Overview of Robotics in Future Industries
Definition of Robotics
At its core, robotics refers to the technology that encompasses the design, construction, operation, and use of robotic systems. These systems are often engineered to perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously, relying on a combination of hardware (physical components) and software (programming). Think of robotics as the bridge between mechanical engineering and computer science, giving rise to machines that can mimic certain human actions, such as lifting, moving, or analyzing data.
Evolution of Robotics in Industries
The journey of robotics in industries has been nothing short of remarkable. Initially, robots were primarily relegated to the automotive sector, where they performed repetitive tasks with precision.
- Decade-by-Decade Growth:
- 1960s-1980s: Introduction in manufacturing for assembly lines.
- 1990s-2000s: Advancement with sensors and AI, expanding into logistics and warehousing.
- 2010s-Present: Growth into diverse sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and service industries.
This evolution not only showcases technological advancements but also reflects how industries have increasingly embraced automation to enhance efficiency. For instance, in the manufacturing sector, robots now assist with quality control, reducing human error and increasing production rates. As industries continue to adapt, the integration of robotics promises to redefine operational possibilities and improve overall productivity.
The role of robotics in future industries will only expand as we move forward, revolutionizing the way we work and live.

Advantages of Implementing Robotics
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
As industries evolve, the pressure to deliver faster and more accurately intensifies. This is where robotics shine, significantly enhancing efficiency and productivity. Robots are designed to operate continuously without fatigue, allowing them to perform tasks at a pace and precision that often surpass human capabilities.
For example, in an automotive assembly line, robots can assemble components several times faster than a human worker. This leads to:
- Faster Production Cycles: Reduced lead times for manufacturing.
- Consistent Quality: Minimization of errors and defects in products.
The cumulative effect is a streamlined operation that ensures businesses can meet customer demand promptly.
Cost Reduction and Return on Investment
While the initial investment in robotics might seem daunting, it’s important to see the broader picture. Companies often witness substantial cost reductions over time due to several factors:
- Labor Cost Savings: Robots can perform the tasks of multiple workers, reducing payroll expenses.
- Lower Operational Costs: With improved efficiency, energy and material costs decrease.
Many businesses find that their return on investment (ROI) appears within months due to the efficiency gains and lower operational costs.
In essence, integrating robotics isn’t just a trend; it’s a crucial step toward sustainable and profitable growth in various industries. As highlighted on our blog, TECHFACK, these advantages make robotics an integral part of the future industry landscape.

Applications of Robotics in Various Industries
Manufacturing Sector
Building on the advantages previously discussed, the applications of robotics in the manufacturing sector are transformative. Robots have revolutionized assembly lines by performing repetitive tasks with precision, from welding to painting. They not only enhance speed but also reduce errors, thereby elevating product quality. For instance, automotive manufacturers utilize robotic arms for consistent assembly processes, leading to faster outputs and reduced waste.
Healthcare Industry
Shifting gears to healthcare, robots are making remarkable strides in improving patient care. Surgical robots, like the da Vinci Surgical System, allow surgeons to perform intricate procedures with greater accuracy through minimally invasive techniques. This technology results in shorter recovery times for patients.
Moreover, robotic assistants in hospitals can manage medication distribution and patient monitoring, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on interpersonal care.
Agriculture and Farming
Finally, in agriculture, robotics are increasingly indispensable. Drones monitor crop health, while robotic harvesters can pick fruits with exceptional speed and care, minimizing damage.
As a personal anecdote, a farmer I spoke with recently shared how robotic technology increased his yield while drastically reducing labor costs.
In conclusion, it’s clear that as we continue to explore the role of robotics in future industries, their applications are vital for efficiency and effectiveness across various sectors.
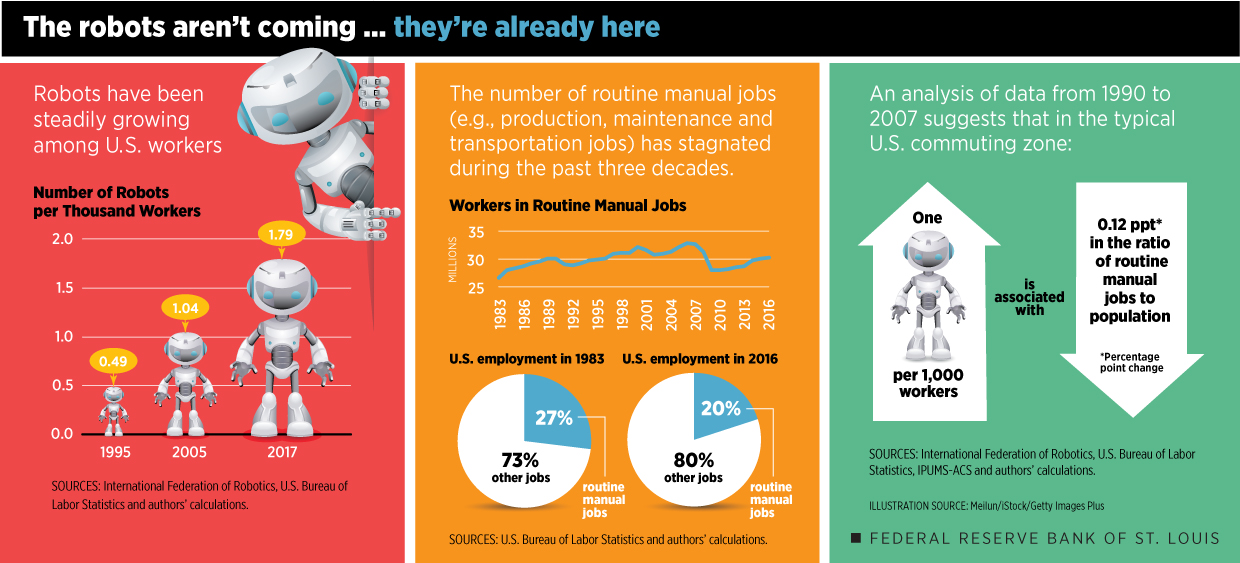
Impact of Robotics on the Workforce
Job Displacement vs. Job Creation
The integration of robotics into various industries inevitably stirs discussions around its impact on the workforce. A common concern centers around job displacement; many fear that automation will lead to job losses in traditional roles. While it’s true that certain repetitive jobs are at risk, the reality is more nuanced.
- Job Losses in Routine Tasks: Positions involving manual labor or repetitive tasks may diminish.
- Emergence of New Opportunities: On the flip side, robotics leads to the creation of roles in programming, maintenance, and oversight.
For instance, in a manufacturing plant utilizing robots, while some assembly line jobs have been replaced, there’s a growing demand for skilled technicians to manage robotic systems.
Upskilling and Reskilling Opportunities
To navigate this evolving landscape, upskilling and reskilling become crucial.
- Investing in Training Programs: Companies can offer training programs to help employees transition into new roles, enhancing their career prospects.
- Collaboration with Educational Institutions: Partnerships with local community colleges can provide a steady pipeline of skilled workers ready for the future.
In my experience, a friend who previously worked on an assembly line enrolled in a robotics program and now enjoys a fulfilling career as a robotics technician.
Thus, the impact of robotics is twofold; while challenges exist, there are equally robust opportunities for workforce evolution in the face of technological advancement.

Challenges and Considerations in Adopting Robotics
Initial Investment Costs
Transitioning to robotic systems can pose significant challenges, particularly regarding initial investment costs. Businesses often find the upfront expenses daunting, which can include purchasing the robots, integrating new software, and training staff.
Consider this:
- Equipment Expenses: Advanced robots, especially those designed for specialized tasks, can be costly.
- Maintenance and Upkeep: Ongoing maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance, adding to long-term costs.
A manufacturing executive I spoke with mentioned that while the initial outlay was high, they realized substantial savings in the long run as productivity soared and labor costs decreased. This highlights the importance of viewing robotics as a long-term investment that, despite initial hurdles, can yield impressive returns.
Ethical and Social Implications
Beyond financial concerns, ethical and social implications must be considered when adopting robotics. Questions arise about:
- Job Displacement: As discussed earlier, what happens to employees whose jobs are automated?
- Data Privacy: With robotic systems collecting data, are companies safeguarding personal information adequately?
These ethical dilemmas cannot be overlooked. Ensuring transparency and fostering open dialogues within organizations can help navigate these complexities. Ultimately, while challenges exist, a thoughtful approach can make the transition to robotics a win-win for businesses and society.

Future Trends and Innovations in Robotics
Artificial Intelligence Integration
As we gaze into the future of robotics, one of the most impactful trends is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). This synergy holds the promise of significantly enhancing robotic capabilities, making them smarter and more adaptive.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI allows robots to analyze data in real-time, adapting to various scenarios and making informed choices autonomously.
- Learning Capabilities: With machine learning, robots can improve their performance over time, learning from past experiences to optimize tasks.
For example, autonomous vehicles utilize AI to navigate complex environments safely, constantly learning from their surroundings. A friend of mine who works in AI development emphasizes that this blending of technologies will create robots capable of performing tasks previously deemed too complicated for machines.
Collaborative Robotics and Human-Robot Interaction
Another exciting frontier is the realm of collaborative robotics, where humans and robots work side by side rather than in a traditional assembly-line format.
- Increased Safety: These robots, or “cobots,” are designed with safety features, allowing them to coexist smoothly with human workers.
- Improved Efficiency: By sharing tasks, productivity often increases, leading to faster turnaround times.
For instance, in warehouses, cobots assist human workers in picking and sorting, reducing physical strain and increasing throughput. The personal stories I’ve encountered from employees in these settings often highlight a newfound sense of teamwork and efficiency that was previously unattainable.
Overall, the future of robotics is bright, enriched by AI and improved human-robot collaboration, paving the way for innovative solutions across industries.

Regulations and Policies Shaping the Future of Robotics
Legal Frameworks and Standards
As robotics continues to evolve, the need for comprehensive legal frameworks and standards becomes paramount. These regulations serve to ensure safety, protect intellectual property, and promote ethical use of technology.
- Safety Standards: Clear guidelines are necessary to ensure that robots operate safely alongside humans, minimizing the risk of accidents.
- Liability Issues: Establishing who is liable in case of malfunctions or errors is essential for accountability.
For example, the European Union has been proactive in drafting legislation around robotics to address these issues. A colleague of mine in regulatory affairs shared how intense discussions are taking place about creating unified standards that could help businesses navigate these complexities more smoothly.
Government Incentives and Support
Alongside legal frameworks, government incentives and support play a crucial role in shaping the robotics landscape.
- Research Grants: Many governments offer funding for research and development in robotics, encouraging innovation within the sector.
- Tax Benefits for Implementation: Some regions provide tax credits to businesses that adopt robotic technologies, easing the financial burden of initial investments.
These incentives can significantly lower barriers for startups and smaller businesses, making advanced robotics accessible to a broader range of industries. Through personal interactions with small business owners, I’ve seen how such supports can be the catalyst for embracing robotics, driving growth and innovation. Together, these regulations and incentives will likely create a more robust and sustainable robotic ecosystem in the years to come.

Conclusion
Recap of Robotics’ Role in Future Industries
Reflecting on the journey we’ve taken through the various aspects of robotics, it’s evident that these intelligent machines are set to play a pivotal role in shaping future industries. From enhancing efficiency in manufacturing and revolutionizing healthcare to transforming agriculture, robotics offers numerous advantages that businesses can leverage. However, this shift is accompanied by challenges, including ethical implications and workforce adjustments, which we must address head-on.
Moreover, the integration of AI and collaborative robotics fosters innovation, while supportive regulations and incentives from governments can pave the way for smoother transitions and greater acceptance.
Future Outlook and Recommendations
Looking ahead, it’s crucial for businesses and stakeholders to:
- Invest in Training: Prioritize upskilling programs to prepare the existing workforce for new roles in a more automated environment.
- Embrace Collaboration: Encourage partnerships between tech companies and educational institutions to create a pipeline of skilled talent.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of regulations and technological advancements to remain competitive.
In essence, the future of robotics holds immense potential. With a proactive approach, industries can harness this technology for sustainable growth while ensuring ethical and responsible deployment. As highlighted in our blog, TECHFACK, embracing robotics is not just a trend; it’s a strategic move toward a more efficient and innovative future.

