
Network Security Fundamentals
Understanding Network Security
Network security is a vital aspect of any organization, serving as the backbone that protects sensitive data and maintains the integrity of digital communications. Think of your network as a well-guarded castle; without security measures, it becomes an open invitation for intruders.
At its core, network security encompasses:
- Data integrity: Ensuring that information is accurate and unaltered.
- Confidentiality: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Availability: Making sure that network resources are available to authorized users when needed.
Common Threats to Networks
Despite robust security measures, networks remain vulnerable to various threats. Understanding these can significantly bolster your defenses.
Some common threats include:
- Malware: Including viruses, worms, and ransomware that can cripple systems.
- Phishing: Deceptive tactics aimed at tricking users into revealing personal information.
- Denial-of-service attacks (DoS): Where attackers overwhelm network resources to disrupt services.
For instance, a recent report highlighted a company that fell victim to a phishing attack, which compromised several accounts and led to significant financial losses. The essence of securing your network lies in staying informed about these threats and implementing effective countermeasures.
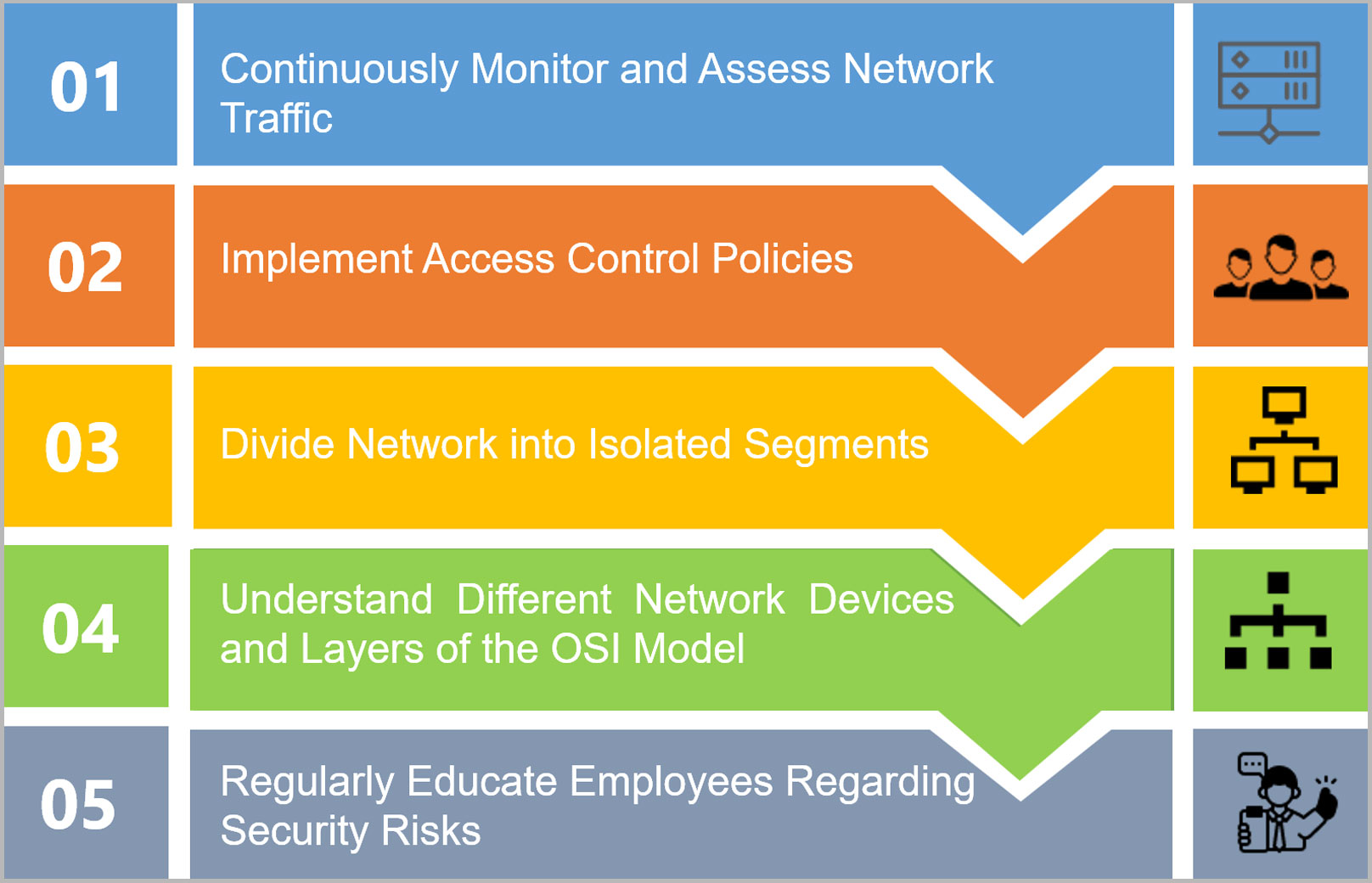
Network Protection Technologies
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Having understood the fundamental aspects of network security, let’s delve into specific technologies designed to safeguard your digital landscape. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are two primary defenses against threats.
- Firewalls act as the first line of defense, controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Imagine them as bouncers at a club, only allowing authorized visitors in while keeping intruders out.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activities or policy violations. They alert administrators to potential threats, enabling swift action. It’s like having a security team watching over your with a keen eye.
Antivirus and Antimalware Software
Complementing firewalls and IDS are antivirus and antimalware solutions. These programs are crucial in detecting and eliminating malicious software before it wreaks havoc on your system.
Consider these protective measures:
- Antivirus software: Scans files and applications to identify known viruses and threats, acting like an air filter for your computer.
- Antimalware solutions: Target broader categories of malware, providing a more comprehensive defense against evolving threats.
For example, a friend of mine once sidestepped a major disaster by having robust antivirus software that quarantined a nasty Trojan before it could cause any damage. This underscores the importance of layered protections in effectively securing your network.

Secure Configuration Practices
Password Management
Building on the foundational technologies of network protection, secure configuration practices are essential for ensuring robust security. One of the most critical components of this is password management. In today’s threat landscape, weak or reused passwords can be a significant vulnerability.
Consider integrating the following practices into your password management:
- Use complex passwords: Incorporate a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols to make passwords harder to guess.
- Password managers: Tools like LastPass or 1Password can help you generate and store unique passwords securely.
- Regular updates: Change your passwords periodically to enhance security.
I once encountered a business that suffered a data breach due to an employee using “password123.” It was a wake-up call that emphasized the importance of stringent password policies.
Secure Network Device Configurations
Beyond password management, securing network devices plays a pivotal role in safeguarding your infrastructure. Proper configurations can prevent unauthorized access and vulnerabilities.
Here are some essential practices for secure configurations:
- Change default settings: Always modify default usernames and passwords on routers and switches.
- Disable unused services: Turn off any services or features not being utilized to reduce potential attack vectors.
- Implement network segmentation: Divide your network into smaller segments to contain potential intrusions and enhance control.
For instance, by segmenting their network, a local healthcare provider minimized the risk of a major breach following a ransomware attack. These secure configuration practices form a crucial part of a comprehensive strategy for protecting your network.
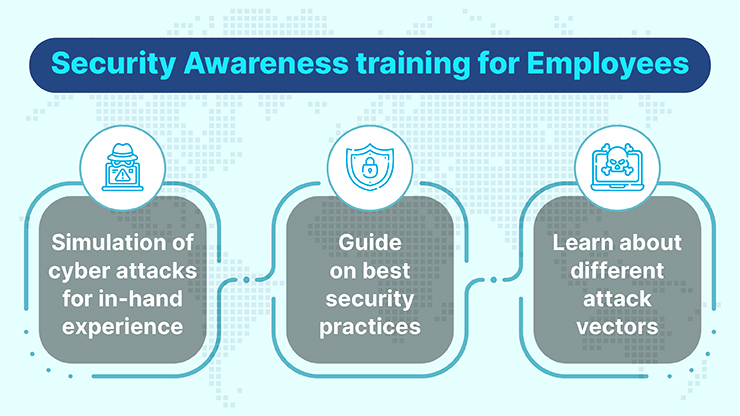
Employee Training and Awareness
Importance of Security Training
As we transition into the people-centric aspect of network security, it becomes clear that technology alone isn’t enough. Employee training and awareness are fundamental to building a strong security culture within organizations. Often, humans are the weakest link in the security chain.
Consider this: a well-trained employee is much less likely to fall victim to phishing attacks or inadvertently expose sensitive data. For instance, a company that invests in regular security training has seen a 50% reduction in security incidents over a year.
Security training not only empowers employees but also instills a sense of responsibility. When staff understand the stakes, they are more likely to adhere to policies and procedures that protect both personal and organizational data.
Best Practices for Employee Awareness
To foster a security-conscious environment, consider these best practices for employee awareness:
- Regular training sessions: Host periodic workshops to refresh employee knowledge.
- Simulated phishing attacks: Test employees with mock phishing emails to train them for real threats.
- Clear communication channels: Encourage employees to report suspicious activities without fear of reprisal.
A personal anecdote: after implementing a ‘security ambassador’ program where enthusiastic employees championed security practices, a notable uptick in reporting suspicious activities was observed. This not only heightened awareness but also enhanced collaboration across the team. By investing in employee training and awareness, organizations can significantly bolster their defenses against cyber threats.
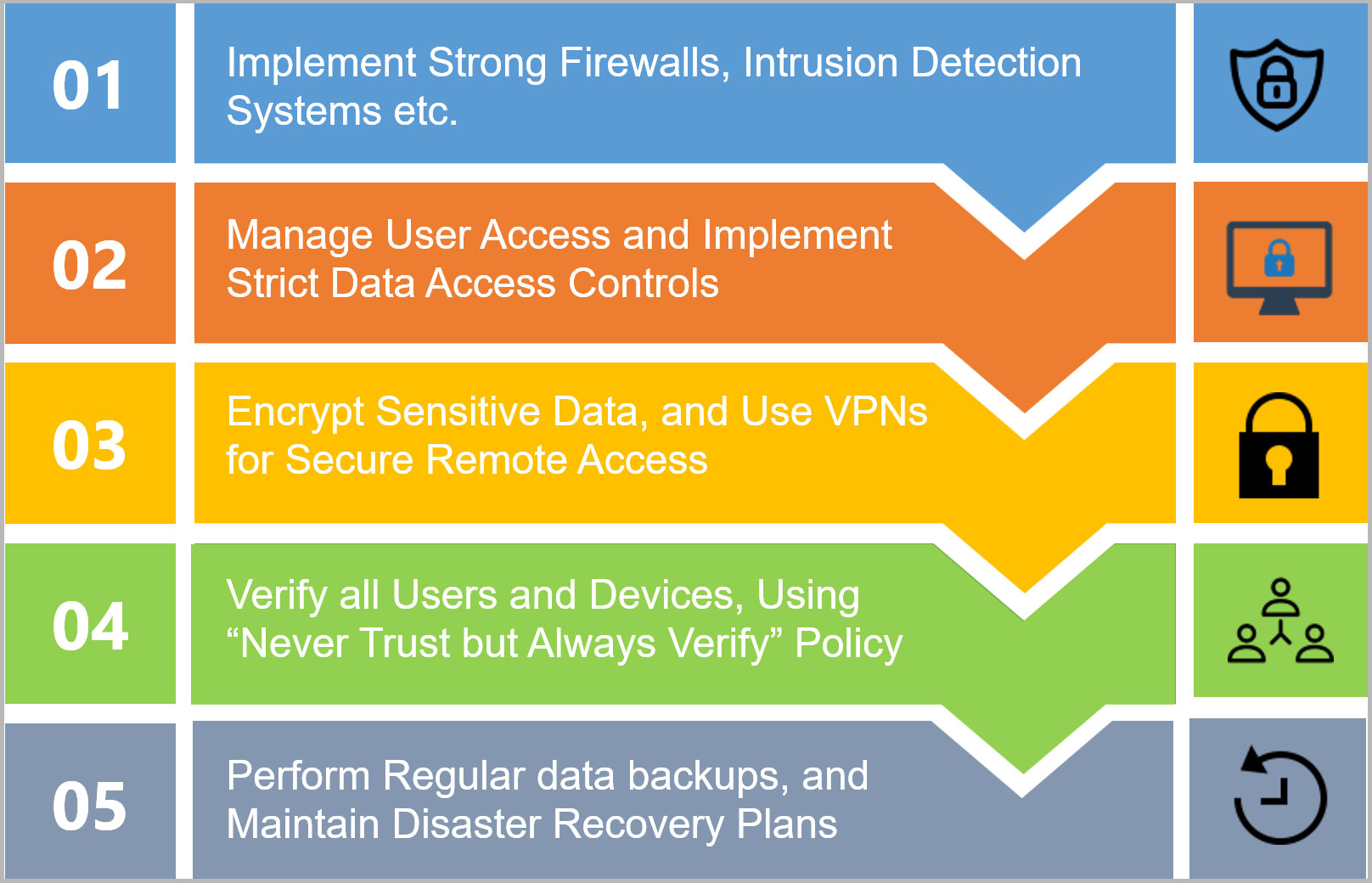
Monitoring and Incident Response
Real-Time Network Monitoring
Building upon the critical foundations of employee training, effective monitoring and incident response measures are essential for maintaining a secure network environment. Real-time network monitoring is like having a security camera system that constantly watches for unusual activities or breaches.
Implementing a robust monitoring system can help organizations:
- Detect anomalies: Monitor traffic flows to identify irregular patterns that may signal a breach.
- Immediate alerts: Receive notifications regarding potential threats, allowing rapid response.
- Data visualization: Use dashboards to gain insights into real-time operations and potential issues.
For instance, a colleague of mine shared how their company thwarted a major attack simply because their monitoring system flagged unusual login attempts late at night. Quick action led to thwarting the breach before it escalated.
Developing an Incident Response Plan
While monitoring is crucial, having a well-defined incident response plan is equally vital. This plan acts as a blueprint for how to react when a security incident occurs.
An effective incident response plan should include:
- Clear roles and responsibilities: Define who is in charge during an incident.
- Step-by-step procedures: Outline the actions to take from detection through recovery.
- Post-incident analysis: Review what happened to improve future responses.
I’ve seen teams turn crises into opportunities for growth simply by following their incident response plan after a breach. Ultimately, combining proactive monitoring with a solid incident response strategy transforms how organizations manage potential threats, enhancing their overall security posture.

Physical Security Measures
Securing Network Equipment
In the realm of network security, physical measures are often overlooked, yet they are just as crucial as digital defenses. Securing network equipment is fundamental in mitigating risks associated with unauthorized access. Picture your network hardware as the backbone of your digital infrastructure; if compromised physically, even the best software defenses won’t suffice.
Here are some best practices for securing network equipment:
- Lockable server racks: Ensure all critical equipment is housed in lockable racks to prevent unauthorized tampering.
- Surveillance systems: Employ CCTV and motion sensors in server rooms to monitor access.
- Environmental controls: Implement climate controls to protect from overheating or moisture damage.
In one instance, a friend lost vital data because their server room was easily accessible. Once they installed a proper locking system and monitored it, security threats were drastically reduced.
Restricted Access Control Policies
Complementing physical security measures are restricted access control policies. By controlling who can access sensitive areas, organizations can significantly cut down the risk of breaches.
Implementing restricted access policies involves:
- Clearly defined access levels: Specify who can enter different areas based on their roles.
- Keycard systems: Use electronic keycards or biometric scanners to track and limit access.
- Regular audits: Review access logs and permissions routinely to spot any anomalies.
For example, my previous workplace had a keycard system that not only restricted access but also provided logs of who entered the server room. This accountability became crucial during security assessments. By prioritizing physical security measures alongside digital strategies, organizations create a comprehensive defense against potential threats.

Compliance and Regulations
Understanding Data Protection Laws
As we shift our focus to compliance and regulations, it’s essential to recognize the role of data protection laws in safeguarding sensitive information. Understanding these laws is crucial for any organization that handles personal data. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S. set strict guidelines on how data should be collected, processed, and stored.
Consider these key points:
- Data subject rights: Individuals have rights over their personal data, including access, correction, and deletion.
- Breach notification: Organizations must report data breaches to authorities within a specified timeframe.
- Consent: Obtaining clear consent from users before processing their data.
In my experience, many businesses underestimate the importance of these laws until they face penalties for non-compliance.
Compliance Audits and Certifications
Once organizations grasp data protection laws, the next step is ensuring adherence through compliance audits and certifications. Regular audits can identify gaps in security practices and confirm that all regulatory requirements are met.
Key practices for compliance include:
- Third-party audits: Hire external experts to conduct thorough assessments of compliance protocols.
- Certifications: Achieving certifications like ISO 27001 signals to clients and stakeholders that data security is taken seriously.
- Continuous improvement: Use audit findings to enhance security measures and train employees.
For instance, after my former employer underwent an ISO certification process, the entire team gained a deeper understanding of compliance obligations, leading to improved data handling practices. Prioritizing compliance and regulations not only helps protect sensitive information but also builds trust with clients, making it an essential element of any security strategy.
Network Security Best Practices for Remote Work
VPN Usage and Security
As we venture into the world of remote work, maintaining strong network security becomes more critical than ever. One of the best practices for safeguarding remote connections is the use of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). VPNs create a secure tunnel between your device and the internet, making it difficult for hackers to intercept your data.
Here are some essential considerations for VPN usage:
- Choose a reputable VPN provider: Ensure your VPN service has a solid track record for security and privacy.
- Enable encryption: Opt for protocols that provide robust encryption to safeguard your data in transit.
- Regularly update VPN software: Keeping your VPN client updated ensures you have the latest security enhancements.
I remember using a VPN during a business trip, allowing me to access sensitive files safely while connected to public Wi-Fi. It provided peace of mind knowing my data was secure.
Securing Home Networks
In addition to using a VPN, securing your home network is vital for remote work security. Many employees may not realize that their home networks can introduce vulnerabilities.
Consider implementing these tips:
- Change default router settings: Modify your router’s admin password and SSID to prevent unauthorized access.
- Use strong Wi-Fi passwords: A complex password can deter intruders from accessing your network.
- Enable network encryption: Use WPA3 encryption for better security.
In a recent discussion, a friend shared how they tightened their home network security after discovering multiple unauthorized devices connected to their Wi-Fi. By adopting these measures, remote workers can significantly enhance their overall security posture, protecting both personal and company data while working from home.
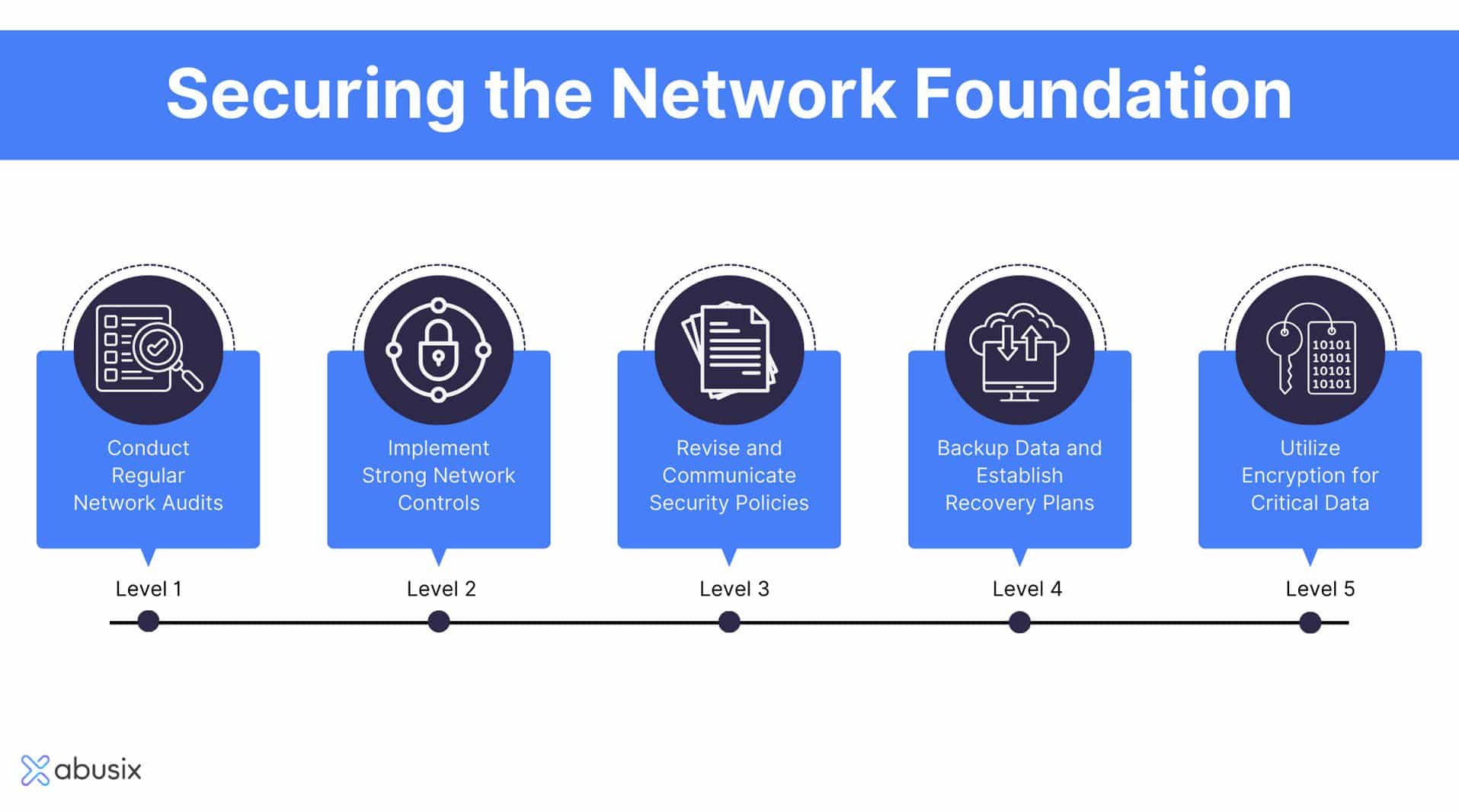
Network Security Risk Assessment
Identifying Vulnerabilities
Transitioning from securing home networks, the next crucial step in strengthening overall security is conducting a network security risk assessment. This assessment begins with identifying vulnerabilities within your network. Recognizing these weaknesses is essential to avoid potential breaches and attacks.
To effectively identify vulnerabilities, consider the following methods:
- Conduct regular audits: Review your network architecture, devices, and applications to spot weaknesses.
- Use vulnerability scanning tools: Employ software solutions that can automatically detect vulnerabilities in your systems.
- Engage in penetration testing: Hire experts to simulate real-world attacks and analyze how well your defenses hold up.
I once worked with a team that discovered an outdated application left unpatched—an easily exploitable vulnerability—during our assessment.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Once vulnerabilities are identified, implementing effective risk mitigation strategies is paramount. The goal is to reduce exposure and minimize the impact of potential threats.
Consider adopting these strategies:
- Regular updates and patch management: Ensure all software and devices are up-to-date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Implement multi-factor authentication: Adding extra layers of security can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Educate employees: Ensure that staff understands potential risks like phishing and how to avoid them.
In my experience, after developing a comprehensive risk mitigation plan, we reduced security incidents by over 30% within six months. Conducting a thorough risk assessment and employing these strategies can create a resilient network, ready to face any challenges head-on.

Future Trends in Network Security
Artificial Intelligence in Security
As we explore future trends in network security, one of the most exciting developments is the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI). AI can analyze vast amounts of data in real time, identifying patterns and anomalies that might take human analysts much longer to detect.
Here are a few ways AI is transforming security:
- Threat detection: AI algorithms can spot unusual behavior indicating a potential breach, allowing for quicker responses.
- Automated incident response: When a threat is detected, AI can take immediate action, isolating affected systems to limit damage.
- Predictive analytics: By assessing historical attack data, AI can predict and minimize future risks.
Having witnessed AI tools alerting us to suspicious activities before they escalated, I can attest to their growing importance in our security arsenal.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security Concerns
Alongside AI advancements, the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) presents both opportunities and significant security concerns. With more devices being connected to networks—from smart cameras to wearable fitness trackers—each device adds potential vulnerabilities.
To address IoT security concerns, consider these strategies:
- Implement network segmentation: Isolate IoT devices from critical systems to contain potential threats.
- Regular updates: Ensure all IoT devices have the latest firmware to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Stricter access controls: Limit who can connect to your IoT devices to reduce exposure to unauthorized users.
In conversations with friends using multiple smart devices, I’ve realized that many overlook the security implications. As IoT continues to expand, staying aware and proactive about these concerns will be crucial for maintaining network security. Balancing AI advancements with IoT security measures will be pivotal in shaping the future of network protection.

