
Introduction
Brief History of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity has transitioned significantly since the inception of computing technologies. It began in the 1970s when early computer systems faced their first threats from malicious insiders and simple viruses. Fast forward to the late 1990s, when the internet expanded, leading to the first large-scale cyberattacks.
- 1970s: Emergence of basic security measures.
- 1980s: Introduction to virus protection software.
- 1990s: Rise of firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
Significance of Cybersecurity Evolution
The evolution of cybersecurity has been crucial for protecting sensitive information as society digitizes. Robust security measures are essential not just for businesses but for individuals too.
Consider this: Every single day, millions of cyber threats emerge, making it imperative to stay updated and informed about the best practices in security. With the continuous rise of sophisticated cyber risks, understanding the journey of cybersecurity helps us appreciate its impact on our daily lives and the digital landscape.
In essence, this evolution signifies our commitment to building a safer cyber world for all.

Evolution of Cybersecurity
Early Days of Cybersecurity
The journey of cybersecurity began with fundamental measures designed to protect the nascent computer systems of the 1970s. During this period, security was mostly an afterthought, focusing primarily on physical access control.
- Physical Locks: Protecting hardware from unauthorized access.
- Password Systems: Introduction of simple username and password combinations.
Transition to Digital Security Measures
As technology advanced, the 1980s ushered in a wave of digital security innovations. The necessity for protection grew with the spread of personal computers and networks.
- Antivirus Software: Companies like Norton emerged to combat burgeoning viruses.
- Firewalls: Early systems began to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
Rise of Advanced Threats and Countermeasures
The new millennium brought an alarming increase in sophisticated cyber threats, including worms, phishing, and targeted attacks. Organizations responded with multi-layered strategies.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Encryption: Secure communication became paramount.
Current State of Cybersecurity
Today, cybersecurity is a critical component of our digital ecosystem. Incidents like the WannaCry ransomware attack exemplify the ongoing battle against cybercrime.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are now used to predict and thwart potential threats.
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations must adhere to stringent data protection laws.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, so too must our approach, highlighting the critical importance of proactive measures and continuous education in protecting our digital lives.

Future Trends in Cybersecurity
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
As we move further into the digital age, artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing cybersecurity. By automating threat detection and response, AI enables organizations to respond faster than ever.
- Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms identify unusual patterns indicative of cyber threats.
- Automated Responses: Rapidly neutralizing threats minimizes potential damage.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security Challenges
The massive adoption of IoT devices introduces unique security challenges. With so many connected devices, each presents potential vulnerabilities.
- Lack of Standardization: Many IoT devices lack uniform security protocols.
- Data Privacy Risks: Increased connectivity raises concerns about personal data exposure.
Quantum Computing and Cybersecurity Implications
Quantum computing holds both promise and peril for cybersecurity. It has the potential to break existing encryption methods, forcing a re-evaluation of digital security.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: The transition to quantum-resistant algorithms is becoming essential.
Predictive Analytics in Cyber Defense
Finally, predictive analytics is emerging as a powerful tool in cyber defense. By analyzing trends and patterns, organizations can anticipate attacks before they happen.
- Risk Scoring: Helps prioritize security efforts based on vulnerability.
- Incident Simulation: Testing responses to potential cyber threats enhances preparedness.
In summary, the future of cybersecurity is marked by both challenges and revolutionary techniques aimed at enhancing our digital defenses.

Cybersecurity Regulations and Compliance
Overview of Data Protection Regulations
As the digital landscape evolves, data protection regulations have become essential for safeguarding personal information. Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) set stringent standards for how organizations handle data.
- GDPR: A European Union regulation emphasizing user consent and data rights.
- CCPA: Focuses on transparency and giving consumers more control over their personal data.
Compliance Frameworks in Cybersecurity
To navigate these regulations, businesses often turn to compliance frameworks. Frameworks such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO 27001 guide organizations in establishing robust security practices.
- NIST: Offers guidelines for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents.
- ISO 27001: Focuses on establishing an information security management system (ISMS).
Impact of Global Data Privacy Laws
With countries introducing their own data privacy laws, organizations face complex compliance landscapes.
- International Consistency Challenges: Different regulations can require significant adjustments to business practices.
- Increased Accountability: Compliance promotes a culture of responsibility, which ultimately strengthens cybersecurity.
As organizations strive to meet these evolving regulations, understanding and adapting to global data privacy laws will be pivotal in mitigating risks and protecting sensitive information.

Cybersecurity Technologies and Innovations
Blockchain Applications in Security
As we continue to seek advanced solutions for cybersecurity, blockchain technology has emerged as a formidable ally. Its decentralized nature enhances data integrity and transparency.
- Immutable Records: Transactions recorded on a blockchain cannot be altered without consensus, making it difficult for hackers to tamper with data.
- Smart Contracts: Automating interactions allows for secure and verified transactions without intermediaries.
Cloud Security Solutions
Cloud computing’s rapid growth has necessitated robust security measures. Cloud security solutions, such as identity and access management (IAM), play a vital role in protecting sensitive data.
- Encryption: Data stored in the cloud can be encrypted, ensuring that even if accessed, it remains unreadable.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification for access.
Biometric Authentication Advancements
Looking ahead, biometric authentication is rapidly evolving as a secure method to verify identity. Technologies like fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and iris scanning provide enhanced user verification.
- User Convenience: Biometric methods reduce the need for passwords, streamlining access while enhancing security.
- Fraud Prevention: Difficult to replicate, biometric data adds a strong layer of defense against unauthorized access.
As these innovative technologies continue to develop, they represent a forward-thinking approach to enhancing cybersecurity measures across various platforms and environments.

Cybersecurity Threat Landscape
Types of Cyber Threats
Navigating the cybersecurity landscape requires an understanding of the various types of threats organizations face. These threats can range from data breaches to advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Phishing: Deceptive emails designed to lure users into providing sensitive information.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts files, demanding payment for access.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering remains one of the most insidious forms of cyber threats. By manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information, attackers exploit human psychology rather than technical weaknesses.
- Phishing Scams: Often disguised as legitimate communications, these scams can have devastating consequences.
- Pretexting: Attackers create a fabricated scenario to obtain sensitive data, often impersonating a trusted individual or authority.
Malware Trends and Prevention
Malware continues to evolve, impacting organizations worldwide. Keeping abreast of emerging threats is crucial for effective defense.
- Types of Malware: Ransomware, spyware, adware, and trojans can disrupt operations and compromise sensitive data.
- Prevention Strategies: Regular software updates, comprehensive antivirus solutions, and employee training are essential to mitigate risks.
Understanding the dynamic cybersecurity threat landscape empowers organizations to implement effective strategies, minimizing risks and safeguarding their digital assets.
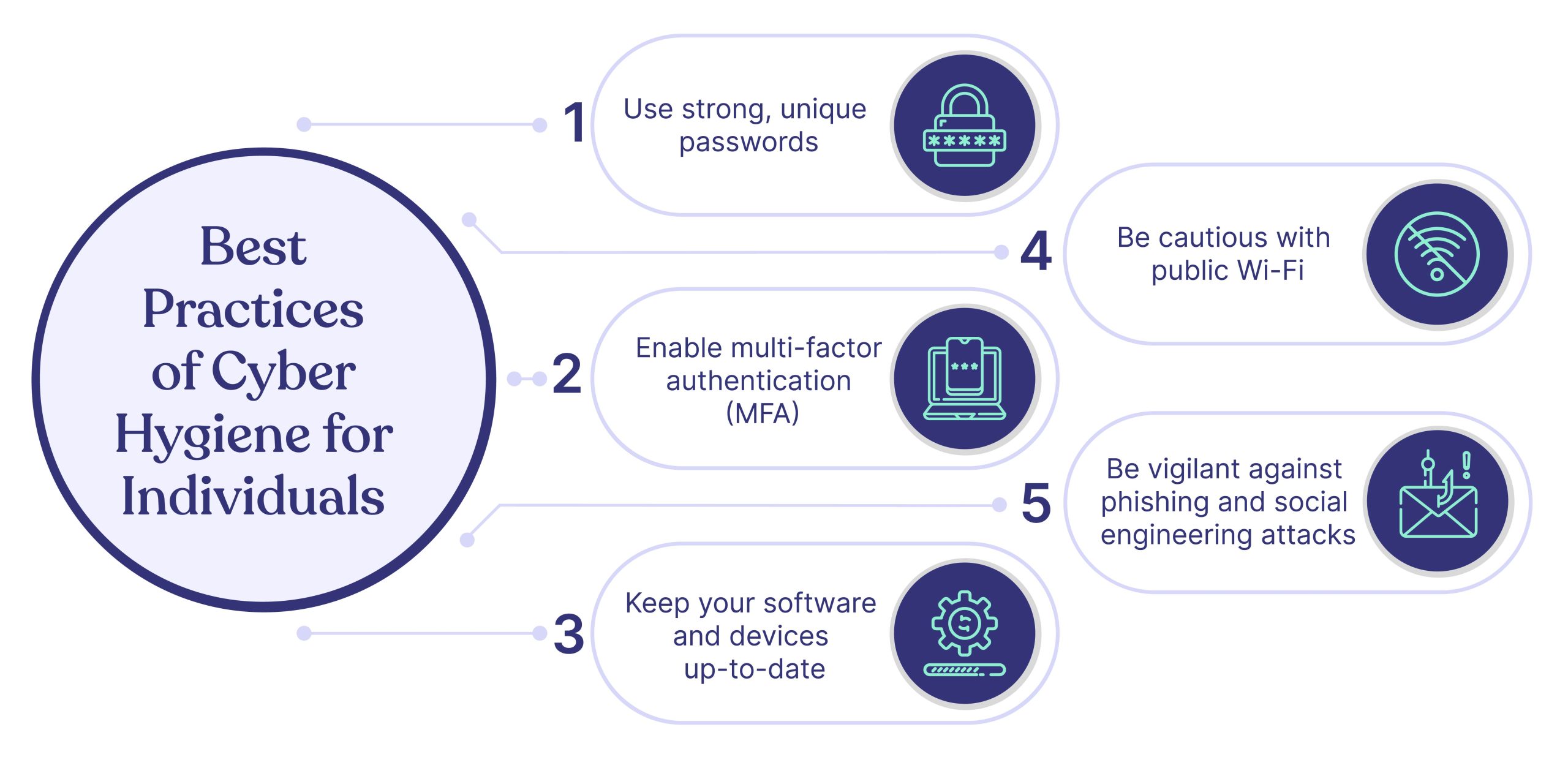
Cyber Hygiene and Best Practices
Importance of Employee Training
In the realm of cybersecurity, employee training stands as a frontline defense. Staff members are often the first line of contact with potential threats, making their education vital.
- Awareness Programs: Informing employees about phishing scams and social engineering can dramatically reduce vulnerabilities.
- Simulated Attacks: Conducting mock phishing exercises helps staff recognize threats in real time.
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
Another essential aspect of cyber hygiene is maintaining up-to-date software. Regular updates and patch management close security gaps, minimizing the risk of exploitation.
- Automated Update Settings: Enabling automatic updates ensures that systems remain current without manual intervention.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regular scans can help identify outdated or weak software components that require urgent attention.
Data Encryption Protocols
Finally, implementing strong data encryption protocols is essential to protect sensitive information.
- End-to-End Encryption: Secures data during transmission, making it indecipherable to unauthorized parties.
- Encryption at Rest: Protects stored data, ensuring that even if accessed, it remains unreadable.
By adopting these best practices, organizations significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture, creating a resilient framework to defend against evolving threats.
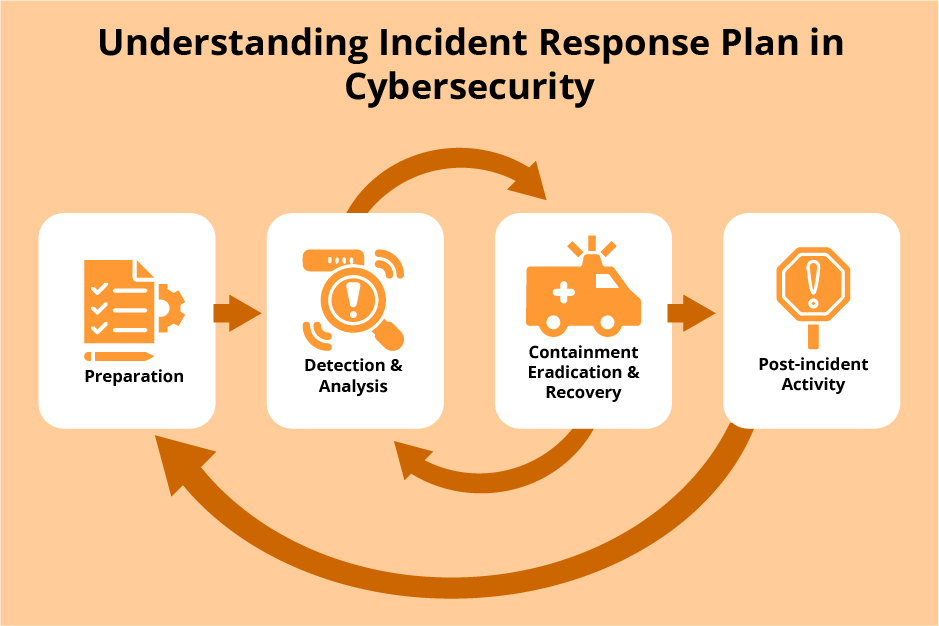
Incident Response and Recovery
Incident Response Plan Development
In the fast-paced world of cybersecurity, having a solid incident response plan (IRP) is crucial. This plan outlines procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents, ensuring that organizations can act swiftly.
- Formation of Response Teams: Designating a skilled team ensures quick decision-making during a crisis.
- Clear Communication Channels: Establishing protocols for internal and external communication helps manage the situation effectively.
Post-Incident Analysis and Improvement
After an incident, analyzing what transpired is vital for future prevention. A thorough post-incident analysis helps identify weaknesses in the response plan.
- Root Cause Analysis: Understanding how the breach occurred can shed light on areas needing improvement.
- Updating Policies: Adjusting existing protocols based on findings fortifies defenses against similar future threats.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Lastly, effective business continuity and disaster recovery plans are paramount for minimizing downtime and data loss.
- Regular Testing: Periodically simulating disaster scenarios prepares teams for real events.
- Backup Strategies: Implementing robust data backups ensures that operations can be resumed quickly after an incident.
With these strategies in place, organizations can navigate Incident Response and Recovery effectively, maintaining resilience in the face of cyber threats.

Collaboration and Information Sharing in Cybersecurity
Threat Intelligence Sharing Platforms
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, collaboration is key to effective cybersecurity. Threat intelligence sharing platforms facilitate the exchange of valuable information related to emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Real-Time Updates: These platforms provide instant alerts regarding new attack vectors, allowing organizations to act promptly.
- Community Insights: Sharing experiences and strategies fosters a collective defense approach, enhancing overall resilience.
Public-Private Partnerships in Cyber Defense
Partnerships between public institutions and private enterprises play a vital role in strengthening cybersecurity. Governments and businesses collaborate to share resources and expertise.
- Resource Pooling: Combining resources leads to enhanced threat detection and response capabilities.
- Joint Training Initiatives: These partnerships often sponsor workshops and training sessions, equipping teams with the necessary skills to combat cyber threats.
Cross-Industry Collaboration Initiatives
Lastly, cross-industry collaborations create a robust framework for cyber defense. By working together, organizations from various sectors can develop best practices and standardized protocols.
- Industry-Specific Forums: These groups allow participants to discuss unique challenges and solutions tailored to their fields.
- Collective Action: A unified front allows for a more significant impact against widespread threats, creating a powerful deterrent for cybercriminals.
As we advance into the future, embracing collaboration and information sharing will be essential components in combating the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.

Ethical and Legal Dimensions of Cybersecurity
Ethical Considerations in Security Research
As cybersecurity professionals investigate vulnerabilities, ethical considerations must guide their research. Balancing the quest for knowledge with the potential impact on privacy and security is crucial.
- Responsible Disclosure: When discovering vulnerabilities, researchers should notify affected parties before publicizing the information, thus minimizing potential harm.
- Ethical Hacking: Engaging in penetration testing with proper authorization enhances security without compromising ethical standards.
Legal Implications of Cyber Attacks
Cyber attacks have far-reaching legal consequences for both perpetrators and victims. Understanding these implications is essential for organizations.
- Liability Issues: Companies may face legal action if they fail to protect customer data adequately, leading to hefty fines.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to relevant laws like GDPR or HIPAA ensures that organizations avoid legal pitfalls while handling sensitive information.
International Cooperation in Cybercrime Investigation
Finally, international cooperation is key in addressing the global nature of cybercrime.
- Shared Resources: Collaborative efforts between nations foster knowledge sharing and better resource allocation in investigations.
- Legal Frameworks: Establishing treaties and agreements can streamline extradition processes and provide clearer jurisdiction lines for cybercriminal prosecutions.
In summary, navigating the ethical and legal dimensions of cybersecurity is essential, enabling organizations and researchers to foster a safer digital environment while maintaining integrity and compliance.

Conclusion and Future Prospects
Recap of Cybersecurity Evolution
Throughout this journey, we have witnessed significant evolution in cybersecurity, from the rudimentary defenses of the early days to today’s multifaceted strategies and technologies. As digital threats grow increasingly sophisticated, so too must our defenses.
- Milestones: Key developments such as the advent of AI, blockchain, and stringent regulations have shaped the landscape.
- Increased Awareness: Organizations now recognize that cybersecurity is not just an IT concern, but a holistic business priority.
Emerging Challenges and Opportunities
However, the horizon is not without challenges. The rise of IoT devices and the implications of quantum computing present new vulnerabilities.
- Adaptive Strategies: Embracing continuous education and innovative technologies can turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and resilience.
- Proactive Approaches: Investing in cybersecurity awareness can fortify an organization’s defenses against evolving threats.
The Road Ahead for Cybersecurity
Looking to the future, a collaborative approach will be paramount.
- Global Alliances: Strengthening partnerships between public and private sectors will enhance collective security efforts.
- Regulatory Adaptations: As new technologies emerge, so will the need for adaptable regulations that protect consumers while fostering innovation.
In conclusion, by understanding the evolution of cybersecurity and remaining vigilant, organizations can navigate the complexities of the digital world and emerge stronger against future threats.

