functional collaboration and clear communication forms the backbone of an effective cybersecurity policy. By ensuring all departments understand their role, organizations can cultivate a culture of security that permeates every level of operation.

Measuring the Effectiveness of a Cybersecurity Policy
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measuring the effectiveness of a cybersecurity policy is crucial for understanding its impact and identifying areas for improvement. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) act as benchmarks to evaluate how well a policy is performing. Important KPIs to consider include:
- Incident Response Time: How quickly does the organization respond to security incidents? A shorter response time generally indicates better preparedness.
- Number of Security Breaches: Keeping track of the number and types of breaches can point to weaknesses in the existing policy.
- Employee Training Completion Rates: Monitoring how many employees have completed security training can reflect the organization’s commitment to fostering a security-aware culture.
A notable example involves a financial institution that tracked response times post-training; they found substantial improvements, showcasing the effectiveness of their educational efforts.
Assessing Policy Efficacy
To further assess the efficacy of a cybersecurity policy, organizations should conduct regular audits and evaluations. This can include:
- Simulated Attacks: Conducting penetration testing or phishing simulations allows organizations to see how employees react under pressure and where policies may fall short.
- Surveys and Feedback: Gathering employee feedback about the policy’s clarity and usability can uncover gaps and inform necessary revisions.
A buddy of mine from an IT department vividly remembers the insightful outcomes from a simulated attack, which revealed critical areas needing attention in their policy.
In sum, by leveraging KPIs and assessing policy efficacy through systematic reviews, organizations can fine-tune their cybersecurity strategies, fostering a safer environment and continuously improving their defenses against evolving threats.
Future Trends in Cybersecurity Policies
Artificial Intelligence and Automation
As we look towards the future, a significant trend in cybersecurity policy is the increasing reliance on artificial intelligence (AI) and automation. These technologies are transforming how organizations approach security, offering the ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data swiftly. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Threat Detection: AI can identify anomalies and potential threats much faster than traditional methods.
- Automated Responses: Automated systems can execute immediate actions without human intervention, such as isolating an infected device.
A colleague in cybersecurity shared how their organization implemented an AI-driven security solution to reduce response times dramatically, leading to proactive rather than reactive security measures.
Zero Trust Security Model Adoption
Another prominent trend is the adoption of the Zero Trust security model, which operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This paradigm shift mandates that every user and device, both inside and outside the network, must be authenticated and continuously verified. Key components include:
- Strict Access Controls: Only granting access to those who absolutely need it, thereby minimizing risk.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly auditing user activity to swiftly detect any suspicious behavior.
For example, a friend’s company successfully transitioned to a Zero Trust model, significantly decreasing their vulnerability to internal and external threats.
In conclusion, as cybersecurity policies evolve, embracing AI and the Zero Trust framework will be crucial for organizations aiming to enhance their security postures. By adopting these forward-thinking approaches, organizations can better navigate the increasingly complex cyber landscape, ensuring stronger defenses against emerging threats.

