Overview of Blockchain and IoT
Definition of Blockchain
Blockchain technology can be described as a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures the security and integrity of the data. Each transaction, or block, is linked to the previous block, forming a chain. This structure not only enhances security but also makes it nearly impossible to alter the information without consensus from the network.
Key features of blockchain include:
- Decentralization: No single point of control, reducing risks of manipulation.
- Immutability: Once recorded, the data cannot be changed or deleted.
- Transparency: All participants in the network can view the transactions, fostering trust.
Definition of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnected network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies aimed at collecting and exchanging data. From smart home appliances to industrial machines, IoT devices enhance operational efficiency and improve user experiences.
Examples of IoT applications:
- Wearable health devices monitoring vitals.
- Smart thermostats adjusting temperature automatically.
Introduction to the Relationship between Blockchain and IoT
The integration of blockchain and IoT presents exciting possibilities. By leveraging blockchain’s security and transparency, IoT networks can ensure data integrity, making devices more reliable. For instance, a smart thermostat can securely log its data on a blockchain, providing a trustworthy record of its performance.
Imagine a secure environment where IoT devices communicate seamlessly and safely, revolutionizing industries. The combination of these technologies is paving the way for smarter solutions that respond to today’s complex challenges.
Benefits of Integrating Blockchain and IoT
Enhanced Security
One of the most compelling benefits of integrating blockchain with IoT is enhanced security. As IoT devices proliferate, so do vulnerabilities. However, blockchain provides an added layer of security through its decentralized structure. Each transaction is recorded on multiple nodes, making it difficult for a malicious actor to tamper with data.
For instance, if a connected security camera stores its footage on a blockchain, even if a hacker gains access to the device, they won’t be able to alter the recorded footage without leaving a trace. This establishes a robust defense against potential breaches.
Improved Transparency
Transparency is crucial in an increasingly connected world. Blockchain enables real-time tracking of data generated by IoT devices. Each transaction or data point can be viewed by all authorized participants, ensuring a clear and accountable flow of information.
Consider the supply chain industry: integrating IoT sensors with blockchain can allow consumers to trace the origin of products, verifying their authenticity and ethical sourcing. This transparency not only builds trust with consumers but also enhances brand loyalty.
Increased Efficiency
Lastly, integrating blockchain and IoT can significantly improve operational efficiency. By automating processes through smart contracts—self-executing contracts on the blockchain—delays and human errors can be minimized.
For example, in a smart factory, IoT devices can communicate directly with the blockchain to automatically reorder supplies when stocks are low, optimizing inventory management. This smarter coordination can lead to substantial cost reductions and accelerated processes, making businesses more competitive in the rapidly evolving marketplace.
Challenges and Limitations
Scalability Issues
Despite the numerous benefits of integrating blockchain with IoT, scalability remains a significant challenge. With millions of devices generating vast amounts of data every second, traditional blockchain networks can struggle to process and store this information efficiently.
For instance, Bitcoin’s network can handle about seven transactions per second, while Visa can handle thousands. This discrepancy illustrates that as IoT networks expand, current blockchain frameworks might become bottlenecks, hindering performance.
Data Privacy Concerns
Another critical challenge revolves around data privacy. While blockchain enhances security, the transparency it offers can conflict with the need to keep sensitive data private.
Imagine a healthcare IoT device collecting personal health data. Although blockchain would ideally store this information securely, anyone within the network could view it. To mitigate this, developers must find a balance between transparency and confidentiality, implementing advanced encryption methods while ensuring easy access for authorized users.
Interoperability Challenges
Lastly, interoperability is a persistent hurdle. With various IoT devices and blockchain protocols in the market, ensuring seamless communication between them can be complex.
Think of it like trying to connect devices from different brands that use varied languages. The lack of standardized protocols can lead to fragmentation, making it difficult for businesses to integrate blockchain solutions easily within their existing IoT frameworks. Addressing these interoperability issues is essential for creating a cohesive, efficient ecosystem that maximizes the potential of both technologies.
Real-world Applications
Supply Chain Management
The integration of blockchain and IoT is revolutionizing supply chain management. By using IoT devices to track goods at every stage of the supply chain, companies can leverage blockchain to securely log each transaction. This not only enhances visibility but also increases accountability.
For example, imagine a farmer using IoT sensors to monitor crop conditions. As the produce is harvested, each batch can be tagged with a blockchain record, detailing its journey from farm to table. This visibility allows consumers to verify the freshness and quality of what they’re purchasing, building trust between producers and customers.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are another compelling application. These self-executing contracts carry terms directly written into lines of code on the blockchain. They automatically enforce processes or agreements when predefined conditions are met, removing the need for intermediaries.
Consider a real estate transaction where an IoT-enabled lock on a property can grant access only after payment is verified through a blockchain-based smart contract. This innovation simplifies processes and mitigates risks of fraud, as actions can happen instantly and transparently.
Data Management and Sharing
Lastly, blockchain enhances data management and sharing. With multiple IoT devices collecting vast amounts of data, the need for a secure and organized method of sharing this information is essential.
Blockchain can provide a structured platform where data ownership is clear, allowing users to share or monetize their data while maintaining control. Industries ranging from healthcare to finance can utilize this model, improving collaboration and accelerating innovation. By recording data on the blockchain, organizations can ensure that everyone involved has access to the most current and trustworthy information.

Future Trends and Opportunities
Adoption in Various Industries
As the integration of blockchain and IoT continues to evolve, we are witnessing a surge in adoption across a variety of industries. Sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and healthcare are among the frontrunners.
For instance, farmers are increasingly using IoT devices to monitor crop conditions, while blockchain records every transaction from planting to harvest. This convergence enhances food safety and traceability, allowing consumers to make informed choices about their food sources. In healthcare, patient data secured on a blockchain can be accessed seamlessly by authorized professionals while ensuring robust privacy.
Potential Innovations
Emerging innovative solutions are being designed to harness the synergy between blockchain and IoT further. Imagine smart cities where IoT devices manage energy consumption in real-time, autonomously recording energy usage on a blockchain to optimize resource allocation.
Other potential innovations include:
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) for managing community resources transparently.
- Blockchain-based identity programs enhancing security and privacy for digital identities in IoT networks.
Market Growth Projections
The market for blockchain and IoT integration is projected to experience significant growth in the coming years. Analysts estimate that this market could reach hundreds of billions in revenue by the next decade.
Investment in these technologies is surging, driven by the demand for automation, security, and efficient data management. This creates ample opportunities for businesses to innovate and differentiate themselves in their respective markets. As organizations become more aware of the unique advantages this integration offers, we can expect to see more widespread implementation and creative applications emerge, propelling us into a more connected and efficient future.

Case Studies
Company A: Implementing Blockchain and IoT
Let’s take a closer look at Company A, a logistics firm that recognized the significant inefficiencies in its supply chain management. By integrating blockchain technology with IoT devices, they created a robust tracking system.
They deployed IoT sensors on cargo containers to provide real-time data on location, temperature, and humidity. This information was simultaneously recorded on a blockchain, ensuring that every change or update was securely logged and accessible to all stakeholders.
As a result, Company A experienced:
- Reduced shipping delays by 30%
- Increased transparency, allowing customers to track their shipments in real-time
- Enhanced trust with partners due to tamper-proof records of the cargo’s journey
Company B: Successful Integration Strategies
Next, we examine Company B, a global retail brand that successfully adopted blockchain and IoT to streamline their operations. They implemented smart contracts to automatically reorder inventory based on IoT data from sensors in their stores.
This strategic move allowed them to:
- Cut down excess inventory by nearly 25%
- Improve efficiency by eliminating manual checks and balances
- Enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring products were always in stock
Company B also focused on staff training to promote a culture of innovation, ensuring that employees were equipped to leverage these new technologies effectively. Their success story illustrates how a thoughtful integration strategy can harness the strengths of both blockchain and IoT, driving meaningful business transformation.
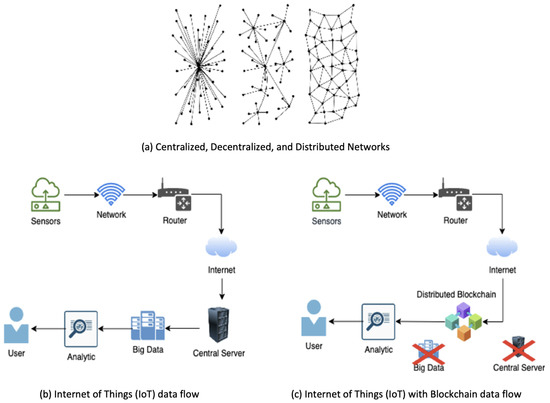
Regulatory Framework and Legal Implications
Compliance Requirements
As blockchain and IoT technologies become more intertwined, regulatory frameworks are slowly catching up. Companies must navigate a complex landscape of compliance requirements to ensure their operations align with local laws and guidelines.
For instance, industries such as healthcare or financial services have specific regulations related to data handling and transaction security. Businesses must implement necessary measures like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies to meet these standards.
A proactive approach to compliance not only fosters trust with customers and stakeholders but can also prevent costly legal repercussions.
Data Protection Laws
Data protection is another crucial concern for companies integrating blockchain and IoT. With various data flowing through devices and stored on decentralized ledgers, organizations must comply with laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
This law mandates transparency about how personal data is collected, processed, and stored, forcing businesses to rethink traditional data management strategies. Ensuring that IoT devices adhere to restrictive data protection principles can enhance user trust and provide a competitive edge in the marketplace.
International Standards
Lastly, establishing international standards is vital to ensuring the seamless collaboration between blockchain networks and IoT devices. Currently, the lack of uniform standards can create challenges related to interoperability and device compatibility.
Organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) are actively working to develop standards that can bridge these gaps. Companies that stay ahead of these emerging standards can position themselves as leaders in innovation and compliance, ultimately paving the way for expansive growth in the global marketplace. By actively engaging with regulatory developments, organizations can better navigate the evolving landscape and leverage the full potential of blockchain and IoT technologies.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Summary of Key Findings
In examining the intersection of blockchain and IoT, several key findings have emerged. Firstly, the integration of these technologies can significantly enhance security, transparency, and efficiency across various sectors.
From the logistics improvements seen in Company A to the efficient inventory management strategies implemented by Company B, it’s evident that leveraging blockchain can drive meaningful business transformations. Furthermore, the challenges associated with scalability, data privacy, and interoperability must be addressed to fully capitalize on these advancements.
Moreover, as companies navigate the regulatory landscape, understanding compliance requirements and data protection laws is crucial. Staying ahead of these developments equips organizations to mitigate risks while reaping the benefits of this technological synergy.
Suggestions for Further Research
As we move forward, further research is essential to unlock the full potential of blockchain and IoT. Areas worth exploring include:
- Developing standards for interoperability to ease integration across diverse devices and platforms.
- Examining the ethical implications of data collection and usage in IoT systems, particularly related to privacy.
- Investigating new business models that emerge from the convergence of these technologies, fostering innovation and economic growth.
By diving deeper into these aspects, researchers, businesses, and policymakers can better understand and harness the capabilities of blockchain and IoT, paving the way for a more efficient and connected future. Collaboration across sectors will be key in addressing challenges and unlocking opportunities.
References
Citations and Sources
In crafting this exploration of the integration of blockchain and IoT, various credible sources have been referenced to provide depth and support for the discussed concepts. Some key citations include:
- Swan, M. (2015). “Blockchain: Blueprint for a New Economy”. This book provides foundational knowledge about blockchain technology and its potential applications.
- Chen, M., et al. (2017). “Wearable 2.0: Enabling Human-Cloud Integration in Next Generation Healthcare Systems”. This paper discusses the implications of IoT in healthcare, emphasizing the importance of security and data integrity.
- Nakamoto, S. (2008). “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”. The original whitepaper that introduced blockchain technology through the Bitcoin network.
These resources offer valuable insights and are highly recommended for anyone looking to delve deeper into the subject matter.
Additional Reading Materials
For those eager to continue expanding their knowledge on this topic, several additional readings can provide further exploration and context:
- “The Infinite Retina: A 2-Part Guide to Blockchain Technology and its Applications” – A comprehensive guide that outlines practical uses of blockchain.
- The Internet of Things: A Technical and Societal Perspective – This book dives into the technological advancements alongside the societal implications of IoT.
- “Smart Contracts and Their Application in the Internet of Things” – An article focusing specifically on how smart contracts can optimize processes in IoT environments.
Engaging with these materials not only reinforces understanding but also reveals new perspectives and potential pathways for innovation in the rapidly evolving landscape of blockchain and IoT technologies.

