
Introduction
Definition of Automation in Supply Chains
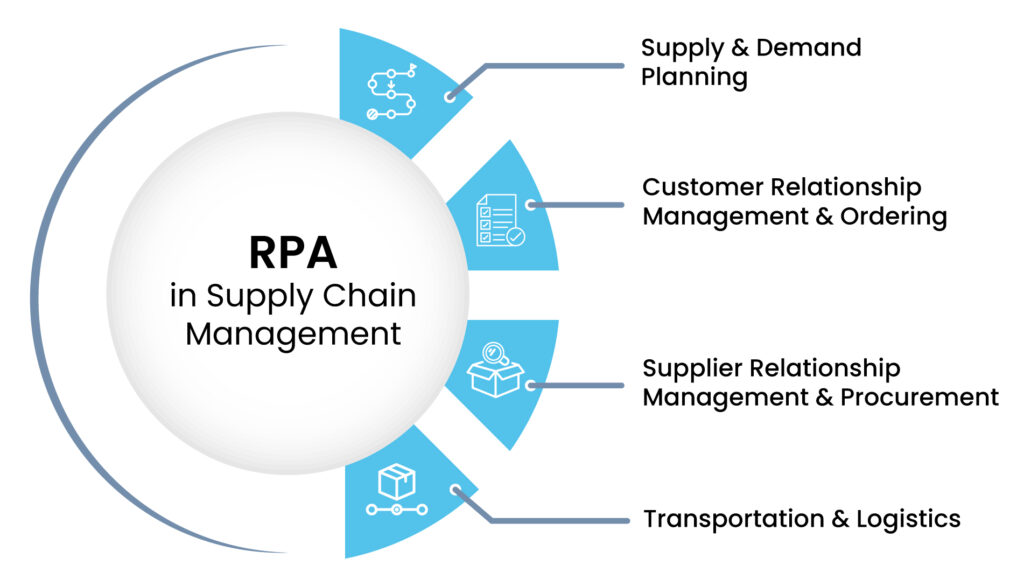
Automation in supply chains refers to the use of technology to perform tasks that were previously done by human hands. This encompasses everything from robotic process automation (RPA) to sophisticated algorithms that manage inventory and logistics. In essence, it streamlines operations, reducing human error and increasing efficiency.
Historical Context of Automation in Supply Chains
The journey of automation in supply chains dates back to the industrial revolution, where mechanized processes began to take shape. Fast forward to the late 20th century, and technology like barcode scanning revolutionized inventory management. Today, we stand at the frontier of an automation evolution with sophisticated technologies driving change.
Significance of Automation in Modern Supply Chains
Today, the role of automation cannot be overstated. It allows companies to:
- Enhance operational efficiency
- React swiftly to market demands
- Maintain competitive advantages
For instance, many organizations now incorporate automation to achieve just-in-time delivery, which leads to cost savings and improved service levels. As we further explore this topic, the implications of automation in global supply chains become increasingly clear—it’s not just a trend, but a robust solution for future challenges.
Benefits of Automation in Global Supply Chains
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The integration of automation in global supply chains drastically boosts efficiency and productivity. For example, automated systems can process orders and manage inventory much faster than manual methods. This leads to quicker turnaround times and helps businesses meet consumer demands without delays.
Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
Cost reduction goes hand in hand with increased efficiency. By utilizing automation:
- Companies minimize labor costs
- Reduce waste through optimized resource management
- Achieve just-in-time supply, decreasing storage costs
Automated systems often identify underutilized resources, allowing companies to allocate their assets more strategically.
Enhanced Accuracy and Quality Control
Precision is another vital benefit of automation. Systems equipped with advanced technologies are less prone to human error, ensuring that orders are fulfilled accurately. Consistent quality control processes enhance product reliability and customer trust.
Embracing automation fosters a more agile and responsive supply chain, paving the way for sustainable growth. As we delve deeper, understanding the challenges and limitations associated with automation is essential.

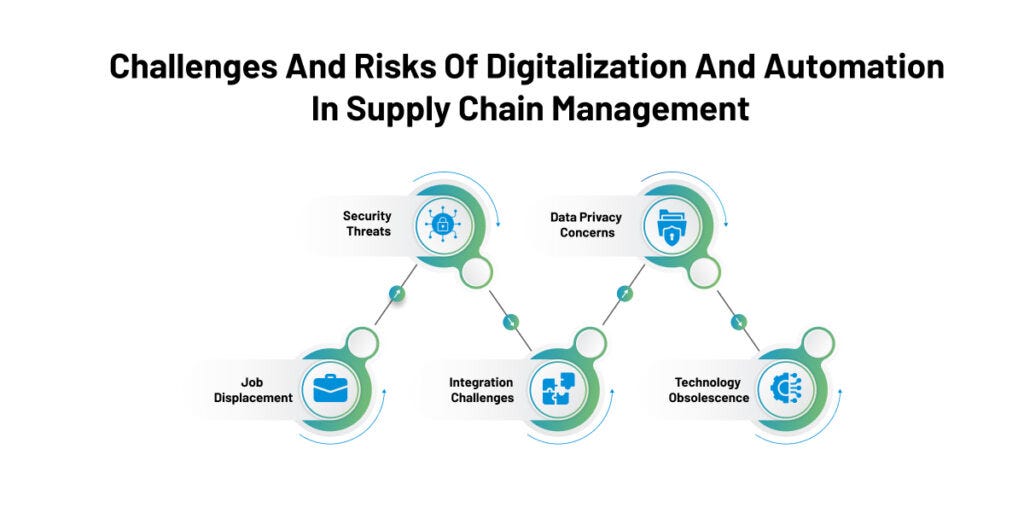
Challenges and Limitations of Automation in Global Supply Chains
Initial Investment Costs
While the benefits of automation in global supply chains are considerable, organizations often face significant initial investment costs. Implementing advanced technologies, purchasing equipment, and integrating systems can strain budgets, particularly for small to mid-sized businesses. Companies must carefully evaluate the return on investment (ROI) to ensure long-term viability, often leading to a cautious approach.
Workforce Displacement and Reskilling Needs
Another challenge revolves around the impact on workforce dynamics. As automation replaces certain jobs, there’s a growing concern about workforce displacement. Organizations must invest in reskilling programs to help employees transition into new roles that focus on overseeing and maintaining automated systems.
Cybersecurity Risks and Vulnerabilities
Lastly, the digital nature of automation introduces cybersecurity risks. Automated systems can become targets for cyber threats, highlighting the need for robust security measures. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring operational continuity require ongoing vigilance and investment in cybersecurity protocols.
As businesses navigate these challenges, understanding the holistic impact of automation becomes critical for achieving sustainable growth.

Impact of Automation on Global Supply Chain Networks
Streamlining Operations and Logistics
Automation profoundly influences global supply chain networks by streamlining operations and logistics. With processes like automated order picking and routing, companies can enhance their response times. For example, automated sorting systems can quickly direct packages to the correct distribution channels, ensuring a seamless flow of goods.
Improving Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is another area where automation shines. Advanced systems track products in real-time, providing businesses with accurate data. This reduces instances of overstocking or stockouts:
- Real-time inventory updates
- Demand forecasting algorithms
- Automated reordering processes
These practices yield improved accuracy and lead to cost savings, ultimately optimizing capital use.
Enhancing Customer Service and Satisfaction
Lastly, the benefits of automation extend to customer service. By automating communication through chatbots and responsive order tracking systems, businesses can offer immediate assistance. Customers appreciate timely updates and fast responses, which enhance overall satisfaction and loyalty.
As we explore further, the future trends in automation hold exciting possibilities for global supply chains.
Future Trends and Innovations in the Automation of Global Supply Chains
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications
As the landscape of global supply chains evolves, one cannot overlook the transformative impact of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies empower businesses to analyze vast amounts of data quickly, leading to monumental insights. For example, predictive analytics can optimize supply chain operations based on historical data and market trends.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
Another game-changer is the Internet of Things (IoT). By connecting devices and sensors throughout the supply chain, companies can monitor operations and inventory levels in real-time. This integration enhances visibility and responsiveness:
- Predictive maintenance of equipment
- Smart warehousing solutions
- Enhanced collaboration across networks
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Finally, innovations in robotics and autonomous systems are poised to revolutionize logistics and warehousing. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) facilitate efficient material handling and can operate with minimal human intervention. Warehouses increasingly rely on robotic pickers, significantly speeding up processes.
As these trends continue to shape the future, the implications for global supply chains are nothing short of exciting. Embracing these advancements will be key to staying competitive in the ever-evolving market.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Automation in Global Supply Chains
Amazon’s Robotics Fulfillment Centers
Amazon stands out as a pioneer in automating fulfillment centers with its advanced robotics technology. These facilities utilize thousands of robotic units that work alongside human employees to improve efficiency. By automating the picking and packing process, Amazon has significantly reduced order processing times. This integration of robotics enables:
- Faster order fulfillment
- Increased storage capacity
- Enhanced scalability during peak seasons
Tesla’s Smart Manufacturing Techniques
Tesla has transformed the automotive industry through its smart manufacturing techniques. With an emphasis on automation, the company employs sophisticated robotics for assembly line tasks, ensuring precision and speed. Their Gigafactories feature advanced technologies that:
- Minimize waste
- Accelerate production cycles
- Improve product quality
By leveraging data analytics, Tesla continuously assesses and optimizes its processes.
Maersk’s Digitized Shipping and Logistics Processes
Finally, Maersk demonstrates innovation in the shipping sector through its digitized logistics processes. Utilizing IoT and big data analytics, Maersk improves visibility across supply chains and optimizes routing. Their solutions provide:
- Real-time tracking of containers
- Enhanced operational efficiency
- Improved customer service
These case studies highlight how leading companies are successfully implementing automation to redefine global supply chains, paving the way for future advancements.

Ethical and Social Implications of Automation in Global Supply Chains
Impact on Employment and Labor Markets
While automation significantly enhances efficiency, it also raises important ethical questions about its impact on employment and labor markets. Many workers fear job displacement as robots and systems take over manual tasks. Companies must ensure they provide reskilling programs, helping employees transition into new roles that automation creates.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is another crucial aspect of automation’s ethical considerations. Automated processes can potentially minimize waste and reduce energy consumption. For instance, smart logistics systems can optimize transportation routes, lowering emissions. However, organizations must evaluate whether the environmental impact of producing automation technologies outweighs these benefits.
Responsible Use of Automation Technologies
Finally, the responsible use of automation technologies is paramount. Companies should strive for transparency in their automation practices and consider the broader social implications. Engaging with stakeholders and prioritizing ethical guidelines will ensure that the benefits of automation contribute to a fairer and more equitable future.
As we look ahead, balancing these ethical considerations with technological advancements will be vital for sustainable growth in global supply chains.
Conclusion
Recap of the Role of Automation in Global Supply Chains
In reflecting on the role of automation in global supply chains, it’s evident that technology has become a game-changer. From streamlining operations to enhancing customer service, automation offers significant enhancements. Companies like Amazon and Tesla exemplify how automated systems can lead to improved efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. However, these advancements also bring forth ethical complexities regarding employment and environmental implications that must be carefully navigated.
Future Outlook and Recommendations
Looking forward, businesses should embrace a balanced approach to automation. Recommendations include:
- Prioritizing employee reskilling programs
- Investing in sustainable technologies
- Engaging with stakeholders to ensure responsible practices
As the future unfolds, adapting to these recommendations will position organizations for lasting success, enabling them to harness the full potential of automation while being mindful of its broader societal impact. Embracing change thoughtfully will ultimately lead to a more resilient and responsive global supply chain landscape.

