
Introduction
Overview of Cloud Environment Security
In today’s digital landscape, the cloud has revolutionized the way businesses operate. But what’s equally essential is understanding how to secure these cloud environments. Cloud environment security encompasses various strategies and technologies used to protect data, applications, and infrastructures hosted in the cloud. This involves considering shared responsibility models, where both cloud providers and users play critical roles in maintaining security.
Importance of Securing Your Cloud Environment
Securing your cloud environment is not just a best practice; it’s a necessity. Without proper security measures, organizations risk exposure to data breaches, which can lead to financial loss and damage to brand reputation. For example, companies like capital one have faced significant ramifications due to insufficient cloud security protocols.
Here are a few reasons why cloud security should be a top priority:
- Data Protection: Safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting industry standards to avoid penalties.
- Business Continuity: Ensuring operations remain uninterrupted despite potential threats.
By prioritizing cloud security, businesses can foster trust and integrity in their operations.

Understanding Cloud Security Risks
Common Threats to Cloud Environments
As we delve deeper into cloud security, it’s vital to recognize the common threats that can compromise these environments. Just like how a house can be vulnerable to break-ins, cloud systems face risks that need addressing. Some prevalent threats include:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive information can lead to data theft or leaks.
- DDoS Attacks (Distributed Denial of Service): These attacks overwhelm systems, causing interruptions or downtime.
- Misconfigured Cloud Settings: Simple mistakes in settings can expose data to unintended users.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data can inadvertently or maliciously cause security breaches.
Impact of Security Breaches
The consequences of security breaches can be profound. Take the infamous Equifax breach as an example, where millions of personal records were compromised, leading to financial losses and a damaged reputation. The impacts can manifest as:
- Financial Loss: Direct costs of rectifying breaches and potential fines.
- Reputation Damage: Loss of customer trust, which can take years to rebuild.
- Legal Consequences: Regulatory penalties from non-compliance with data protection laws.
By taking the time to understand these risks, organizations can better prepare for, and mitigate, potential threats to their cloud environments.

Essential Tips for Securing Your Cloud Environment
Implementing Strong Authentication Measures
Now that we grasp the risks, let’s discuss how to secure your cloud environment effectively. One of the first steps is to implement strong authentication measures. Relying solely on passwords is like leaving your front door unlocked; it’s inviting trouble. Here’s how to bolster your security:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Require a second form of verification, like a text message or authentication app.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Simplifies user access while maintaining security.
Encryption Best Practices
Next, ensure your data is encrypted. Encryption acts as a safeguard, converting readable data into unreadable code. This means that even if data is intercepted, it can’t be easily accessed. Always use:
- Strong Encryption Algorithms: AES-256 is a popular choice.
- Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit: Protect data both when stored and during transmission.
Regular Data Backups
Regular data backups are essential as well. Think of backups as an insurance policy; they ensure you can recover from unexpected events. Establish a routine for:
- Automated Backups: Schedule backups to minimize human error.
- Offsite Storage: Keep copies in different geographical locations for added security.
Monitoring and Logging Strategies
Lastly, employ monitoring and logging strategies to watch for unusual activities in real-time. Monitoring acts like a security camera, alerting you to potential breaches. Implement:
- Real-time Alerts: Set up notifications for suspicious activities.
- Comprehensive Logging: Keep detailed records for audits and investigations.
By integrating these essential tips, you significantly enhance the security of your cloud environment and better protect your organization’s sensitive data.

Cloud Provider Security Features
Evaluating Security Offerings from Cloud Providers
As organizations embrace the cloud, understanding the security features offered by providers becomes crucial. Not all cloud providers are created equal, so it’s essential to evaluate their security offerings meticulously. While selecting a provider, consider factors such as:
- Compliance Certifications: Look for certifications like ISO 27001, HIPAA, or GDPR compliance, which indicate a commitment to security standards.
- Access Controls: Ensure they have robust identity and access management systems in place.
- Data Security Policies: Review their policies on data encryption, backup procedures, and incident response strategies.
Putting these elements together can help you choose a provider that aligns with your security needs.
Utilizing Built-in Security Tools
Once you’ve opted for a cloud provider, take advantage of their built-in security tools. These tools often come equipped with advanced features that can enhance your security posture:
- Firewall Protection: Many providers offer customizable firewalls to protect against unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems can detect and alert you to suspicious activities within your cloud environment.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Utilize SIEM tools to analyze logs and monitor for potential security incidents.
By leveraging these built-in security tools, businesses can add an additional layer of security to their cloud environments, making it harder for threats to penetrate and ensuring better overall protection.
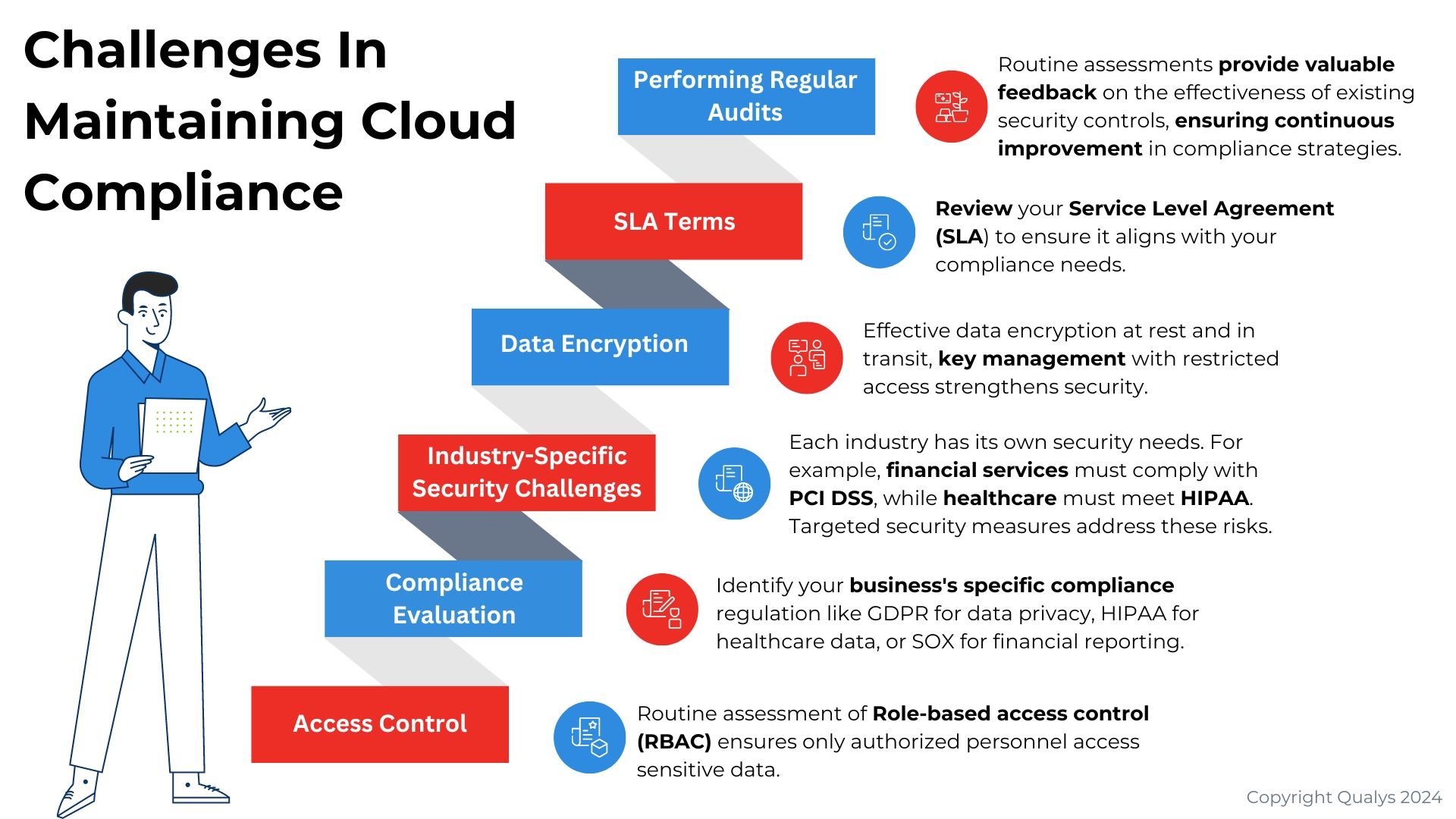
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations in Cloud Security
Importance of Compliance in Cloud Security
Moving forward in the realm of cloud security, let’s talk about compliance and its critical role. Compliance is more than just ticking boxes; it ensures that organizations adhere to legal standards, protecting both customer information and corporate integrity. Ignoring compliance can lead to severe penalties and reputational damage.
For instance, a data breach that results in non-compliance can cost organizations thousands, if not millions, in fines and lawsuits. By prioritizing compliance, businesses can also demonstrate their commitment to data security, fostering trust with customers and stakeholders.
Overview of Key Regulations and Standards
So, what regulations should organizations be aware of? Here’s an overview of some key standards:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This EU law focuses on data privacy and protects the personal data of EU citizens.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): For organizations handling healthcare data, compliance with HIPAA is crucial for protecting patient information.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Essential for organizations that handle credit card transactions, ensuring data is secure.
Understanding and adhering to these regulations helps maintain the integrity of cloud environments and secures sensitive information against breaches. Leveraging compliance frameworks can further enhance your organization’s security posture while mitigating risks.

Incident Response and Disaster Recovery Planning
Developing an Incident Response Plan
With compliance and security standards in place, it’s time to address what happens when the unexpected occurs—like a cyberattack or data breach. Developing a solid incident response plan is essential for minimizing damage and restoring control. Think of it as a fire drill but for data security. Here’s how to get started:
- Establish Clear Roles: Assign specific responsibilities to team members for efficient communication during incidents.
- Create an Incident Classification System: Differentiate between various incident types to tailor responses effectively.
- Develop Communication Protocols: Ensure that key stakeholders are informed promptly, maintaining transparency and trust.
By preparing for incidents in advance, organizations can respond swiftly and effectively, mitigating potential damages.
Creating a Disaster Recovery Strategy
Next is formulating a robust disaster recovery strategy. A good disaster recovery plan ensures business continuity and minimizes downtime. Consider including:
- Data Backups: Regularly backing up data and storing it offsite protects against loss.
- Recovery Time Objectives (RTO): Define critical timeframes for restoring operations.
- Regular Testing and Updates: Routine drills and assessments guarantee that your plan stays relevant and effective.
By incorporating these elements, businesses are better positioned to withstand adverse events and can quickly bounce back, maintaining stakeholder confidence and operational stability.

Employee Training and Awareness
Importance of Security Training for Employees
As we transition into the human aspect of cloud security, it becomes evident that technology alone isn’t enough. Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats, making security training indispensable. Just like learning to use a fire extinguisher in a real fire situation, understanding security practices can prevent major catastrophes.
Consider incorporating a few key training initiatives:
- Phishing Awareness: Teach team members to recognize suspicious emails and avoid falling victim to scams.
- Password Management: Emphasize the importance of strong password practices and the use of password managers.
- Incident Reporting: Ensure everyone knows how to report security issues swiftly to minimize potential harm.
By investing in training, organizations empower employees to contribute proactively to security efforts.
Building a Security-Aware Culture
Furthermore, building a security-aware culture is crucial. When security becomes part of the organizational ethos, it shapes behaviors and attitudes. Here’s how to cultivate such a culture:
- Regular Reminders: Use newsletters or bulletin boards to share security tips.
- Leadership Involvement: Encourage top management to participate in training, demonstrating commitment.
- Recognition Programs: Acknowledge employees who exemplify good security practices, motivating others to follow suit.
A strong security culture not only reduces risks but also instills confidence in employees and clients alike, promising that security is a shared responsibility.

Continuous Security Improvement
Implementing Regular Security Audits and Assessments
As we shift our focus towards continuous security improvement, one of the most effective strategies is implementing regular security audits and assessments. Think of audits as health check-ups for your security infrastructure; they identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Here are some essential steps to consider:
- Scheduled Audits: Conduct audits at regular intervals, perhaps quarterly or semi-annually, to ensure ongoing vigilance.
- Third-party Assessments: Hiring external security professionals can provide fresh insights and unbiased evaluations.
- Document Findings: Keep detailed records of vulnerabilities detected and actions taken, which can inform future audits.
Engaging in these practices helps organizations remain proactive in their security efforts.
Adapting to Evolving Threat Landscape
Additionally, adapting to the evolving threat landscape is crucial for maintaining effective security. Cyber threats are continuously changing, so businesses must stay informed and agile. Here’s how to stay ahead:
- Threat Intelligence: Utilize threat intelligence services to receive updates on emerging threats specific to your industry.
- Training Updates: Continuously update employee training programs to address the latest tactics used by cybercriminals.
- Flexibility: Develop policies that are adaptable and responsive to new threats as they arise.
By embracing a mindset of ongoing improvement and adaptability, organizations can fortify their defenses against potential security breaches, ensuring a more resilient cloud environment.

Conclusion
Recap of Essential Cloud Security Tips
As we wrap up our exploration of cloud security, it’s important to reflect on the essential tips we’ve discussed. Securing your cloud environment isn’t just about technology; it’s about fostering a secure mindset within your organization. Here’s a quick recap of the key components:
- Strong Authentication: Implement measures like two-factor authentication for user access.
- Data Encryption: Always encrypt data both at rest and in transit to protect sensitive information.
- Regular Training: Equip employees with the knowledge to identify and respond to potential threats.
- Continuous Monitoring: Conduct regular audits and stay informed about the evolving threat landscape.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can create a robust defense against security breaches.
Final Thoughts on Securing Your Cloud Environment
In conclusion, securing your cloud environment is an ongoing journey rather than a one-time task. Just as technology evolves, so too must your security practices. A strong security posture not only protects sensitive data but also builds trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders. As companies navigate this complex landscape, prioritizing cloud security should be a fundamental aspect of their operations, promoting resilience in an increasingly digital world. Keep the dialogue open and always stay vigilant, because in the world of cybersecurity, complacency can be the biggest risk of all.

