
Introduction
Overview of Biometric Security Measures
In a world increasingly driven by digital technology, biometric security measures have emerged as cutting-edge solutions for safeguarding identity and access. By leveraging unique biological traits, such as fingerprints, facial patterns, and retinal scans, these methods provide a seamless approach to authentication. Unlike traditional security measures, biometric systems are inherently more difficult to replicate, making them indispensable in various fields.
Significance of Biometric Security in the Future
The potential of biometric security measures in the future cannot be overstated. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the demand for robust security solutions will elevate. Personal anecdotes illustrate this need—imagine trying to access confidential financial information; a simple password could fall prey to hacks, while biometric verification offers an extra layer of defense.
Key Reasons for Future Significance:
- Heightened Security: Less susceptibility to fraud or unauthorized access.
- Improved User Experience: Streamlined processes eliminate time-consuming password resets.
- Growth in Applications: Expanding use in finance, healthcare, and governmental services enhances overall security.
As the landscape of security evolves, embracing the potential of biometric security measures becomes a necessity for both individuals and organizations alike.
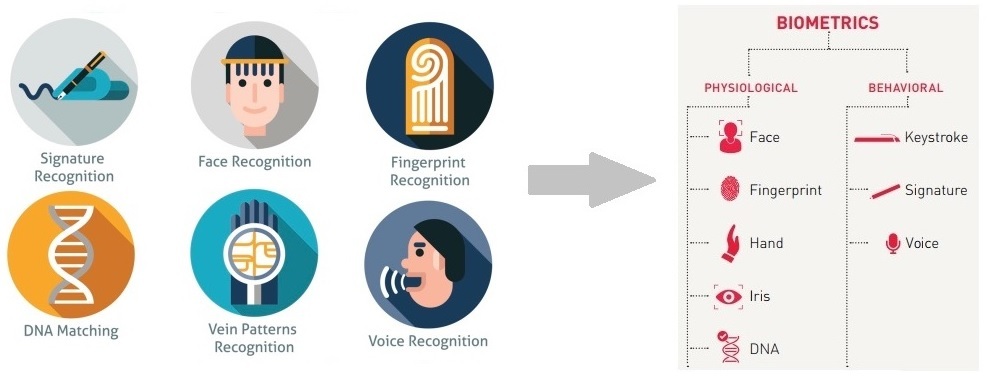
Types of Biometric Security Measures
Fingerprint Recognition
Fingerprint recognition is one of the most widely used biometric security measures. Each person’s fingerprints are unique, making this method a reliable choice. Devices equipped with fingerprint scanners, like smartphones, showcase how seamlessly this technology integrates into daily life.
Iris Scanning
Iris scanning takes security a step further by analyzing the intricate patterns of the colored part of the eye. It’s highly accurate and difficult to deceive, often seen in secure facilities and airports. The initial experience can be like peering into a scanner while the screen lights up with your identity, providing a surge of confidence in the security of your surroundings.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology has become increasingly popular, especially with the rise of social media platforms that automatically tag friends in photos. This tool maps facial features to identify individuals in mere seconds. While convenient, it also raises questions about privacy that cannot be overlooked.
Voice Authentication
Voice authentication, though less common, is another form of biometric security that uses a person’s unique voiceprint. Imagine placing a call to your bank and confirming your identity simply by talking. This method is proving to be a convenient option that’s gaining traction in customer service.
DNA Matching
Finally, DNA matching represents one of the most accurate forms of biometric security, often used in law enforcement and forensic science to verify identities. The complexity and uniqueness of an individual’s DNA make it a foolproof method, albeit less practical for everyday applications.
With these diverse types of biometric security measures, the landscape of protection is evolving, paving the way for safer and more user-friendly experiences in various sectors. Each method offers unique advantages, catering to different needs and situations.

Advantages of Biometric Security
Enhanced Security
One of the standout advantages of biometric security measures is their ability to provide enhanced security. Unlike traditional methods that rely on passwords or PINs, biometric traits are difficult to replicate or steal. For instance, a bank using fingerprint recognition adds an impenetrable layer to account security that can’t be easily bypassed.
Convenience in Authentication
Moreover, biometric systems offer unparalleled convenience in authentication. Imagine never having to remember another password again! With just a fingerprint or a glance, users can quickly access their accounts. This ease of use not only enhances user experience but also reduces frustration, particularly in scenarios where passwords might be forgotten or misplaced.
Resistance to Fraudulent Activities
Lastly, biometric security measures are notoriously resistant to fraudulent activities. Credentials like passwords can be shared or intercepted, putting accounts at risk. However, unique biological identifiers make it virtually impossible for someone to impersonate another individual. For example, in high-security environments, DNA matching has been instrumental in preventing identity fraud.
In a nutshell, the advantages of biometric security are not just theoretical—they are practical benefits that enhance safety, simplify processes, and protect against fraud in an increasingly digital world. Each type of biometric security brings its own strengths to the table, forming an essential part of contemporary security architectures.
Challenges and Concerns
Privacy Issues
While biometric security offers many advantages, it also raises significant challenges and concerns. One of the paramount issues is privacy. The use of personal biometric data, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, brings about fears of surveillance and unauthorized access. Many individuals worry about how their data is stored and who has access to it. For instance, sharing personal biometric information with a service provider can create anxiety about potential misuse or data breaches.
Accuracy and Reliability
Another critical concern revolves around accuracy and reliability. Biometric systems, while sophisticated, can sometimes misidentify individuals, leading to wrongful denials of access or compromised security. For example, instances of misreading facial features due to poor lighting or changes in appearance highlight the need for consistent performance.
Implementation Costs
Implementation costs also pose a significant barrier, especially for smaller organizations. Setting up biometric systems can be expensive, requiring specialized hardware and software. Moreover, the ongoing maintenance and updates can add to the financial burden.
As the conversation around biometrics continues to evolve, addressing these challenges is essential for ensuring a balanced approach that prioritizes security without compromising individual rights and affordability.

Future Innovations in Biometric Security
Behavioral Biometrics
As we look toward the future, innovations in biometric security are set to revolutionize the way we authenticate our identities. One exciting area gaining traction is behavioral biometrics. Unlike traditional methods that rely on static traits, this approach analyzes patterns in user behavior, such as typing speed, mouse movements, and even the way one walks. For instance, imagine your device recognizing your unique typing rhythm, automatically granting you access without needing a password.
Multi-Modal Biometrics
Another promising trend is multi-modal biometrics, which combines multiple biometric traits (e.g., fingerprints and facial recognition) for enhanced security. The integration of various types improves accuracy and mitigates risks associated with relying on a single method. This innovative approach could be particularly useful in high-security sectors where reliable authentication is crucial.
Continuous Authentication
Lastly, continuous authentication is set to reshape user experience. Rather than a one-time authentication process, it involves ongoing verification throughout a session. Picture this: you’re in a secure environment, and your device continuously checks your biometric traits, ensuring someone else isn’t using your credentials without permission. This innovative concept provides a robust security layer while allowing for seamless and frictionless user interactions.
The future of biometric security is bright, with these innovations promising to enhance safety, accessibility, and user experience across various applications and industries. As these technologies develop, they will reshape how we think about and utilize security in everyday life.

Applications of Biometric Security
Banking and Finance
The applications of biometric security measures are vast and varied, with significant impacts in areas such as banking and finance. Many banks now utilize fingerprint and facial recognition technologies to enhance security for online banking and ATM transactions. This reduces the risk of fraud while providing customers with a convenient and secure way to access their accounts. Imagine walking up to an ATM and simply scanning your fingerprint, eliminating the need for cards or PINs altogether.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, biometric security plays a critical role in protecting patient data and identity verification. Hospitals are increasingly implementing systems that use fingerprints to identify patients, ensuring that sensitive information is securely accessed by only authorized personnel. This not only boosts privacy but also reduces the risk of medical identity theft.
Government Services
Government services have also adopted biometric security measures for various applications. From voter identification to secure access for government officials, biometric verification aids in streamlining processes while safeguarding sensitive information. For example, in many countries, citizens now use biometrics when applying for passports, making identity verification faster and more reliable.
Travel and Immigration
Finally, in the realm of travel and immigration, biometric security systems are transforming how we cross borders. Airports are increasingly using facial recognition technology at check-in and immigration checkpoints, significantly speeding up the process and enhancing security. Travelers can flow through airports with ease, removing the stress of lost boarding passes or confusing procedures.
These diverse applications demonstrate how biometric security is becoming an integral component of modern society, providing enhanced safety, improved efficiency, and a seamless user experience across various sectors. As these measures continue to evolve, their impact on daily life will only grow.

Regulation and Ethical Considerations
Compliance with Data Protection Laws
As biometric security measures become more prevalent, regulation and ethical considerations are critical in ensuring responsible use. One of the most pressing issues in this area is compliance with data protection laws. Governments around the world have implemented regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, to safeguard individual privacy rights. For instance, organizations must obtain informed consent before collecting biometric data and ensure that it is used only for the intended purpose. Imagine a healthcare provider using fingerprints for patient identification; they must strictly follow guidelines to protect sensitive information from misuse.
Ethical Use of Biometric Data
Equally important is the ethical use of biometric data. Organizations must strive to maintain transparency about how they collect, store, and use biometric information. Consumers should feel confident that their data won’t be exploited or shared without their permission. An example of this ethical dilemma arises when companies employ facial recognition for targeted advertising or surveillance, sparking concerns over privacy invasion and discrimination.
Addressing these considerations not only helps organizations build trust with their users but also lays the groundwork for a more responsible and ethical approach to implementing biometric security technologies. Balancing innovation with respect for personal data is essential for fostering a secure and fair digital landscape.

Integration with Emerging Technologies
Internet of Things (IoT)
The integration of biometric security measures with emerging technologies heralds a new era of enhanced security features. Take the Internet of Things (IoT), for instance, where connected devices can utilize biometric authentication for seamless interactions. Imagine your smart home system recognizing your voice or face to unlock doors or grant access to sensitive areas. This integration not only boosts convenience but heightens security for everyday activities.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Incorporating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into biometric systems further amplifies their effectiveness. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to improve the accuracy of fingerprint or facial recognition technologies, allowing for real-time adjustments and enhanced pattern recognition. For example, AI can study a person’s walking gait, making it a second layer of identification that expands the possibilities for secure access.
Blockchain
Finally, the combination of biometric security and blockchain technology represents a revolutionary approach to safeguarding sensitive data. By securing biometric information on a blockchain, organizations can create a decentralized and tamper-proof record of access permissions. This system ensures that biometric data remains private and secure while allowing only authorized access. Imagine healthcare providers sharing patient information securely and transparently through a blockchain, ensuring compliance and preserving patient trust.
Together, these technological integrations pave the way for smarter, more secure systems that can redefine how we interact with technology in our daily lives. As innovations continue to evolve, the potential for biometric security in conjunction with IoT, AI, and blockchain is vast, aiming to create a more secure and efficient future.

Adoption and Implementation Challenges
User Acceptance
Despite the promising potential of biometric security measures, several adoption and implementation challenges remain. One major hurdle is user acceptance. Many individuals harbor concerns about privacy and data security, questioning whether they should entrust sensitive biometric information to organizations. For example, someone might hesitate to use facial recognition technology at an airport due to fears of surveillance and misuse. Overcoming this skepticism requires transparent communication from organizations about data protection measures and benefits.
Interoperability
Another challenge lies in ensuring interoperability across different systems and devices. Biometric solutions often vary in standards, making it difficult for organizations to implement cohesive systems that work seamlessly together. Imagine trying to access your banking app with a fingerprint in one instance and a facial recognition system in another—it can lead to user frustration and inefficiency.
Scalability
Lastly, scalability is a crucial consideration, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises. As organizations grow, their biometric security systems must be able to accommodate increasing data volumes without compromising performance. A startup might initially adopt fingerprint scanning for employee access, but as the workforce expands, they may find that the system doesn’t scale effectively.
Addressing these challenges is essential for the successful adoption of biometric security measures. As organizations navigate user concerns, technical compatibility, and growth demands, they can create a more secure and user-friendly experience for all. This proactive approach will ultimately enable biometric technologies to gain widespread acceptance and efficacy.

Conclusion
Recap of the Potential of Biometric Security Measures
In summary, the potential of biometric security measures is vast and transformative. From enhancing security in banking to streamlining processes in travel and healthcare, biometrics offers a multifaceted solution that combines convenience with robust protection. We’ve explored various types, advantages, challenges, and applications, highlighting how these measures are not just a passing trend but an essential aspect of a secure digital future.
Future Outlook and Implications
Looking ahead, the future of biometric security is bright, albeit not without its challenges. As user acceptance grows and technology advances, we can expect to see improvements in accuracy, accessibility, and ethical use. Organizations that proactively adopt these innovative systems will likely gain a competitive advantage.
Ultimately, as we embrace the potential of biometric security measures, society stands to benefit from a safer environment that prioritizes user experience without compromising privacy. Just as smartphones revolutionized communication, biometric technologies are set to redefine how we secure our identities and information, promising an exciting frontier for businesses and consumers alike.

