
Understanding HIPAA Compliance in Healthcare
Overview of HIPAA Regulations
HIPAA, or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, was enacted in 1996 with the primary goal of safeguarding patient information in healthcare settings. The regulations under HIPAA lay out strict standards for the protection of health information, especially Protected Health Information (PHI).
The key components include:
- Privacy Rule: This rule governs the use and disclosure of PHI, ensuring that patients’ rights are respected.
- Security Rule: It sets standards for safeguarding electronic PHI, requiring administrative, physical, and technical safeguards.
- Breach Notification Rule: Mandates that healthcare organizations notify affected individuals and the government in the event of a data breach.
Healthcare professionals and organizations alike must be diligent in upholding these regulations to maintain trust and compliance in their practices.
Importance of Cybersecurity in Healthcare
As healthcare increasingly integrates technology, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. Cyber threats such as ransomware and phishing attacks are rampant, targeting sensitive patient data.
Consider this: in a recent incident, a hospital found itself locked out of critical patient files, resulting in delayed treatments and a breach of trust with their community. This situation highlights the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures in the healthcare sector.
Effective cybersecurity involves:
- Regular updates and patches to systems.
- Employee training on recognizing phishing attempts.
- Implementation of advanced encryption methods.
Healthcare organizations must prioritize cybersecurity to protect not only their data but the very lives of their patients. By investing in secure systems and continuous training, they can uphold HIPAA compliance and foster a safer environment for everyone involved.

Key Components of HIPAA Compliance
Protected Health Information (PHI)
At the heart of HIPAA compliance is the concept of Protected Health Information (PHI). This term encompasses any personal health information that can identify an individual. For example, names, addresses, social security numbers, and medical records all fall under this category.
The necessity of safeguarding PHI cannot be overstated. A breach could lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and loss of trust. Here are examples of what constitutes PHI:
- Names
- Birthdates
- Medical history
- Health insurance information
Hospitals and clinics diligently train their staff on the significance of protecting this information, understanding that once compromised, the impact can be devastating not only for patients but for their own credibility.
Security Rule and Privacy Rule
Next in line are the HIPAA Security Rule and Privacy Rule, which serve distinct but complementary roles. The Privacy Rule primarily deals with how PHI is used and shared, granting patients rights over their information. For instance, patients have the right to access their records and request corrections.
Conversely, the Security Rule sets forth safeguards to protect electronic PHI (ePHI). This includes:
- Administrative safeguards: Policies and procedures to manage the selection, development, and execution of security measures.
- Physical safeguards: Access controls to facilities and equipment where ePHI is stored.
- Technical safeguards: The utilization of technology to protect ePHI, such as encryption and firewalls.
Without the synergy of these two rules, the integrity of PHI would be at risk, leaving healthcare organizations vulnerable to breaches.
Breach Notification Rule
In the event of a security breach, the Breach Notification Rule comes into play, requiring organizations to notify affected individuals, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and even the media if the breach affects more than 500 individuals. This transparency is crucial, allowing patients to take appropriate measures in light of potential identity theft.
Healthcare organizations must have a well-documented incident response plan that outlines how to handle breaches, ensuring compliance with HIPAA while also protecting their patients. Notably, learning from past breaches can guide organizations in strengthening their security posture for the future, reflecting the commitment necessary to uphold HIPAA compliance and maintain trust with patients.

Cybersecurity Measures for Healthcare Organizations
Encryption and Data Security
As healthcare organizations navigate the complexities of HIPAA compliance, implementing strong cybersecurity measures is vital to protect sensitive patient information. One of the most effective tools in this arsenal is encryption. By converting data into a coded format, encryption ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they cannot decipher it.
For example, a hospital recently experienced a data breach where sensitive patient records were compromised. However, because they had implemented robust encryption protocols, the hackers were left with unreadable files, greatly mitigating the impact of the breach.
Key aspects of data security include:
- Data encryption: Encrypting both stored data and data in transit to safeguard it from potential threats.
- Secure backup solutions: Regularly backing up data in secure locations to ensure it can be restored in case of a cyber incident.
Access Control and Authentication
Another crucial element in the cybersecurity framework is access control and authentication. Ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information helps prevent data leaks and unauthorized access.
Effective strategies may include:
- Role-based access: Granting different levels of access based on job responsibilities. For instance, only physicians may have access to detailed medical records, while administrative staff might only access billing information.
- Two-factor authentication: Implementing this additional layer of security requires users to provide two forms of identification before gaining access to sensitive systems.
This not only hinders unauthorized access but also reinforces accountability within the organization.
Regular Security Audits and Risk Assessments
No cybersecurity strategy is complete without regular security audits and risk assessments. These practices help healthcare organizations identify vulnerabilities and assess their ability to comply with HIPAA regulations.
Consider this: an organization conducts routine audits that reveal outdated software and unpatched systems. By addressing these vulnerabilities proactively, they safeguard against potential attacks. Conducting regular assessments enables organizations to:
- Identify weaknesses in their security posture.
- Ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations.
- Adjust policies and protocols based on emerging threats.
Through a combination of strong encryption, tight access control, and diligent assessments, healthcare organizations can enhance their cybersecurity measures significantly, thereby instilling confidence in their patients and better protecting their sensitive information.

Importance of Employee Training in Ensuring HIPAA Compliance
Role-Based Training Programs
As the backbone of any healthcare organization, employees play a crucial role in maintaining HIPAA compliance. One of the most effective strategies for achieving this is through role-based training programs. By tailoring training to the specific responsibilities of employees, organizations can significantly enhance understanding and compliance with HIPAA regulations.
For instance, consider a recent workshop at a local clinic where administrative staff focused on the Privacy Rule. They learned how to handle patient records securely and handle requests for information while respecting patient privacy. On the other hand, clinical staff underwent training on the Security Rule, emphasizing the protection of electronic health records (EHRs).
Key components of role-based training include:
- Specific content: Catering training sessions based on job functions ensures employees receive relevant information.
- Practical scenarios: Incorporating real-life scenarios helps staff understand the implications of HIPAA compliance in their daily work.
Security Awareness Best Practices
In addition to role-specific training, fostering a culture of security awareness is imperative in today’s healthcare environment. Employees must be educated on best practices for maintaining the security of PHI for the organization’s integrity.
Some security awareness best practices include:
- Recognizing phishing attempts: Training employees to identify suspicious emails and understand the importance of verifying sources before clicking links.
- Password management: Encouraging the use of strong passwords and regular password updates to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Reporting suspicious activities: Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting potential security incidents immediately.
For example, a nursing team that was well-trained in these best practices was able to identify a phishing attempt quickly, thereby preventing a significant security breach.
By investing in ongoing employee training and promoting a strong culture of security awareness, healthcare organizations can better ensure HIPAA compliance, protect sensitive information, and ultimately foster trust with their patients.

Business Associate Agreements and HIPAA Compliance
Understanding Business Associate Relationships
In the realm of healthcare, maintaining HIPAA compliance extends beyond the walls of hospitals and clinics. Many organizations partner with outside vendors or service providers—collectively referred to as business associates (BAs)—to deliver essential services, whether it’s billing, data processing, or IT support. Understanding these relationships is vital in preserving patient information’s confidentiality and security.
For instance, imagine a small medical practice that outsources its billing to a third-party company. This vendor, while not directly providing healthcare, will have access to sensitive patient information to process claims. Thus, both the healthcare provider and the business associate share the responsibility of protecting that data under HIPAA.
Requirements for Business Associate Agreements
To formalize this shared responsibility, HIPAA mandates the creation of Business Associate Agreements (BAAs). These legally binding contracts outline the expectations for maintaining patient privacy and the security measures both parties must implement.
Key requirements for BAAs include:
- Clear definitions: The agreement should explicitly define what constitutes PHI and the obligations that the business associate must meet to protect it.
- Usage limitations: BAs can only use PHI as stipulated in the BAA and are prohibited from unauthorized disclosures.
- Termination conditions: The agreement should specify the course of action in case of a data breach or non-compliance, including the necessity for notifying the healthcare provider.
For instance, a recent hospital partnership with a cloud storage provider required a comprehensive BAA that specified data encryption protocols and breach notification procedures. This proactive step ensured that both the hospital and the vendor were aligned in their commitment to safeguarding patient data.
Through clear understanding and robust BAAs, healthcare organizations can cultivate fruitful relationships with their business associates while ensuring rigorous adherence to HIPAA compliance, ultimately leading to enhanced patient trust and information security.

Implementing Technology Solutions for HIPAA Compliance
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Security
In today’s digital landscape, Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have become essential for healthcare delivery. However, the transition to electronic systems poses unique challenges in ensuring HIPAA compliance. EHR security is paramount, as these systems harbor vast amounts of sensitive patient information.
To enhance EHR security, healthcare organizations should prioritize:
- Data encryption: Ensure that all patient records stored digitally are encrypted both at rest and in transit. This safeguards the data from unauthorized access.
- Regular updates: Keeping EHR software up to date not only adds new features but also patches security vulnerabilities that may expose patient data.
- User access controls: Establishing strict access controls allows only authorized personnel to view or modify patient records, further protecting sensitive information.
For instance, a community clinic that recently switched to a new EHR system implemented multi-factor authentication for accessing patient records. This measure added an extra layer of security, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Secure Communication Platforms
Alongside EHR security, secure communication is vital for maintaining HIPAA compliance. Healthcare professionals must communicate sensitive information without risking data leaks.
Implementing secure communication platforms can include:
- Encrypted messaging services: Such platforms specifically designed for healthcare ensure that messages containing PHI are transmitted securely.
- Telehealth solutions: With the rise of telemedicine, using HIPAA-compliant telehealth platforms safeguards patient interactions and consultations.
- Audit trails: Keeping records of all communications can help track access and usage, contributing to accountability and compliance.
For example, a large hospital recently adopted a secure messaging application for internal communications, enabling staff to share patient data quickly without compromising security. The hospital also set up training sessions to educate employees on the secure platform’s features, ensuring everyone was equipped to comply with HIPAA regulations.
By leveraging technology solutions for EHR security and secure communication platforms, healthcare organizations can not only meet HIPAA compliance requirements but also enhance operational efficiency and maintain patient trust in their services.

Incident Response and Reporting Procedures
Developing a Response Plan
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare cybersecurity, having a robust incident response plan is crucial. A well-thought-out response plan not only minimizes the impact of security breaches but also aligns with HIPAA compliance requirements. The key to an effective plan is a proactive approach that outlines specific steps to take when an incident occurs.
Successful incident response plans typically include:
- Identification: Clearly define what constitutes a security incident, such as unauthorized access to PHI or a ransomware attack.
- Assessment: Quickly assess the scope of the incident to determine the potential impact on patient data and services.
- Containment: Implement immediate actions to contain the breach and prevent further unauthorized access.
For instance, a regional healthcare provider faced a data breach last year. Upon discovery, their incident response team quickly sprang into action. By swiftly isolating affected systems, they contained the breach before it expanded, demonstrating the importance of a predefined response plan.
Reporting Security Incidents to Authorities
Once an incident is contained, the next critical step is compliance with reporting requirements. Under HIPAA, healthcare organizations must report certain breaches to affected individuals and the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) promptly.
Key components of reporting security incidents include:
- Timeliness: Organizations must notify individuals within 60 days of discovering a breach, ensuring that patients are informed in a timely manner.
- Detailed documentation: Thoroughly document what occurred, including how the breach was discovered, the type of PHI involved, and the steps taken to mitigate the breach’s impact.
For example, a facility that experienced a phishing attack communicated with affected patients through direct mail. They provided information on what steps to take if they suspected their information had been compromised. This not only met legal requirements but also helped rebuild trust with their patients.
By developing an effective incident response plan and understanding the importance of timely reporting, healthcare organizations can navigate security incidents more confidently. This proactive approach ensures compliance with HIPAA regulations while safeguarding the sensitive information that patients entrust to them.

Continuous Monitoring and Improvement of Cybersecurity Measures
Compliance Audits and Assessments
In the realm of healthcare, the landscape of cybersecurity threats is constantly evolving, making continuous monitoring and improvement essential. Conducting regular compliance audits and risk assessments is a vital component of any successful cybersecurity strategy. These audits not only help organizations ensure adherence to HIPAA regulations but also provide a clear picture of vulnerabilities that need addressing.
For example, a medium-sized hospital recently underwent a comprehensive compliance audit. The findings revealed outdated encryption protocols and gaps in employee training regarding phishing attacks. By identifying these weaknesses, the hospital was able to implement targeted improvements before any breaches occurred.
Key elements of compliance audits and assessments include:
- Regular schedule: Establish a routine for audits to ensure ongoing compliance, ideally on a bi-annual or quarterly basis.
- Third-party assessments: Engage external cybersecurity experts to provide an objective evaluation of your security posture.
Updating Policies and Procedures
Following the insights gained from audits and assessments, updating policies and procedures is critical to staying ahead of potential threats. Organizations should not only revise existing protocols but also integrate lessons learned from past incidents into their future strategies.
Effective strategies for updating policies include:
- Incident reviews: After experiencing a security incident, conduct a thorough review to refine response plans and preventive measures.
- Stakeholder involvement: Engage employees from various departments in the policy revision process to ensure all perspectives are considered.
For instance, a healthcare facility transitioned to telehealth in response to increased demand during the pandemic. By updating policies to include security measures specific to telehealth platforms, they ensured patient confidentiality and HIPAA compliance amidst rapid technological changes.
By committing to continuous monitoring through compliance audits, regular assessments, and ongoing updates to policies, healthcare organizations can create an adaptive cybersecurity framework. This proactive stance not only protects sensitive patient data but also fosters a culture of security awareness and accountability within the organization.
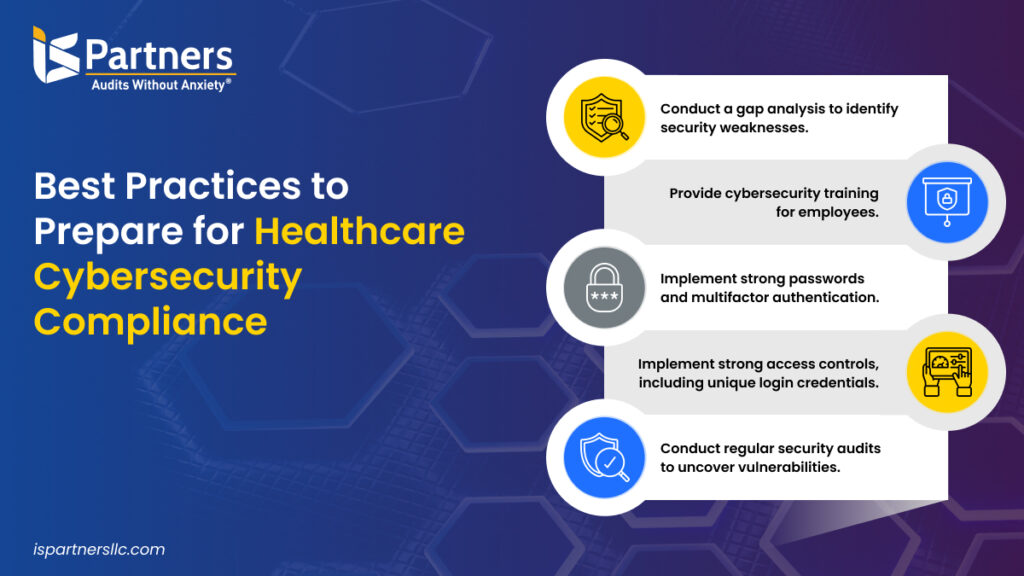
Challenges and Common Pitfalls in Achieving HIPAA Compliance
Human Error and Insider Threats
While technology plays a crucial role in maintaining HIPAA compliance, human elements often represent the biggest challenge. Human error, whether intentional or accidental, can lead to serious lapses in security protocols, exposing sensitive patient information. Insider threats also pose a significant risk, as employees with access to Protected Health Information (PHI) can inadvertently or maliciously compromise data security.
For example, a healthcare worker at a hospital accidentally sent an email containing patient records to the wrong recipient. This misstep not only breached HIPAA regulations but also eroded trust between the hospital and its patients.
To mitigate such risks, organizations can implement:
- Comprehensive training: Regular training sessions focusing on HIPAA compliance, security best practices, and the significance of data privacy.
- Monitoring systems: Employing software tools that detect unusual activity and flag potential insider threats, ensuring timely intervention when necessary.
Evolving Cyber Threat Landscape
Another significant challenge in achieving HIPAA compliance is navigating the rapidly evolving cyber threat landscape. Cybercriminals constantly develop more sophisticated tactics, making it difficult for healthcare organizations to stay ahead of potential breaches.
For example, ransomware attacks in healthcare have surged, crippling systems and demanding hefty ransoms for data retrieval. Such incidents highlight the importance of not only having robust cybersecurity measures in place but also updating them continuously.
To combat these threats, organizations should focus on:
- Staying informed: Regularly monitoring industry news and threat intelligence sources to stay aware of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Adopting advanced technologies: Utilizing artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to predict and prevent security events before they occur.
By acknowledging the challenges posed by human error and the evolving cyber threat landscape, healthcare organizations can develop more effective strategies for achieving HIPAA compliance. This proactive approach ensures the protection of patient data while fostering a culture of security that permeates every aspect of the organization.

Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
As we’ve explored, achieving HIPAA compliance in healthcare necessitates a multifaceted approach that encompasses a wide range of strategies and solutions. From understanding the intricacies of HIPAA regulations to implementing strong cybersecurity measures, it’s clear that diligence is essential in protecting sensitive patient data.
Key points discussed include:
- Encryption and Data Security: Vital to safeguarding patient information from unauthorized access.
- Employee Training: Raising awareness about compliance and security best practices to mitigate human error and insider threats.
- Ongoing Audits and Assessments: Ensuring continuous evaluation of cybersecurity measures to adapt to new threats.
- Incident Response: Planning for quick action to mitigate damage from potential security breaches.
Each of these components contributes to a larger framework aimed at maintaining trust and integrity in the healthcare system.
Future of Cybersecurity in Healthcare
Looking ahead, the future of cybersecurity in healthcare is likely to be shaped by the rapid pace of technological advancement. As organizations adopt innovations like artificial intelligence and telemedicine, the need for robust security measures will only increase.
For instance, with the rise of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices, healthcare providers must be prepared for new vulnerabilities that come with connected technology. Cybersecurity strategies must evolve accordingly, incorporating advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
Moreover, collaboration across the industry will be crucial, as sharing information about breaches and threats can empower organizations to bolster their defenses.
In summary, while challenges exist, proactive measures can transform the healthcare landscape. It’s an exciting time for cybersecurity, and by prioritizing compliance and security, healthcare organizations can ensure the safety of patient data for generations to come. By fostering a culture of vigilance and continuous improvement, the industry can confidently navigate towards a more secure future.

