Introduction
Overview of Criminal Cyber Activity
In today’s hyper-connected digital landscape, the rise of criminal cyber activity presents an alarming reality. Cybercriminals have become more sophisticated, employing an array of tactics, tools, and techniques to exploit unsuspecting individuals and organizations. From phishing scams to elaborate ransomware attacks, the threats are ever-evolving. A 2023 report indicated that over 60% of businesses experienced some form of cyber incident last year; this statistic underscores the urgent need to understand the intricacies of cybercrime.
Cybercriminals often operate in shadows, making it imperative for both individuals and businesses to stay informed and vigilant. Examples of everyday cyber threats include:
- Ransomware: Locking systems for financial gain.
- Phishing: Deceptive emails tricking users into divulging sensitive information.
- DDoS Attacks: Overwhelming servers to disrupt services.
Significance of Monitoring Trends and Predictions
Keeping an eye on trends and predictions in cybercrime is crucial. Just as businesses adjust their strategies in response to market changes, understanding these trends helps organizations bolster their defenses. For instance, monitoring the rise of cybercrime-as-a-service can reveal vulnerabilities within industry sectors.
Engaging in continuous education and awareness programs can significantly mitigate risks, ensuring we adapt proactively to this evolving threat landscape. By staying observant of emerging patterns, we create a better shield against the relentless tide of cybercriminal activities.

Historical Overview of Cybercrime
Evolution of Cyber Attacks
As we delve into the historical overview of cybercrime, it is important to recognize the rapid evolution of cyber attacks over the decades. What started as harmless computer pranks in the 1970s has transformed into sophisticated tactics that can disrupt entire economies. Initially, cybercriminals utilized basic methods like virus propagation; however, as technology advanced, so did their techniques.
Consider these pivotal moments:
- 1971: The first computer worm, “Creeper,” was detected, marking the start of malicious software.
- 1988: The Morris Worm introduced denial-of-service attacks, affecting nearly 10% of the Internet at the time.
- 2000s: The rise of malware and phishing scams became prevalent, leading to issues that businesses are still combating today.
Notable Cybercrime Incidents
Several notorious incidents have left indelible marks on the landscape of cybercrime. One notable example is the 2007 Estonian Cyberattack, which crippled government and bank websites, showcasing the destructive potential of coordinated cyber warfare.
Similarly, the 2017 Equifax data breach, which compromised the personal data of 147 million individuals, serves as a stark reminder of how vulnerable even large organizations can be.
These historical incidents highlight the need for robust cybersecurity measures as cybercriminals continue to refine their craft. As we reflect on this evolving history, it becomes clear that monitoring these developments is essential to staying ahead of the curve.

Current Trends in Criminal Cyber Activity
Ransomware Attacks
Transitioning from the historical context, today we witness a sharp increase in criminal cyber activity, particularly in ransomware attacks. These attacks have evolved significantly, shifting from targeting major corporations to focusing on small businesses and even individuals. In fact, a recent study suggested that a staggering 70% of small businesses experience ransomware incidents yearly.
- Note: Ransomware-related costs can reach millions, often forcing organizations to pay hefty ransoms to regain access to their data.
Data Breaches and Identity Theft
Alongside ransomware, data breaches and identity theft have become alarmingly prevalent. Cybercriminals exploit weaknesses in security systems to access sensitive information, leaving victims vulnerable to financial ruin. For instance, the 2023 Corporate Data Breach report revealed that more than 40% of organizations experienced a data breach last year, affecting thousands of individuals’ personal information.
- The impacts include:
- Financial loss
- Long-lasting credit damage
- An increased risk of identity theft
Social Engineering Techniques
Lastly, social engineering techniques are on the rise, with cybercriminals leveraging psychological manipulation to deceive individuals. This includes tactics such as phishing emails that mimic reputable organizations to gain sensitive information.
- Common tactics include:
- Pretexting: Creating a fabricated scenario to steal information.
- Baiting: Offering something enticing to trick victims into downloading malware.
As technology advances, these trends will likely continue to evolve, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity measures and ongoing education on the methods employed by cybercriminals.

Emerging Technologies in Cybercrime
Exploitation of IoT Devices
Diving deeper into the landscape of criminal cyber activity, one cannot overlook the exploitation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. As smart devices become increasingly integrated into our daily lives—from home security systems to health monitors—they simultaneously create new vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals often target these inadequately secured devices to gain unauthorized access to networks.
For example, an unsecured smart thermostat could serve as an entry point for attackers, allowing them to infiltrate a home’s Wi-Fi system. The real danger lies in the potential for large-scale attacks, such as botnets formed from compromised IoT devices, enabling criminals to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assaults.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cyber Attacks
Adding another layer of complexity, we now see the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) being utilized by cybercriminals. These technologies empower attackers to automate and enhance their techniques, allowing them to conduct sophisticated phishing scams or identify vulnerabilities faster.
Notable advancements include:
- Automated phishing campaigns: AI models generating convincing emails tailored to individual targets.
- Behavioral analysis: ML algorithms predicting and exploiting user behaviors for fraud.
This fusion of technology and cybercrime not only raises security challenges but also demands that organizations adapt their defenses proactively. As we navigate these emerging threats, understanding the tools and tactics employed by cybercriminals becomes essential for effective cyber defense strategies.
Impact of Cybercrime on Individuals and Organizations
Financial Losses
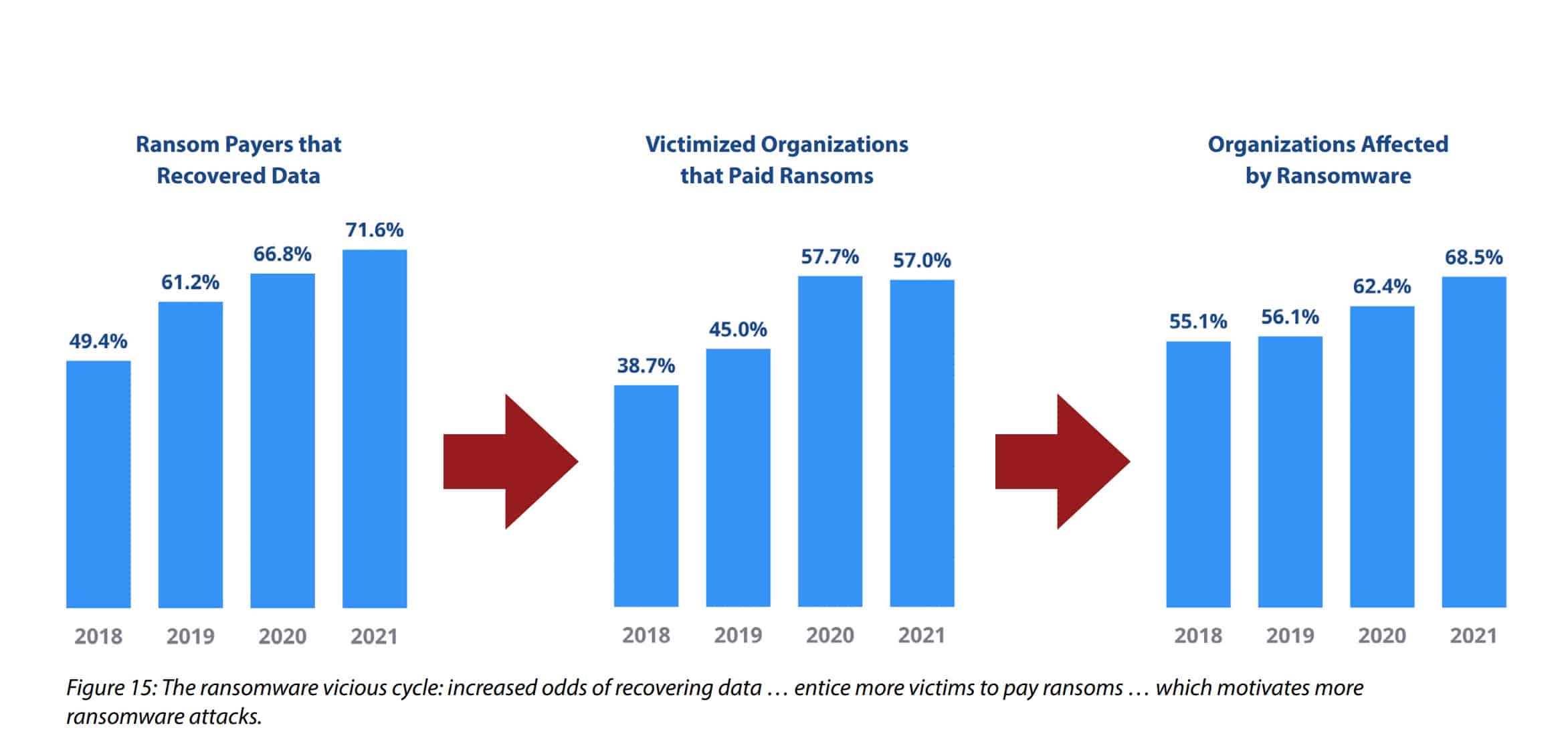
As we explore the impact of cybercrime, one of the most immediate consequences is financial loss. The monetary implications of a cyber attack can be staggering, affecting not just organizations but also individuals. For instance, the average cost of a ransomware attack is estimated to exceed $300,000 for small businesses. Costs can arise from:
- Ransom Payments: Direct payments demanded by cybercriminals.
- Recovery Expenses: Costs associated with restoring systems and data.
- Legal Fees: Expenses related to regulatory compliance and potential lawsuits.
Individuals are not immune either; identity theft and financial fraud can lead to devastating losses, prompting many to tighten their financial security measures.
Reputational Damage
Additionally, the reputational damage from a cyber incident can be long-lasting. Organizations that fall victim to cybercrime often face a loss of customer trust, which can severely impact revenue and market position.
- Some consequences of reputational damage include:
- Decreased customer loyalty
- Declining stock prices
- Negative media coverage
A case in point is the Target data breach, where millions of customer records were compromised, resulting in significant reputational fallout and billions in losses. As cyber threats grow in complexity and frequency, addressing these impacts becomes critical for maintaining organizational integrity and trust in an increasingly digital world.
Law Enforcement and Cybersecurity Measures
International Collaboration
Transitioning to the response strategies against cybercrime, international collaboration has become essential in combating this pervasive threat. Cybercriminals often operate across borders, exploiting gaps in jurisdictional authority. To counteract this, law enforcement agencies worldwide are increasingly pooling their resources and expertise. An excellent example is INTERPOL’s Operation Kilos, which brought together over 20 countries to dismantle international cybercriminal networks.
Key aspects of international collaboration include:
- Information Sharing: Agencies can exchange intel on cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
- Joint Operations: Coordinated efforts to take down large-scale cybercriminal operations.
- Training Programs: Enhanced skills and knowledge in cybersecurity for law enforcement personnel.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations
Alongside collaboration, robust legal frameworks and regulations are vital to regulate digital spaces and facilitate effective cybercrime responses. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe have set high standards for data protection, while also imposing severe penalties for non-compliance.
- Ongoing initiatives include:
- Cybersecurity policies that mandate organizations implement protective measures.
- Legislation on cybercrime aimed at closing loopholes that criminals exploit.
As we forge ahead, the importance of coordinated international efforts and effective regulatory measures cannot be overstated. Together, they form the backbone of a resilient defense against the ever-evolving landscape of cybercrime.

Predictions and Future Outlook
Rise of Nation-State Cyber Attacks
As we look toward the future, one prominent trend emerging is the rise of nation-state cyber attacks. Countries are increasingly leveraging cyber capabilities to achieve political, economic, and military objectives. For instance, the recent attacks attributed to state-sponsored actors aim to infiltrate critical infrastructure, steal sensitive government data, or disrupt national security systems.
Key indicators of this trend include:
- Increased funding for cyber warfare initiatives.
- Targeted attacks on sectors such as energy, healthcare, and finance.
- Escalating conflicts in cyberspace that mirror geopolitical tensions.
Governments must remain vigilant as these attacks become more sophisticated, requiring a unified approach to bolster national defenses.
Growth of Cybercrime-as-a-Service
In tandem with nation-state threats, we are witnessing a significant growth in cybercrime-as-a-service. This model allows novice cybercriminals to access advanced tools and resources for a fee, often using platforms that operate much like legitimate businesses.
Features of this burgeoning market include:
- User-friendly interfaces for launching attacks, making it easier for less skilled individuals to get involved.
- Subscription models for continuous access to malware or hacking tools.
- Forums and support networks where criminals can exchange knowledge and advice.
As these trends develop, both individuals and organizations must be proactive in adapting their cybersecurity measures to stay ahead of increasingly organized and resourceful cybercriminals. In this rapidly changing landscape, awareness and preparedness are more critical than ever.

Mitigation Strategies and Recommendations
Cybersecurity Best Practices
In countering the escalating threats posed by cybercrime, employing robust mitigation strategies is critical. Organizations should adopt cybersecurity best practices to create a formidable defense. Some effective strategies include:
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping systems and applications updated to patch vulnerabilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing additional layers of security beyond just passwords.
- Data Encryption: Protecting sensitive data so that even if it is accessed, it remains unreadable without decryption keys.
Moreover, conducting regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify potential weak points before they can be exploited.
Importance of Education and Awareness Programs
Equally important is fostering a culture of cyber awareness among employees and individuals. Education and awareness programs play a pivotal role in equipping everyone with the knowledge to recognize and respond to cyber threats effectively.
- Regular training sessions can cover topics like:
- Identifying phishing attempts.
- Best practices for password management.
- Safe browsing habits.
Personal experiences often reveal that an informed workforce can be the first line of defense, reducing the chances of successful attacks. As cyber threats continue to evolve, enhancing knowledge and preparedness remains essential, fostering a proactive approach to cybersecurity.

