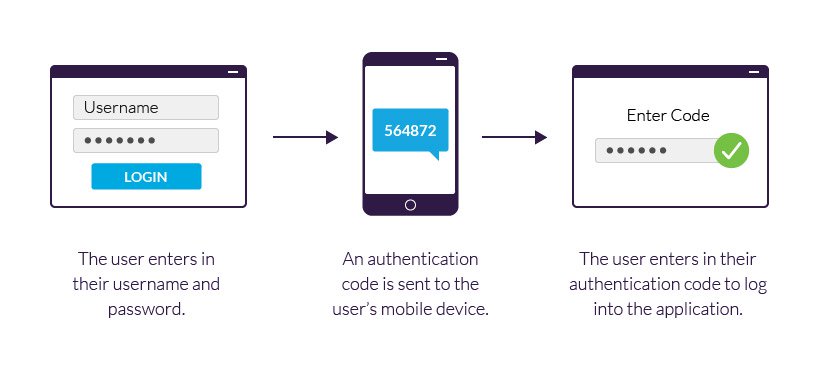
Introduction
Definition of Two-Factor Authentication
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security protocol that requires users to provide two different forms of identification before accessing an account. This typically involves something the user knows (like a password) and something the user possesses (like a smartphone app or a hardware token). For example, when logging into an online banking account, after entering your password, you might receive a text message with a code that you need to enter to gain access.
Significance of Two-Factor Authentication
The significance of Two-Factor Authentication cannot be overstated in today’s digital world. Cyber threats are rampant, and passwords alone can no longer provide adequate security.
Consider the following points:
- Enhanced Security: Even if a password is compromised, the second factor is required for access.
- Reduced Risk of Identity Theft: It adds an additional layer of defense against unauthorized access.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your accounts are more secure brings reassurance, particularly when sensitive information is involved.
Implementing Two-Factor Authentication is a critical step toward improving overall security and protecting personal and professional data.

Why Implement Two-Factor Authentication
Increased Security
Implementing Two-Factor Authentication significantly enhances security for both personal and organizational accounts. By requiring two distinct forms of validation, it effectively creates an additional barrier against cyber-attacks.
Imagine this scenario: You’ve just set up your online profile with a strong password, but what happens if that password is leaked? With 2FA, even if someone obtains your password, they would also need that second factor to gain access. Some key benefits include:
- Complexity Reduction for Passwords: Users can maintain simpler passwords, knowing there is an additional layer of protection.
- Constant Vigilance: Continuous prompts for verification cultivate a habit of security awareness among users.
Protection Against Unauthorized Access
The foremost advantage of Two-Factor Authentication is its ability to protect against unauthorized access. This protection is crucial in an era where data breaches are an everyday reality.
Consider data-sensitive industries, like finance or healthcare. Implementing 2FA helps maintain the integrity of client data and builds trust. Moreover, with features like:
- Real-time alerts when a login attempt is made from an unknown device,
- Temporary access codes that expire quickly,
organizations can confidently safeguard their digital assets, ensuring that only authorized users can access critical information. This proactive approach not only deters potential hackers but also fortifies the overall security posture.

Types of Two-Factor Authentication
Knowledge-Based Authentication
Knowledge-Based Authentication (KBA) is the first type of two-factor authentication, relying on something the user knows. Common examples include security questions, like “What was your first pet’s name?” or “What city were you born in?” While this method leverages personal information, it’s essential to choose questions that are not easily guessable.
Here’s why KBA can be effective:
- User Familiarity: Most users can easily recall personal information, making the process straightforward.
- Quick Implementation: Many platforms already integrate KBA, ensuring a seamless setup.
Possession-Based Authentication
Possession-Based Authentication requires users to have a physical object. This often takes the form of:
- Mobile Apps: Applications like Google Authenticator or Authy generate unique, time-sensitive codes.
- Hardware Tokens: USB keys or fobs that provide a code upon interaction.
This method strengthens security by ensuring that even if someone has your password, they still need the physical device for access.
Inherence-Based Authentication
Inherence-Based Authentication takes security a step further by relying on biometrics. It encompasses fingerprint scans, facial recognition, or voice recognition.
Benefits include:
- Uniqueness: Biometric traits are inherently individual, making them difficult to replicate.
- User Convenience: Users often find biometrics faster and more straightforward than remembering codes.
These three types showcase the versatility of Two-Factor Authentication in catering to various user needs and security preferences.
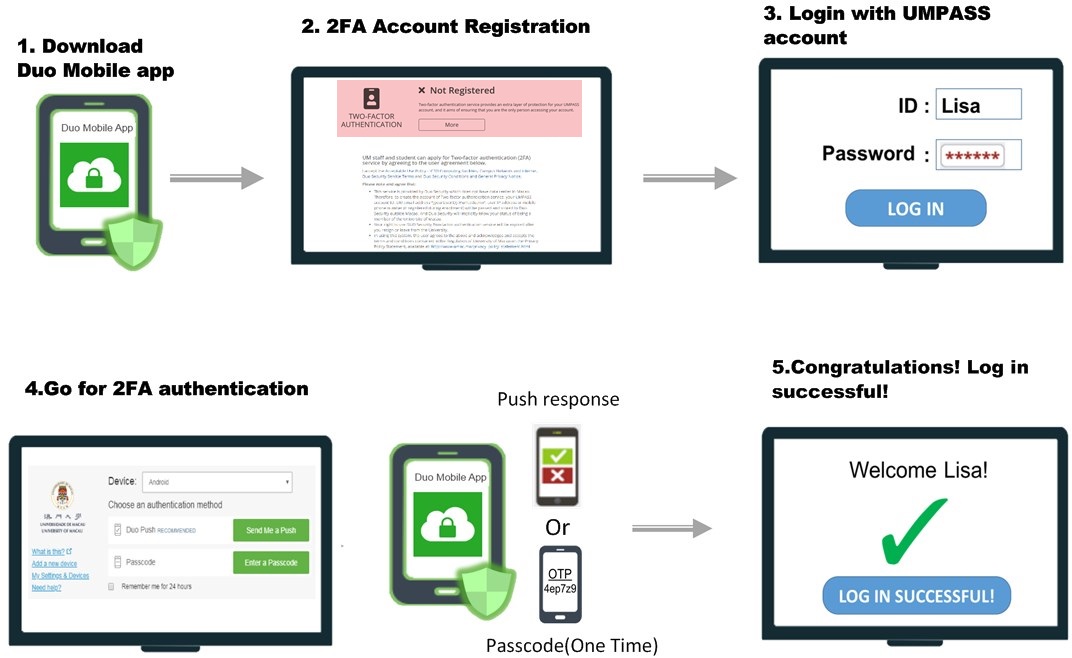
Implementing Two-Factor Authentication
Setting Up Two-Factor Authentication
Setting up Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a straightforward process that can significantly enhance your digital security. Most platforms offer simple steps to enable this feature. Typically, it involves:
- Accessing Security Settings: Navigate to the account settings or security section of your profile.
- Choosing the 2FA Option: Look for the Two-Factor Authentication or Multi-Factor Authentication settings.
- Selecting a Method: Choose your preferred authentication method, such as SMS, email, or an authenticator app.
- Verification: Follow the prompts to verify your identity, which might include entering a code sent to your device.
Remember, the initial setup only takes a few minutes but can save hours of headaches later!
Choosing the Right Authentication Methods
With various authentication methods available, selecting the right one is crucial for effective security. Consider these factors when making your choice:
- Usability: How easy is it for you and your team to use?
- Security Level: Some methods provide stronger security than others; for example, biometric options (like fingerprint scanning) are typically more secure than SMS.
- Accessibility: Ensure it’s accessible from devices you commonly use, such as smartphones or laptops.
Finding the right balance between security and user convenience will make implementing Two-Factor Authentication a more effective solution for safeguarding your accounts.

Two-Factor Authentication Best Practices
Regularly Updating Security Measures
To ensure the continued effectiveness of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), it’s essential to regularly update security measures. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and so should your defenses. Here are a few best practices to keep in mind:
- Routine Reviews: Revisit your 2FA settings periodically to check for any updates or changes in security policies.
- Upgrade Authentication Methods: Consider shifting to more robust methods, such as biometrics or hardware tokens, especially if your current method feels outdated.
- Stay Informed: Follow security news to remain aware of new threats that may compromise your chosen authentication methods.
This proactive approach ensures that your digital assets are safeguarded effectively over time.
Educating Users About Two-Factor Authentication
User education is equally crucial in implementing 2FA successfully. Even with the best security measures, if users are unaware of how 2FA works, its effectiveness will be compromised. Strategies for effective user education include:
- Workshops and Training Sessions: Conduct sessions that explain the significance and process of 2FA.
- Resource Materials: Provide easy-to-follow guides, infographics, or videos.
- Encourage Questions: Foster an open atmosphere for users to ask questions and clarify doubts about 2FA.
By prioritizing security updates and user education, organizations can significantly enhance their defense against cyber threats while empowering users to take control of their online safety.
Challenges and Considerations
User Convenience vs. Security
One of the key challenges in implementing Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is balancing user convenience with robust security measures. While 2FA significantly enhances security, it can also add steps to the login process, which may frustrate some users. An example is when users are in a hurry, and the additional code generation momentarily delays access to their accounts.
To tackle this dilemma, consider these strategies:
- Flexible Options: Provide users with various authentication methods, allowing them to choose what works best for them.
- Trust Levels: Allow users to establish trusted devices, reducing the frequency of 2FA prompts on their personal devices.
- Feedback Mechanism: Enable users to share feedback on their experience with 2FA, paving the way for improvements.
Potential Integration Issues
Integrating 2FA can also present challenges, particularly in existing systems. Organizations may encounter compatibility problems with legacy systems that do not support modern authentication protocols.
To mitigate these issues:
- Thorough Testing: Ensure various systems and devices are tested before full implementation.
- Scalable Solutions: Choose a 2FA solution that can scale and adapt to technological advancements.
- Support Resources: Provide ample support for users facing integration hurdles.
By proactively addressing these challenges, organizations can create a more secure yet user-friendly environment that encourages the effective use of Two-Factor Authentication.

Two-Factor Authentication for Different Platforms
Two-Factor Authentication for Mobile Devices
When it comes to mobile devices, implementing Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) has become essential due to their ubiquitous use and the sensitivity of information they carry. Most smartphones support various 2FA methods, allowing users to easily secure their data.
For instance, users can leverage:
- Authenticator Apps: Applications like Google Authenticator or Duo Mobile provide time-sensitive codes to verify logins securely.
- Push Notifications: Some services send push notifications to your phone, allowing you to approve or deny logins instantly.
This versatility enables users to select methods that best suit their lifestyle, enhancing both security and convenience.
Two-Factor Authentication for Online Accounts
Online accounts, whether for social media, banking, or email, are prime targets for cybercriminals, making 2FA crucial for safeguarding them. Most major platforms, including Facebook, Google, and Amazon, now offer robust 2FA options.
When setting up 2FA for online accounts, consider:
- SMS Codes: While convenient, these can be intercepted, so use them cautiously.
- Backup Codes: Services often provide backup codes in case your primary method fails, ensuring you won’t be locked out of your account.
By utilizing 2FA across both mobile devices and online accounts, users can significantly bolster their security while enjoying a seamless digital experience.

Future Trends in Two-Factor Authentication
Biometric Authentication
As we look to the future of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), Biometric Authentication stands out as a prominent trend. This method relies on unique physiological traits, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, to verify identity.
Many modern smartphones now come equipped with biometric sensors, allowing seamless and secure login experiences. Here’s why biometric authentication is gaining traction:
- Convenience: Gone are the days of fumbling for passwords. A simple scan can grant users access in seconds.
- High Security: Biometric traits are nearly impossible to replicate, providing an excellent layer of protection.
Furthermore, as technology continues to advance, we can expect biometric methods to become even more sophisticated and widely adopted across platforms.
Behavioral Biometrics
Another fascinating trend on the horizon is Behavioral Biometrics, which assesses patterns in user behavior to authenticate identity. This includes analyzing:
- Typing Speed: How quickly or slowly someone types their password.
- Mouse Movements: Tracking the way users navigate websites can reveal unique patterns.
The beauty of behavioral biometrics lies in its unobtrusiveness; it continuously monitors user actions without requiring additional steps for the user. As organizations strive for enhanced security, incorporating both biometric and behavioral biometrics could be pivotal in achieving a robust and user-friendly authentication process. This marks an exciting future for Two-Factor Authentication.

Conclusion
Benefits of Two-Factor Authentication
In conclusion, the implementation of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is undeniably a game changer in the realm of digital security. By requiring more than just a password, 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive accounts.
Consider the following benefits:
- Enhanced Security: The dual-layer protection serves as a formidable barrier against cyber threats.
- Increased User Confidence: Knowing that their accounts are more secure encourages individuals to engage more freely online.
- Adaptability: With various authentication methods (biometrics, SMS, apps), users can find options that fit their lifestyle.
Encouraging Adoption for Enhanced Security
Encouraging the adoption of Two-Factor Authentication is crucial for organizations and individuals alike. With cyberattacks on the rise, fostering a culture of security awareness can make a significant difference.
Effective strategies include:
- Providing Clear Guidance: Help users understand the setup process and benefits.
- Creating Incentives: Offer rewards for users who enable 2FA on their accounts.
By championing 2FA adoption, we can collectively enhance our digital safety, ensuring a more secure online environment for everyone.

