
Introduction
Overview of Web Scraping
Web scraping is an essential technique that allows individuals and businesses to extract vast amounts of data from websites quickly. By automating the process of gathering information from the web, users can efficiently collect needed data for various applications, such as market research, data analysis, and competitive intelligence. Imagine a data analyst wanting to track pricing trends across e-commerce sites. Instead of visiting each site manually, web scraping offers a streamlined solution.
Importance of Web Scraping in Python
Python has become the go-to language for web scraping due to its simplicity and the powerful libraries it offers. Here are a few reasons why:
- Ease of Use: Python’s syntax is clear and easy to learn, making it accessible even for beginners.
- Libraries: With powerful tools like BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, and Selenium, developers can handle a variety of web scraping tasks with ease.
- Community Support: Python boasts a strong developer community, providing a wealth of resources and forums for aspiring web scrapers.
In TECHFACK, we often stress that mastering web scraping with Python can unlock endless possibilities, whether for academic research or business insights.

Basics of Web Scraping with Python
Installing Required Libraries
Once you’ve grasped the fundamentals of web scraping, the first step is to set up your Python environment by installing the necessary libraries. The most popular ones include:
- BeautifulSoup: Excellent for parsing HTML and XML documents.
- Requests: Simplifies sending HTTP requests to access web pages.
- Scrapy: A robust framework for scalable web scraping.
- Selenium: Ideal for handling dynamic content generated by JavaScript.
To get started, you can easily install these libraries via pip. For instance, running the command pip install beautifulsoup4 requests scrapy selenium in your terminal will load the essential tools onto your system.
Choosing the Right Tools
The tool you choose for web scraping often depends on your specific needs. Here are a few considerations to help guide your selection:
- Static vs. Dynamic Content: For static pages, BeautifulSoup and Requests suffice. Conversely, if your target site uses JavaScript extensively, Selenium is your best bet.
- Data Volume: If you’re scraping large datasets, Scrapy offers advanced features for scalability and performance optimization.
In my journey with TECHFACK, I’ve learned that selecting the right combination of these tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and success rate of your scraping projects.

Understanding HTML and XPath
Basics of HTML
To effectively scrape data from a web page, it’s crucial to understand HTML (HyperText Markup Language). HTML is the backbone of web content, structuring text, images, and links into easily navigable elements. Here’s a quick breakdown of its parts:
- Tags: Every element, such as paragraphs (
), headings (
to
), and links (), is enclosed in tags.
- Attributes: These provide additional information, like
hrefin links, which directs where the link leads. - Nested Elements: Elements can be nested within other elements, enabling complex page layouts.
With a good grasp of HTML, one can easily identify where the desired information resides on a page.
Working with XPath for Web Scraping
XPath (XML Path Language) is a powerful tool for navigating XML and HTML documents. It enables you to pinpoint the exact location of an element within the document structure. Here are a few tips for effective XPath usage:
- Absolute vs. Relative Paths: Absolute paths start from the root, while relative paths begin at the current node, making them more versatile.
- Functions: XPath supports functions such as
contains()andstarts-with(), which help to refine your queries.
From my experience with projects at TECHFACK, mastering XPath can drastically improve your web scraping accuracy, allowing you to extract precisely what you need from complex web structures.
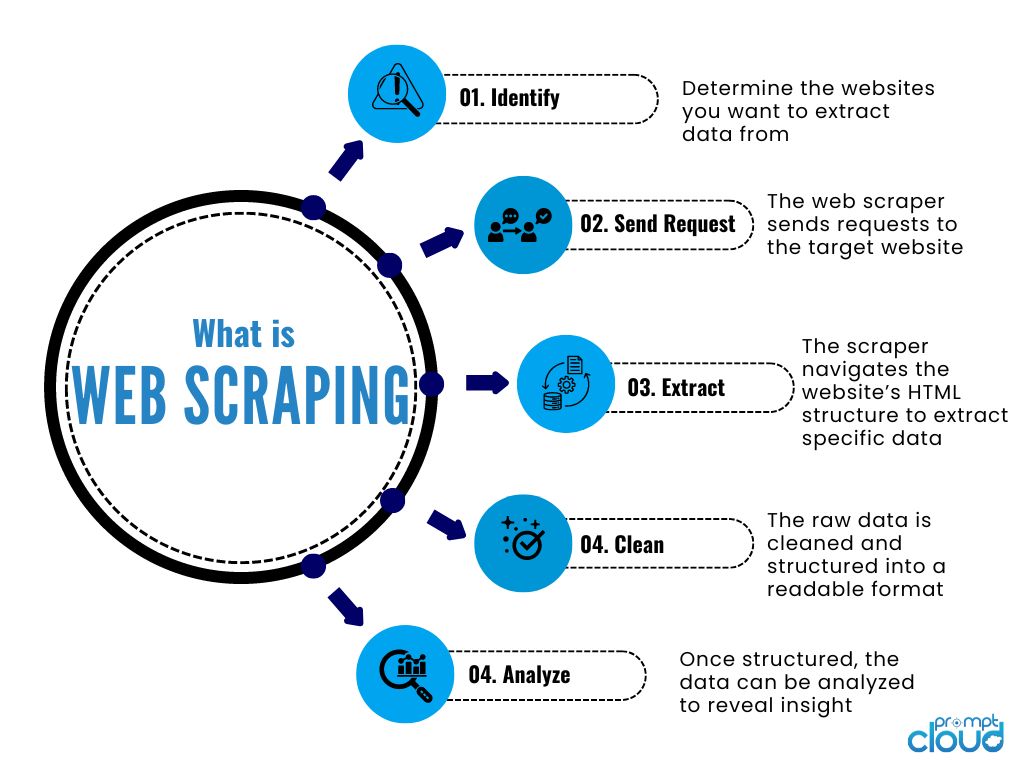
Handling Dynamic Content
Dealing with JavaScript-rendered Pages
In today’s web landscape, many websites use JavaScript to load content dynamically, making traditional scraping methods fall short. For instance, suppose you want to extract products from an e-commerce site that renders its catalog through JavaScript. In that case, the information you see is often not present in the HTML source code initially loaded by the browser.
To navigate this challenge, consider the following strategies:
- Inspect Network Traffic: Use browser developer tools to check how content is loaded over the network.
- APIs: Some sites offer public APIs that provide data in a structured format, making scraping unnecessary.
Using Selenium for Dynamic Content
Selenium comes to the rescue when you need to interact with JavaScript-driven web pages effectively. It simulates user actions in a web browser, allowing you to navigate through dynamic content seamlessly. Here are some benefits of using Selenium:
- Automated Browsing: You can programmatically click buttons, fill forms, and scroll through pages.
- Wait for Elements: It can wait for elements to load, ensuring that your script extracts data only when it’s fully available.
At TECHFACK, we’ve leveraged Selenium for projects that involve heavy JavaScript rendering, streamlining our web scraping processes and achieving remarkable success in data extraction.

Data Parsing and Cleaning
Extracting Data from Web Pages
Once you’ve navigated the challenges of dynamic content, the next step is to focus on extracting the data from web pages. You’ll often find yourself looking for specific information amid a sea of HTML tags. Here’s how to simplify the extraction process:
- Identify Patterns: Use CSS selectors or XPath expressions to pinpoint the HTML elements containing your desired data.
- Utilize Libraries: Leverage libraries like BeautifulSoup for Python, which provide intuitive methods for traversing and searching the parse tree, making it much easier to extract the information you need.
For example, when scraping product details from an e-commerce website, you might extract the name, price, and availability status by targeting the appropriate HTML classes.
Cleaning and Structuring Scraped Data
Now that you have raw data, it’s crucial to clean and structure it to make it usable. Raw data often contains inconsistencies or unnecessary information. Here are steps to clean it up:
- Remove Duplicates: Use Python’s
pandaslibrary to eliminate duplicate entries easily. - Standardize Formats: Ensure uniformity in data formats (such as dates or prices) to enable effective analysis.
- Handle Missing Values: Develop strategies for addressing missing data without compromising the dataset’s integrity.
At TECHFACK, organizing our scraped data into a structured format has been instrumental in facilitating insightful analyses and generating valuable reports, showcasing the transformable power of well-prepared data.

Scalability and Performance Optimization
Efficient Scraping Techniques
As your web scraping projects grow larger in scope, efficiency becomes paramount. To manage scalability effectively, consider these techniques:
- Concurrent Requests: Use libraries like
aiohttporScrapythat support asynchronous scraping, allowing you to make multiple requests simultaneously. This can significantly reduce scraping time. - Data Chunking: Split large data sets into smaller, more manageable pieces, processing them in batches rather than all at once. This can simplify error handling and improve overall efficiency.
During my tenure with TECHFACK, implementing these practices allowed us to scale our scraping efforts without compromising on speed or performance.
Avoiding IP Bans and Captchas
One of the common pitfalls of web scraping is the risk of getting your IP banned due to excessive requests or suspicious behavior. Here’s how to mitigate that risk:
- Rotate IP Addresses: Use proxy services to switch IPs frequently, so it appears as if multiple users are accessing the site.
- Throttling: Implement delays between requests, mimicking human browsing behavior. This reduces the chances of triggering anti-scraping measures.
- CAPTCHA Solving: Use third-party services or libraries designed to handle CAPTCHAs when faced with these challenges.
At TECHFACK, utilizing these strategies has been vital in maintaining our scraping capabilities without facing excessive restrictions, ensuring our ongoing data acquisition remains seamless and uninterrupted.

Ethical and Legal Considerations
Respecting Website Policies
When venturing into the realm of web scraping, it’s important to respect the websites you are targeting. Each site may have a robots.txt file—a protocol that defines what can and cannot be scraped. Here are some key considerations:
- Check
robots.txt: Before scraping, analyze the site’srobots.txtto see if your intended pages are allowed for scraping. - Terms of Service: Always read the website’s terms. Some sites explicitly forbid scraping, while others may allow it under specific conditions.
During my time with TECHFACK, adhering to these protocols not only helped maintain goodwill with web owners but also led to smoother scraping experiences.
Avoiding Legal Issues
While scraping is a valuable tool for data gathering, it can also pose legal risks. To steer clear of potential legal pitfalls, follow these guidelines:
- Data Ownership: Understand that the data belongs to the site owner. Misusing or redistributing scraped data without permission can lead to copyright claims.
- Avoid Mass Scraping: Excessive scraping of a website can be interpreted as a denial of service attack, leading to lawsuits or IP bans.
By taking these ethical and legal considerations seriously, as emphasized within our projects at TECHFACK, you safeguard your scraping endeavors and build a respectful relationship with online data sources.

Advanced Techniques and Tools
Web Scraping APIs
As web scraping becomes more prevalent, various APIs have emerged to simplify the process and enhance productivity. Using a web scraping API can streamline your workflow by handling many technical aspects of data extraction for you. Here are some benefits:
- Ease of Use: Most APIs offer simple endpoints that allow you to retrieve data quickly without diving deep into complex scraping code.
- Data Formats: Many APIs provide data in formats like JSON or CSV, making it easy to use in analytics and application development.
In my experience with TECHFACK, leveraging web scraping APIs has been a game-changer, especially when working with multiple websites simultaneously, ensuring quick and reliable data extraction.
Headless Browsers for Scraping
Headless browsers are another excellent tool for web scraping, especially for sites that heavily rely on JavaScript. Unlike traditional browsers, headless browsers operate without a graphical user interface, allowing for faster execution of scraping tasks. Here’s why they’re useful:
- Speed: Since they don’t render a visual interface, they can load and scrape pages at lightning speeds.
- Complex Interactions: They can simulate user interactions more effectively, allowing you to click buttons and navigate through web pages.
During projects at TECHFACK, implementing headless browsers like Puppeteer and Playwright has significantly improved our scraping efficiency on complex sites, enabling us to extract dynamic content seamlessly.

Real-World Applications and Case Studies
E-commerce Price Monitoring
One of the most tangible applications of web scraping is in e-commerce price monitoring. Businesses can track competitor pricing, analyze trends, and adjust their own pricing strategies accordingly. For example, an online retailer may use web scraping to automate the collection of price data from competitors’ websites.
- Dynamic Pricing: By monitoring prices frequently, retailers can implement dynamic pricing strategies to remain competitive.
- Inventory Insights: It can also help in tracking stock availability across different platforms, providing a comprehensive view of market dynamics.
At TECHFACK, we’ve seen clients boost their pricing strategies through comprehensive scraping of competitive e-commerce sites, resulting in increased sales and market share.
Sentiment Analysis from Social Media
Another powerful application is sentiment analysis, where data scraped from social media platforms can provide valuable insights into public opinion. Companies can analyze customer feedback, reviews, and comments about their products or services.
- Brand Monitoring: By scraping social media, businesses can gauge sentiment around their brand in real-time, enabling quick responses to negative feedback.
- Trend Identification: It helps identify trending topics and public emotions associated with specific events or campaigns.
In our projects at TECHFACK, leveraging sentiment analysis tools on social media data has allowed clients to adapt their marketing strategies proactively, ensuring they resonate well with their audience.
Best Practices for Successful Web Scraping
Managing Error Handling
In the world of web scraping, encountering errors is almost inevitable. Whether it involves changes in website structure, server issues, or data format inconsistencies, having a robust error handling strategy is crucial. Here’s how to set up effective error management:
- Try-Except Blocks: Utilize these blocks in your code to catch exceptions and continue the scraping process without crashing.
- Logging: Implement a logging system to keep track of errors. This will help in diagnosing issues later on.
- Retry Logic: Include a mechanism to retry requests after a failure. Sometimes, a temporary glitch might prevent data retrieval.
At TECHFACK, we prioritize error handling in our scraping scripts, ensuring minimal downtime, and consistent data collection even when faced with challenges.
Monitoring and Maintenance Strategies
Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential for successful web scraping projects. Here are some strategies to keep your scraping efforts running smoothly:
- Scheduled Runs: Automate your scripts to run at scheduled intervals using tools like cron jobs or task schedulers to ensure timely data collection.
- Review Updates: Websites often undergo changes; regularly reviewing and updating your selectors or scraping logic is essential to stay aligned.
- Data Integrity Checks: Periodically validate the scraped data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
By implementing these strategies, as learned from our comprehensive projects at TECHFACK, you not only ensure the integrity of your data but also maintain the overall efficacy of your scraping operations.

