Introduction
Understanding Blockchain Technology
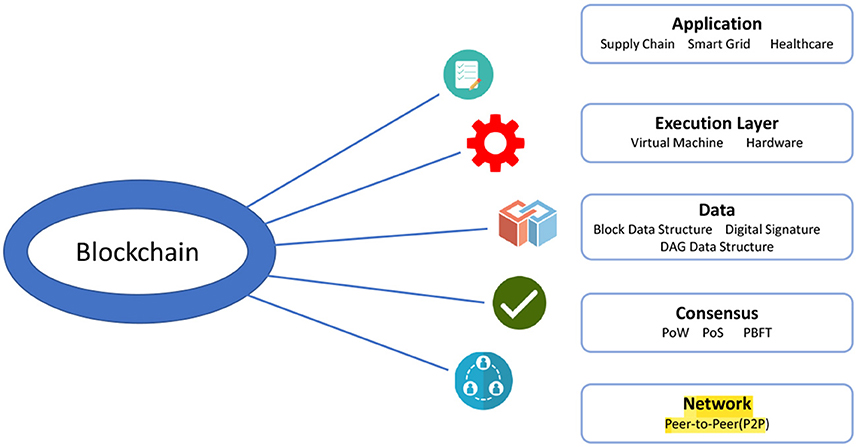
Blockchain technology is a term that has gained significant traction over the past decade, particularly with the rise of cryptocurrencies. However, its applications extend far beyond digital currencies and finance. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger that records transactions across many computers. This technology ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered retroactively without the consensus of the network, fostering trust and transparency.
Imagine a digital ledger where every interaction you make is recorded transparently for all stakeholders to see. This way, everyone relies on the same information, significantly reducing the possibility of fraud or errors. It’s like having a communal notebook — everyone can review it, but no one can erase what’s already written.
Key features of blockchain include:
- Decentralization: No central authority controls the data, which minimizes the risk of manipulation.
- Transparency: Changes made to the ledger are visible to all participants, promoting accountability.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded, it is extremely difficult to alter it, providing a secure data environment.
Significance of Blockchain in Government Sector
The potential benefits of blockchain technology in the government sector are manifold. Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing that this technology can enhance the efficiency and integrity of public services. By replacing traditional bureaucratic processes with blockchain-enabled systems, governments can offer:
- Better Service Delivery: Streamlining processes means citizens can access services faster, reducing wait times and improving satisfaction.
- Enhanced Security: With sensitive data protected by cryptographic principles, the risk of hacks and data breaches can be significantly mitigated.
- Increased Public Trust: When citizens can verify transactions and see how their data is used, trust in government institutions often improves.
Consider Estonia, which has adopted blockchain for various e-governance solutions, effectively showing how this technology can modernize public services. The use of such innovative solutions promises not just a shift in how government operates but also a transformation in how citizens perceive and interact with their governments.
As we delve further into the specific applications of blockchain in government sectors, it becomes evident that the future is ripe for change and innovation.
Blockchain in Government Services
Improving Public Service Delivery
As governments seek to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of their services, blockchain technology stands out as a transformative solution. By integrating blockchain into public service delivery, governments can significantly streamline operations and improve user experiences.
Imagine a scenario where citizens no longer face long queues or complicated paperwork when applying for permits, healthcare services, or social benefits. With blockchain, services can be automated and processed digitally in real time. For instance:
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They can automate various government processes, such as issuing licenses or managing regulatory compliance. This not only speeds up the process but also reduces human error.
- Integrated Systems: Blockchain can connect various government departments, allowing for seamless data sharing. When a citizen applies for a service, their verified data can be accessed across departments without redundant data entry.
Such efficiencies translate into faster responses and improved citizen satisfaction. By removing bureaucratic bottlenecks, governments are better positioned to serve their communities more effectively.
Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
In an era where trust in government institutions is paramount, blockchain can play a significant role in enhancing transparency and accountability. By providing a public ledger, blockchain allows citizens to verify transactions related to their interactions with government entities.
Consider these benefits:
- Real-time Monitoring: With blockchain, citizens can track how funds are allocated and spent. For instance, if a government is distributing aid after a natural disaster, individuals can see exactly where those funds are going, ensuring that resources reach the intended beneficiaries.
- Immutable Records: The integrity of transactions is preserved, as records stored on a blockchain cannot be tampered with. This reduces the chances of fraud and corruption in government operations.
By fostering an environment where data is accessible and transparent, governments can build trust with their citizens. In a personal anecdote, a resident in a city that adopted blockchain for its budget transparency noted how refreshing it was to see where their tax dollars were going, leading to increased civic engagement and participation.
In conclusion, the application of blockchain in government services not only enhances public service delivery but also cultivates a culture of transparency and accountability. As we explore further, we will uncover specific use cases where these benefits are realized in real-world scenarios.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Government
Land Registration and Title Deeds
One of the most impactful applications of blockchain in government services is in the realm of land registration and title deeds. Traditional systems of land management are often plagued by inefficiencies, fraudulent claims, and disputes regarding ownership. Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary solution to these persistent challenges.
Imagine a land registry system where every property transaction — whether it’s a sale, transfer, or lease — is recorded on a secure, immutable ledger. This not only simplifies the process but also significantly reduces disputes and fraud. Here’s how:
- Clear Ownership Records: Blockchain provides a transparent way to establish and maintain ownership records that can be easily accessed by all parties involved. This clear traceability helps prevent fraudulent claims on property.
- Fast and Secure Transactions: Title transfers can be completed in a matter of minutes rather than weeks or months. Using smart contracts, ownership can automatically transfer once payment is confirmed, similar to a digital handshake.
Countries like Sweden and Georgia have already started implementing blockchain for land registration. In Sweden, a pilot program demonstrated how quicker transactions could be achieved, enhancing productivity and empowering citizens.
Personal anecdotes from homeowners in Georgia highlight how the use of blockchain has not only streamlined processes but also instilled greater confidence in property ownership — a win-win scenario for both the government and its citizens.
Voting Systems and Elections
Another critical area where blockchain can significantly enhance government services is in voting systems and elections. Recent events globally have shown that trust in the electoral process is crucial for the stability of democracies. Blockchain technology can help ensure fair, transparent, and secure elections.
Consider the challenges faced during traditional elections, such as voter fraud, ballot tampering, and the complexities of counting votes. Here’s how blockchain addresses these issues:
- Secure Voter Identification: Using blockchain, voters can verify their identities digitally without compromising personal information. This leads to increased confidence in who is casting votes.
- Tamper-Proof Ballots: Once votes are cast and recorded on a blockchain, they cannot be altered or deleted. This resistance to tampering ensures the integrity of the election process.
Countries like Sierra Leone have explored blockchain for its voting system, and early trials have indicated a boost in voter participation and trust. A citizen who voted in this pilot program shared their sense of empowerment, knowing their vote was securely stored and could not be altered — a testament to the potential of blockchain in safeguarding democratic processes.
In summary, the application of blockchain in land registration and voting systems illustrates its transformative potential for government services. These use cases not only enhance efficiency but also build trust with citizens, paving the way for more secure and reliable public service delivery.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Blockchain
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
While blockchain technology holds immense promise for improving government services, it also brings significant challenges, particularly when it comes to data privacy and security. These concerns are crucial, given that governments handle sensitive and often personal information.
At first glance, the transparency that blockchain offers may seem contradictory to privacy needs. Consider these key points:
- Public vs. Private Blockchains: Public blockchains, while transparent, allow anyone to access transaction details. This openness might inadvertently expose personal data unless carefully managed. Private or permissioned blockchains can help address this issue by restricting access to authorized parties.
- Data Immutability: The very feature that enhances security — immutability — can pose a problem for privacy. If incorrect information is recorded on a blockchain, rectifying it can be challenging. For instance, think about an individual whose identity is mistakenly linked to a fraud case; erasing that record can be complicated.
Moreover, personal anecdotes highlight the unease citizens feel regarding data privacy. A resident in a country experimenting with blockchain for public services expressed concerns about their sensitive information being permanently stored, believing that such data could become a target for hackers despite blockchain’s security measures.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Framework
Navigating the regulatory landscape is another significant challenge for governments considering blockchain implementation. The technology operates on decentralized principles that may clash with existing regulations designed for centralized systems.
Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Establishing Legal Recognition: For blockchain records to hold up in court or meet compliance standards, legal frameworks must evolve. Governments need to work closely with legal experts to create regulations that embrace this new technology while safeguarding citizens’ rights.
- Interoperability with Existing Systems: Many government agencies rely on legacy systems that might not be compatible with blockchain technology. This creates a dual challenge: ensuring that new blockchain systems can integrate with existing workflows without disruption.
For instance, a government department that attempted to introduce blockchain found that their outdated infrastructure hampered progress and highlighted the need for a comprehensive strategy to modernize systems alongside implementing blockchain.
In summary, while the potential benefits of blockchain in government are vast, addressing data privacy and regulatory compliance is essential for successful implementation. Understanding these challenges will not only foster more thoughtful decision-making but also ensure that the technological shift toward blockchain is beneficial and secure for both governments and citizens alike.
Case Studies of Successful Blockchain Implementation in Government
Estonia’s e-Residency Program
Estonia has emerged as a pioneer in the use of blockchain technology within government. Its e-Residency program exemplifies how digital innovation can empower citizens and entrepreneurs worldwide. Launched in 2014, this program allows non-Estonians to apply for a digital identity issued by the Estonian government, effectively turning the nation into a global hub for digital business.
The e-Residency program is transformative for several reasons:
- Global Accessibility: Anyone, regardless of their physical location, can become an e-resident and access Estonian e-services. This inclusivity has attracted thousands of entrepreneurs worldwide.
- Secure Digital Identity: Utilizing blockchain, the program ensures that all transactions and data are secure, immutable, and transparently recorded. This significantly reduces the risk of fraud and enhances trust in digital interactions.
Personal anecdotes from e-residents reveal the impact of this program. One entrepreneur from South Africa shared how gaining e-residency allowed him to establish a European business entity quickly, opening doors to new markets without needing to relocate.
Dubai’s Blockchain Strategy
Dubai’s commitment to becoming a “smart city” includes an ambitious blockchain strategy aimed at transforming government services to enhance efficiency and reduce paperwork. The vision is to ensure that by 2024, all governmental documents will be stored on the blockchain, making Dubai the first city in the world with a fully paperless government.
Key aspects of Dubai’s blockchain strategy include:
- Smart Government Services: By digitizing and automating government services, residents can access services quickly and conveniently. For instance, applying for a visa now involves streamlined online processes, eliminating tedious paperwork.
- Increased Transparency: The use of blockchain enhances accountability by allowing citizens to track government projects and expenditures in real-time.
Stories from Dubai residents paint a picture of the tangible benefits. One local entrepreneur emphasized the substantial reduction in bureaucratic delays, allowing her business to thrive without the usual red tape associated with government transactions.
Both Estonia’s e-Residency program and Dubai’s blockchain strategy illustrate the remarkable potential of blockchain technology in government services. These case studies not only highlight efficient public service delivery but also showcase how innovation can empower citizens and businesses, paving the way for a more connected and transparent future in governance.
Future Trends and Potential of Blockchain in Government
Smart Contracts for Public Procurement
As governments seek to harness the power of blockchain, smart contracts are poised to revolutionize public procurement processes. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code, and they significantly enhance efficiency and transparency in government operations.
Imagine a scenario where procurement processes are automated, reducing the need for intermediaries. Here are some key benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Smart contracts can automate various stages of the procurement process, from issuing tenders to processing payments once conditions are met. This eliminates delays caused by paperwork and manual approvals.
- Enhanced Transparency: Each transaction is recorded on the blockchain, allowing all stakeholders — including suppliers and government officials — to view contract details and execution status. This transparency reduces the likelihood of corruption and favoritism.
A personal anecdote from a government procurement officer reveals that implementing a smart contract pilot significantly expedited contract approvals and minimized disputes. Officers noted how clear terms and real-time visibility fostered better relationships with suppliers, ultimately leading to higher quality goods and services delivered in a timely manner.
Integration with Internet of Things (IoT)
Another exciting trend is the integration of blockchain with the Internet of Things (IoT). As governments increasingly adopt IoT devices for various services — from smart city management to public safety systems — combining this technology with blockchain can provide enhanced security, data integrity, and operational efficiency.
Consider the potential applications:
- Improved Data Collection: IoT devices can collect real-time data about public infrastructure, traffic conditions, and even environmental factors. When this data is processed through blockchain, it ensures accuracy and authenticity, which governmental decisions can rely on.
- Enhanced Security: The decentralized nature of blockchain can protect IoT networks from hacking attempts. By storing IoT-generated data in a blockchain, governments can significantly improve data security and mitigate risks associated with centralized systems.
For instance, a city that deployed smart sensors across public utilities shared how integrating these devices with blockchain allowed for real-time monitoring of resource usage, leading to optimized energy consumption and substantial cost savings.
In conclusion, the future of blockchain in government holds vast potential, particularly through smart contracts and IoT integration. These innovations promise not just to streamline operations but to build a more transparent, efficient, and responsive government, ultimately enhancing citizen engagement and trust. As we continue to witness these advancements, the intersection of technology and governance presents new opportunities for a better tomorrow.

Conclusion
Recap of Benefits of Blockchain in Government
Having explored the various facets of blockchain technology in government, it becomes clear that its potential benefits are both profound and multifaceted. As a transformative force, blockchain can enhance the way governments operate, engage with citizens, and provide services.
Let’s outline some key benefits:
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures that transactions are permanent and visible. This transparency builds trust between governments and citizens, reducing opportunities for corruption.
- Streamlined Processes: By automating processes through smart contracts, governments can significantly reduce bureaucratic delays. Quick approval processes not only save time but also improve citizen satisfaction.
- Enhanced Security: With sensitive data protected by cryptographic principles, the risk of data breaches is mitigated. This enhancement is crucial for governments handling personal and sensitive information.
- Empowerment of Citizens: Programs like Estonia’s e-Residency showcase how blockchain can empower individuals and businesses globally, promoting inclusivity in government services.
A personal anecdote shared by a government employee who transitioned to blockchain solutions highlighted how witnessing real-time updates on public projects fostered a deeper connection with citizens. This newfound transparency led to increased civic engagement and participation.
Potential Impact on Governance and Citizen Services
The implications of implementing blockchain in government extend far beyond mere efficiency improvements. As we look ahead, we must consider how these technological advancements could reshape governance and citizen services.
The potential impact includes:
- Better Citizen Engagement: With more streamlined and transparent processes, citizens are more likely to engage with their government. This interaction can lead to feedback loops that enhance policy-making.
- Trust and Accountability: As governments adopt blockchain, they can foster a culture of accountability. This trust can encourage citizen participation in democratic processes, such as voting and public discussions.
- Innovative Service Delivery: Integrating blockchain with technologies like IoT can revolutionize public services, from smart waste management to efficient public transportation systems, ultimately enhancing quality of life.
In summary, as we reflect on the transformative capabilities of blockchain, it becomes evident that its implementation in government holds the promise of not just improving existing processes but ushering in a new era of governance. The journey toward widespread adoption may have its challenges, but the potential rewards for governance and citizen services are too significant to overlook. Embracing this technology could pave the way for a more connected, efficient, and responsive governmental framework, enhancing the relationship between citizens and their governments.

