
Introduction
Importance of Cybersecurity in Business
In today’s digital age, the importance of cybersecurity in business cannot be overstated. With cyber threats evolving daily, businesses are at increased risk of data breaches, ransom attacks, and various hacks. A recent anecdote from a small business owner revealed that a simple phishing email led to a significant financial loss, showcasing how even minor lapses in security can have severe consequences.
- Financial Implications: Costs can range from recovery expenses to legal fees.
- Reputation Damage: Customers lose trust when a business suffers a breach.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries now require stringent security measures to protect sensitive data.
For these reasons, investing in cybersecurity is no longer optional; it’s essential for safeguarding assets and maintaining customer trust.
Overview of Cybersecurity Tools
To effectively tackle the myriad of cyber threats, businesses must equip themselves with a comprehensive suite of cybersecurity tools tailored to their unique needs. Although the variety can be overwhelming, distinguishing the right tools can be straightforward. Key categories include:
- Network Security Tools: Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems, and VPNs.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Antivirus software, EDR, and MDM systems.
- Secure Email Gateways: Anti-phishing tools and email encryption.
By understanding and implementing these must-have cybersecurity tools, businesses can create a robust defense against potential threats and ensure a secure operational environment.

Network Security Tools
Firewall Protection
When it comes to securing a business network, firewall protection is often the first line of defense. This tool acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks. Imagine a firewall as a security guard that checks all data entering or leaving your premises. It blocks unwanted traffic while allowing legitimate communications through.
- Types of Firewalls:
- Network Firewalls: Control traffic between different networks.
- Host-based Firewalls: Protect individual devices.
One small business owner recounted how implementing a firewall stopped a significant number of unauthorized access attempts. Such proactive measures are invaluable.
Intrusion Detection Systems
Next up are Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), which monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. Think of an IDS like a smoke detector; it alerts you when something isn’t right. By analyzing network behavior, an IDS can identify potential threats, enabling you to respond promptly.
- Types of IDS:
- Network-Based IDS: Monitors traffic on specific segments.
- Host-Based IDS: Focuses on individual machines.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Last but certainly not least, a Virtual Private Network (VPN) secures connections over less secure networks, such as public Wi-Fi. This tool encrypts data, making it unreadable to potential eavesdroppers. A friend who travels frequently emphasized how a VPN has given them peace of mind while accessing sensitive business information on the go.
In summary, combining firewall protection, IDS, and VPNs creates a fortress for your network, ensuring robust protection against evolving cyber threats.
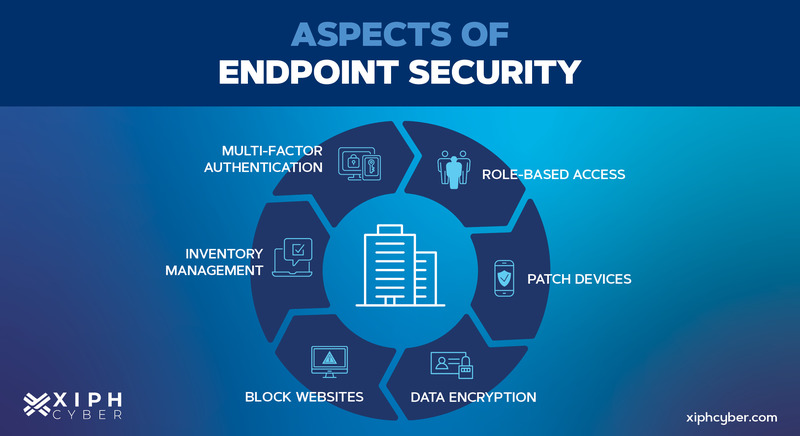
Endpoint Security Solutions
Antivirus Software
Following robust network security, businesses must turn their attention to endpoint security solutions to safeguard their devices. Antivirus software is perhaps the most recognizable tool in this arena. It scans devices for malware, adware, and other malicious threats. Think of it as a digital bug spray that keeps harmful agents at bay.
- Features of Antivirus Software:
- Real-time scanning to detect threats instantly.
- Regular updates to address new malware signatures.
A small business owner shared how a simple antivirus program saved their system from a serious ransomware attack, underscoring its value in daily operations.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Next is Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), which goes a step further than traditional antivirus solutions. EDR tools continuously monitor endpoint devices, identifying and responding to potential threats in real-time.
- Benefits of EDR:
- Advanced threat detection using behavioral analysis.
- Automated responses to mitigate risks immediately.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
Finally, Mobile Device Management (MDM) is crucial in today’s mobile workforce landscape. MDM solutions help businesses secure and manage employee devices, whether they’re company-owned or personal.
- Key Functions of MDM:
- Remote wipe capabilities to protect sensitive data.
- Policy enforcement to ensure compliance and security across the board.
In summary, employing antivirus software, EDR, and MDM creates a robust endpoint security strategy, effectively shielding devices from cyber threats and vulnerabilities.

Secure Email Gateways
Anti-Phishing Tools
As we delve deeper into cybersecurity measures, Secure Email Gateways emerge as crucial players in protecting businesses from email-based threats. One of the primary components of these gateways is anti-phishing tools, which guard against deceptive emails that attempt to trick employees into divulging sensitive information. Imagine these tools as vigilant lifeguards at a pool, always on the lookout for someone who might be in trouble.
- Key Features of Anti-Phishing Tools:
- URL filtering to identify harmful links.
- Suspicious attachment scanning to prevent breaches.
A small business owner recounted an incident where an anti-phishing tool detected a fraudulent email that could have compromised sensitive client information, illustrating its life-saving potential.
Email Encryption Solutions
Next, we have email encryption solutions that secure message content and attachments against unauthorized access. This is particularly important when sensitive data is involved, akin to sending a message in a sealed envelope.
- Benefits of Email Encryption:
- Protects confidentiality during transmission.
- Complies with data protection regulations.
Spam Filters
Lastly, spam filters play an essential role in maintaining inbox integrity by automatically identifying and redirecting unwanted or potentially harmful emails.
- How Spam Filters Work:
- Analyzing sender reputation.
- Recognizing common spam characteristics.
In sum, integrating anti-phishing tools, email encryption solutions, and spam filters into your secure email gateways equips your business with a formidable defense against email threats, ensuring that communication remains safe and reliable.

Web Security Applications
Secure Web Gateways
Continuing our exploration of essential cybersecurity tools, we now turn our attention to web security applications, which are vital for safeguarding online activities. At the forefront are Secure Web Gateways (SWGs), which serve as a filtering mechanism between users and the internet, blocking malicious threats from reaching your network.
- Benefits of Secure Web Gateways:
- Monitors and controls employee web usage.
- Enforces data loss prevention policies.
A tech manager shared how implementing an SWG dramatically reduced risky internet behavior among employees, creating a more secure browsing environment.
Web Application Firewalls
Next on the list are Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), designed to protect web applications from various threats, including SQL injection and cross-site scripting. These tools act as gatekeepers, checking incoming traffic to ensure it’s safe.
- Key Features of WAFs:
- Application-layer filtering to catch specific attacks.
- Custom rules to adapt to the unique needs of a business.
Website Security Scanners
Finally, Website Security Scanners assess website vulnerabilities, identifying potential weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
- How Website Security Scanners Work:
- Automated scans for common vulnerabilities.
- Detailed reports highlighting areas for improvement.
In summary, by utilizing Secure Web Gateways, Web Application Firewalls, and Website Security Scanners, businesses can create a robust web security infrastructure that mitigates online threats and ensures a safer browsing experience.
Data Loss Prevention Tools
Data Encryption Software
As we transition to the realm of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools, it’s crucial for businesses to protect their sensitive information from unauthorized access. Data encryption software is foundational in this effort, transforming readable data into a secure format. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the decryption key.
- Key Features of Data Encryption Software:
- Encryption at rest and in transit to secure data both on devices and during transmission.
- User-friendly interfaces that simplify the encryption process for employees.
One business owner shared how implementing encryption software allowed them to safely share confidential client information, instilling confidence in their security measures.
Backup and Recovery Solutions
Moving on, effective backup and recovery solutions are a must-have for ensuring business continuity. These tools create copies of important data and enable easy restoration in the event of data loss due to accidents or cyber incidents.
- Benefits of Backup Solutions:
- Automated backup schedules to minimize the risk of human error.
- Cloud-based options for off-site data storage.
Secure File Sharing Platforms
Finally, secure file sharing platforms are essential for safe collaboration. These platforms provide encrypted environments for sharing documents, preventing unauthorized access.
- Key Functions:
- User permissions to control who can access and modify files.
- Activity tracking for added oversight.
In conclusion, by leveraging data encryption software, robust backup and recovery solutions, and secure file sharing platforms, businesses can significantly enhance their data loss prevention strategies, ensuring sensitive information remains protected and accessible when needed.
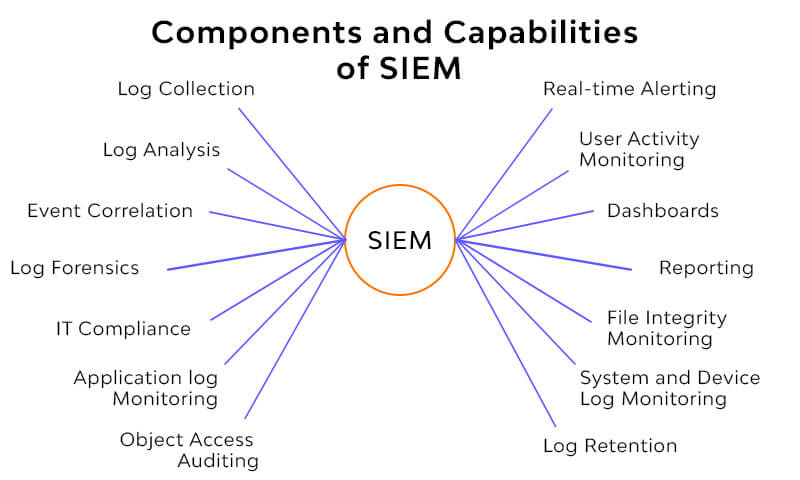
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Log Management
As we dive into Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), one of its core components is log management. This involves collecting, analyzing, and storing log data from various sources, such as servers, applications, and network devices. Proper log management can be the key to identifying security incidents and understanding system performance.
- Benefits of Efficient Log Management:
- Centralized visibility to keep track of all activities across the network.
- Historical record-keeping for compliance and auditing purposes.
A network administrator shared how streamlined log management helped them uncover a series of unauthorized access attempts, enabling quick remediation before any significant damage was done.
Threat Intelligence Integration
Next up is threat intelligence integration, which enhances SIEM effectiveness by providing real-time data on emerging threats. This means organizations can proactively address vulnerabilities instead of waiting for attacks to happen.
- Key Features:
- Automated threat feeds to stay updated on the latest risks.
- Correlation with internal logs for a comprehensive security stance.
Real-Time Monitoring Capabilities
Lastly, real-time monitoring capabilities are vital for effective incident response. SIEM solutions can continuously scan for anomalies or suspicious activities, allowing for immediate action.
- Highlights of Real-Time Monitoring:
- Alerts for unusual behavior or potential breaches.
- Customized dashboards for quick analysis and decision-making.
In summary, utilizing SIEM tools such as log management, threat intelligence integration, and real-time monitoring enables businesses to build a proactive security posture, making it easier to detect and respond to potential threats swiftly.

Incident Response Platforms
Investigation and Analysis Tools
As we wrap up our discussion on cybersecurity essentials, incident response platforms emerge as critical components in managing and mitigating security breaches. At the forefront are investigation and analysis tools, which help teams examine the circumstances surrounding an incident. These tools not only facilitate a deep dive into what occurred but also assist in identifying vulnerabilities.
- Key Features:
- Forensic analysis to trace attacker activities.
- Correlation of data from various sources for a holistic view.
A cybersecurity analyst reflected on how a robust investigation tool enabled their team to pinpoint the source of a breach efficiently, leading to quicker remediation efforts.
Incident Containment Features
Next, incident containment features are designed to limit the damage during an attack. This involves isolating affected systems or blocking malicious traffic to prevent widespread impact.
- Benefits of Containment Options:
- Automated triggers to isolate breaches as they happen.
- Manual controls for the security team to take immediate action.
Reporting and Documentation Functions
Finally, effective reporting and documentation functions are essential for maintaining a clear record of incidents.
- Highlights of Reporting Tools:
- Customized reports for stakeholders detailing incident response and lessons learned.
- Compliance documentation for regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, by harnessing investigation and analysis tools, incident containment features, and reporting functions, incident response platforms empower organizations to respond decisively to threats, ensuring that lessons are learned and systems strengthened against future vulnerabilities.

