
Overview of CCPA and Cybersecurity
Introduction to CCPA
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), implemented on January 1, 2020, is a groundbreaking piece of legislation aiming to enhance privacy rights and consumer protection for residents of California. It’s not just a set of rules; it’s a paradigm shift in how businesses handle personal data.
Businesses are now mandated to be transparent about their data collection practices and give consumers greater control over their personal information. For instance, consumers can request disclosures about the data collected, demand deletions, and opt out of the data sale. This empowers individuals, fostering trust and accountability within the marketplace.
Understanding Cybersecurity and Its Importance
As organizations adapt to the demands of CCPA, the role of cybersecurity has never been more critical. Cybersecurity refers to the practices and measures taken to protect networks, devices, and data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage. The stakes are high; a security breach can lead to:
- Significant financial losses: Estimates suggest companies can lose millions due to data breaches.
- Reputational damage: Trust once broken can take years to rebuild.
- Legal repercussions: Non-compliance with CCPA can result in substantial fines.
Cybersecurity is not merely an IT issue; it is a fundamental aspect of business strategy. By applying robust cybersecurity practices, organizations can not only comply with CCPA but also safeguard their assets and customer trust. For instance, adopting encryption and regular security audits can be effective ways to bolster data protection.
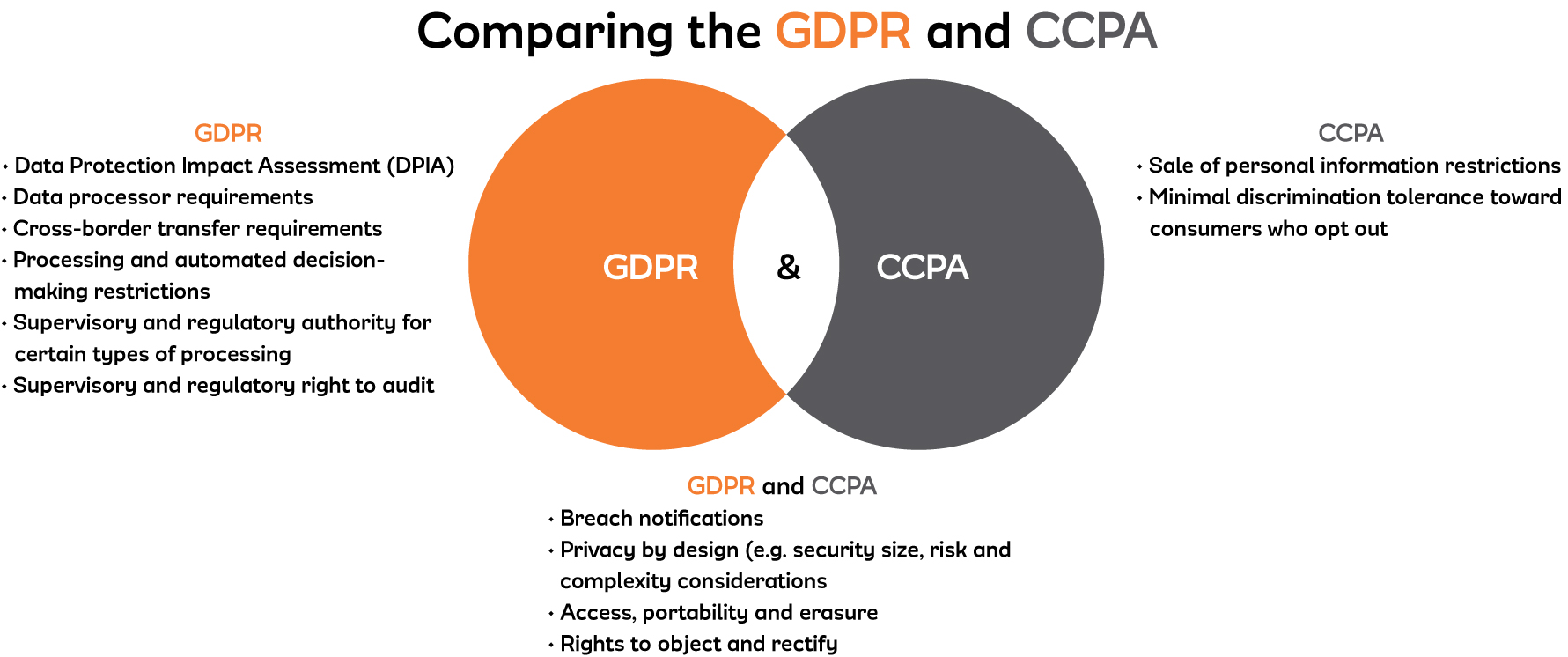
CCPA Compliance Requirements
Data Protection Standards Under CCPA
As organizations navigate the complex landscape of the CCPA, they must adhere to stringent data protection standards to ensure compliance effectively. The law mandates that companies implement measures to protect personal information, which has broad implications for how data is managed.
Some critical data protection standards include:
- Transparency: Businesses must inform consumers about the categories of personal data collected and the purposes for which that data is used.
- Security Measures: Companies are required to adopt reasonable security procedures to protect personal information from breaches.
- Consumer Rights: Consumers have specific rights under CCPA, including the right to access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
These standards not only promote consumer trust but also push organizations to reevaluate and fortify their data governance frameworks.
Impact on Data Collection and Processing
The CCPA’s stringent requirements have a profound effect on how businesses approach data collection and processing. Organizations are now compelled to:
- Revise Data Collection Policies: Many companies have had to update their privacy policies to align with CCPA mandates, ensuring consumers are well-informed.
- Limit Data Collection: Under CCPA, businesses should only collect information that is necessary for specified purposes, reducing unnecessary exposure to sensitive data.
- Train Employees: Organizations must educate their staff on compliance and the importance of data protection, fostering a culture of accountability.
For instance, a tech startup might find that by limiting data collection to what is essential for their app functionality, they not only comply with the CCPA but also strengthen their cybersecurity posture. By strategically revising their data practices, companies will enhance their data integrity and customer confidence as they adapt to a new era of privacy regulations.

Cybersecurity Practices in Light of CCPA
Enhancing Data Security Measures
With the CCPA placing a spotlight on data privacy, enhancing cybersecurity measures has become a top priority for organizations. Businesses need to go beyond basic protections to secure sensitive consumer data effectively.
Here are some strategies to strengthen data security:
- Implementing Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit can prevent unauthorized access, acting as a vital barrier against potential breaches.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: Conducting periodic security assessments and audits allows businesses to identify vulnerabilities in their systems and rectify them proactively.
- Access Controls: Restricting access to personal data on a “need-to-know” basis can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized exposure.
For example, a retail company that has customer payment information must ensure that only essential personnel have access to this data, thus minimizing the chances of a security incident.
Ensuring Compliance with CCPA Regulations
As organizations enhance their cybersecurity measures, ensuring compliance with CCPA regulations remains paramount. This means implementing specific practices that align with the law while also championing data protection.
Businesses must:
- Maintain Comprehensive Records: Documenting data collection and processing practices helps fulfill transparency obligations and allows for easier audits.
- Conduct Staff Training: Regular training sessions about CCPA compliance should be conducted to inform employees of their roles in safeguarding data and any legal consequences of negligence.
- Establish Response Plans: In the event of a data breach, having a clear response plan can help company leaders react swiftly and effectively, minimizing damage.
By embedding compliance practices into their security frameworks, organizations not only adhere to CCPA but also build a resilient cybersecurity culture. For instance, a financial institution that combines robust security measures with ongoing employee training can foster a secure environment that prioritizes consumer privacy while fulfilling legal obligations.

Challenges and Opportunities
Addressing Security Gaps
As organizations strive to comply with the CCPA, they inevitably encounter various challenges, mainly related to security gaps. Identifying and addressing these vulnerabilities is crucial for creating a robust cybersecurity framework.
Some common issues include:
- Legacy Systems: Many businesses rely on outdated technology that may not support modern security protocols, leaving them vulnerable.
- Insufficient Incident Response Plans: Without a solid response strategy, organizations may struggle to contain breaches, putting sensitive data at even greater risk.
- Resource Constraints: Smaller businesses often lack the budget for advanced security measures or the personnel needed to maintain compliance effectively.
For instance, a mid-sized retail company may face challenges in upgrading its IT infrastructure, yet implementing phased improvements can help close these gaps over time, bolstering its security posture.
Leveraging CCPA for Improved Cybersecurity
Despite these challenges, the CCPA also presents significant opportunities for businesses to enhance their cybersecurity practices. By embracing the regulation, organizations can build stronger data management frameworks that inherently improve their security measures.
Here are ways to leverage CCPA for better cybersecurity:
- Establishing a Data Governance Framework: The need to comply with CCPA encourages companies to create effective policies for managing and protecting data, fostering a proactive approach.
- Investing in Technology: CCPA compliance can justify investments in cybersecurity tools, such as advanced encryption or intrusion detection systems, that not only satisfy legal requirements but also enhance overall security.
- Promoting Transparency: By prioritizing transparency with consumers regarding data use, companies cultivate trust and, in the process, encourage a security-first mentality within the organization.
For instance, a tech startup might find that by updating its privacy policy to align with CCPA, it creates a culture of accountability that extends to its cybersecurity efforts. Ultimately, embracing CCPA not only aids in compliance but can also catalyze meaningful improvements in cybersecurity practices across the board.

Future Implications and Trends
Evolution of Cybersecurity Post-CCPA
As the dust settles on CCPA’s initial implementation, the landscape of cybersecurity is evolving. Companies are rethinking their data protection strategies and bolstering their cyber defenses in response to new obligations, which paves the way for significant advancements in this space.
Key trends include:
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Organizations are increasingly using AI to analyze vast amounts of data for potential threats, streamlining their ability to detect breaches before they escalate.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Emphasizing that no one should be trusted by default, this security model is becoming more popular. Companies are implementing strict identity verification processes for every user and device attempting access.
- Focus on User Education: Organizations are investing more in training their employees, equipping them with the skills to recognize cyber threats, thus building a human firewall.
For example, a financial services company could transition to a Zero Trust model to ensure that even internal users undergo rigorous verification before accessing sensitive data.
Potential Impact on Global Data Privacy Laws
The implications of CCPA extend well beyond California’s borders, influencing a shift in global data privacy laws. As consumers become increasingly conscious of their data rights, jurisdictions around the world are studying CCPA as a model for their own regulations.
Potential impacts include:
- Harmonization of Standards: Countries may adopt similar consumer privacy laws, leading to a more unified approach to data protection worldwide.
- Increased Scrutiny on Multinational Companies: Organizations operating in multiple countries will face escalating compliance challenges, encouraging them to standardize their data protection practices.
- Consumer Empowerment: As global awareness grows, consumers will increasingly demand rights similar to those granted by CCPA, compelling businesses to adapt.
For instance, if the European Union chooses to strengthen its General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in light of CCPA’s principles, it could lead to more robust protections for data privacy worldwide. Ultimately, as CCPA sets the precedent, businesses must proactively adapt to these evolving legal landscapes while enhancing their cybersecurity measures.
