
Introduction
Overview of Smart Farming
Smart farming, often referred to as precision agriculture, is revolutionizing the way we approach food production. This innovative approach utilizes technology to enhance crop yield and reduce environmental impact, paving the way for sustainable agricultural practices. Imagine walking through a field where sensors monitor the soil’s moisture levels, drones survey the crops from above, and artificial intelligence analyzes data to inform decisions. This is not a distant future—it’s happening now.
- Key Components of Smart Farming:
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- Drones and satellite imaging
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms
- Automation and robotics
These technologies allow farmers to make data-driven decisions, optimizing resources and improving efficiency.
Evolution of Agriculture Technology
The journey of agriculture technology has been remarkable. From the traditional plow to today’s automated machinery, there have been significant milestones that have transformed farming practices.
- Timeline of Agricultural Technology Evolution:
- The Plow Era: Manual labor and basic tools
- The Industrial Revolution: Introduction of tractors and fertilizers
- Late 20th Century: Rise of biotechnology
- 21st Century: Smart farming innovations
Each phase has brought us closer to understanding and maximizing crop production while maintaining sustainability.

Internet of Things (IoT) in Agriculture
IoT Applications on Farms
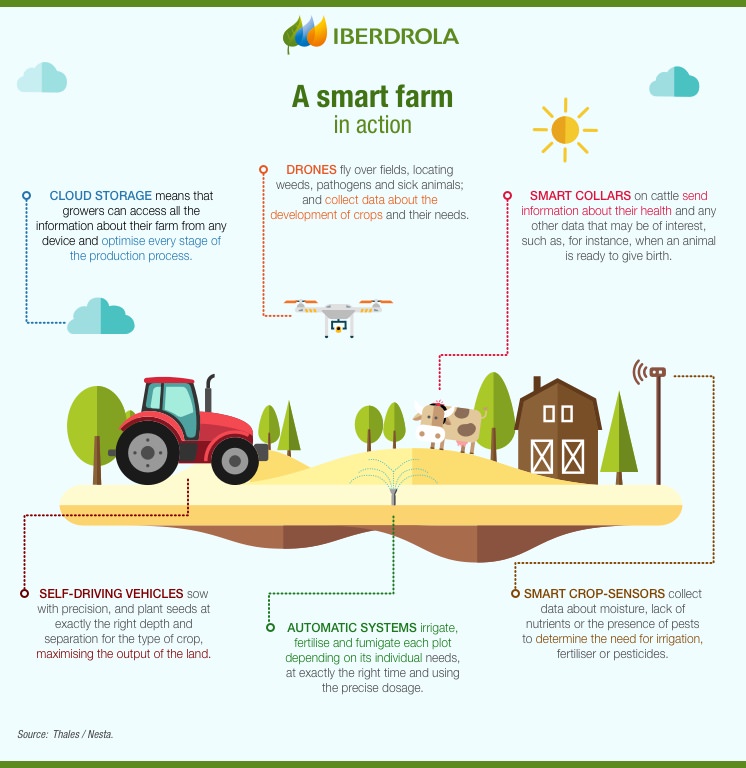
As we delve deeper into smart farming, the Internet of Things (IoT) emerges as a game-changer in the agricultural landscape. IoT devices and sensors are transforming traditional farming practices, turning fields into data-rich environments.
Consider this: a farmer can remotely monitor soil conditions using wireless sensors that report moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels in real-time. Some common IoT applications on farms include:
- Soil Monitoring Systems: Collects data on soil health, leading to better crop management.
- Weather Stations: Provides localized weather updates to anticipate changes that impact farming decisions.
- Livestock Tracking: Wearable devices monitor the health and location of animals, ensuring their welfare and productivity.
- Automated Irrigation Systems: Adjusts water usage based on moisture levels, conserving resources.
Benefits of IoT Integration
Integrating IoT into agriculture yields numerous benefits that can significantly enhance productivity and profitability. For instance:
- Resource Optimization: By monitoring conditions closely, farmers can tailor their inputs, reducing waste.
- Increased Efficiency: Data-driven decisions minimize the time spent on manual oversight.
- Enhanced Crop Yield: Timely interventions based on real-time data can lead to healthier plants.
Embracing IoT means more than simply deploying technology; it is about fostering a connected ecosystem that supports sustainable agriculture.

Artificial Intelligence in Farming
AI in Crop Monitoring
Following the exciting advancements in IoT, artificial intelligence (AI) is further elevating smart farming. One area where AI shines is in crop monitoring, providing farmers with powerful tools to oversee and assess plant health. Imagine a farmer walking through a vast field, equipped with a smartphone app that utilizes AI-driven algorithms to analyze images of crops, identifying issues like disease or pest infestations instantly.
Some key applications of AI in crop monitoring include:
- Image Recognition: Drones or cameras scan fields, with AI analyzing the images to detect anomalies.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms predict potential crop failures, allowing farmers to act swiftly.
- Growth Pattern Analysis: AI processes historical data to provide insights into growth trends, leading to optimized care schedules.
Predictive Analytics for Yield Optimization
Moreover, AI extends its capabilities to predictive analytics, offering farmers the means to forecast crop yield with impressive accuracy. By processing vast amounts of data—from weather patterns to soil conditions—AI can provide insights that support effective decision-making.
- Yield Prediction Models: Utilize machine learning to project anticipated harvest outcomes based on various factors.
- Resource Allocation: Optimize input usage (water, fertilizer) by predicting the needs for maximum yield.
The integration of AI not only streamlines farming practices but also empowers farmers to make informed decisions, ensuring a bountiful harvest while promoting sustainability.
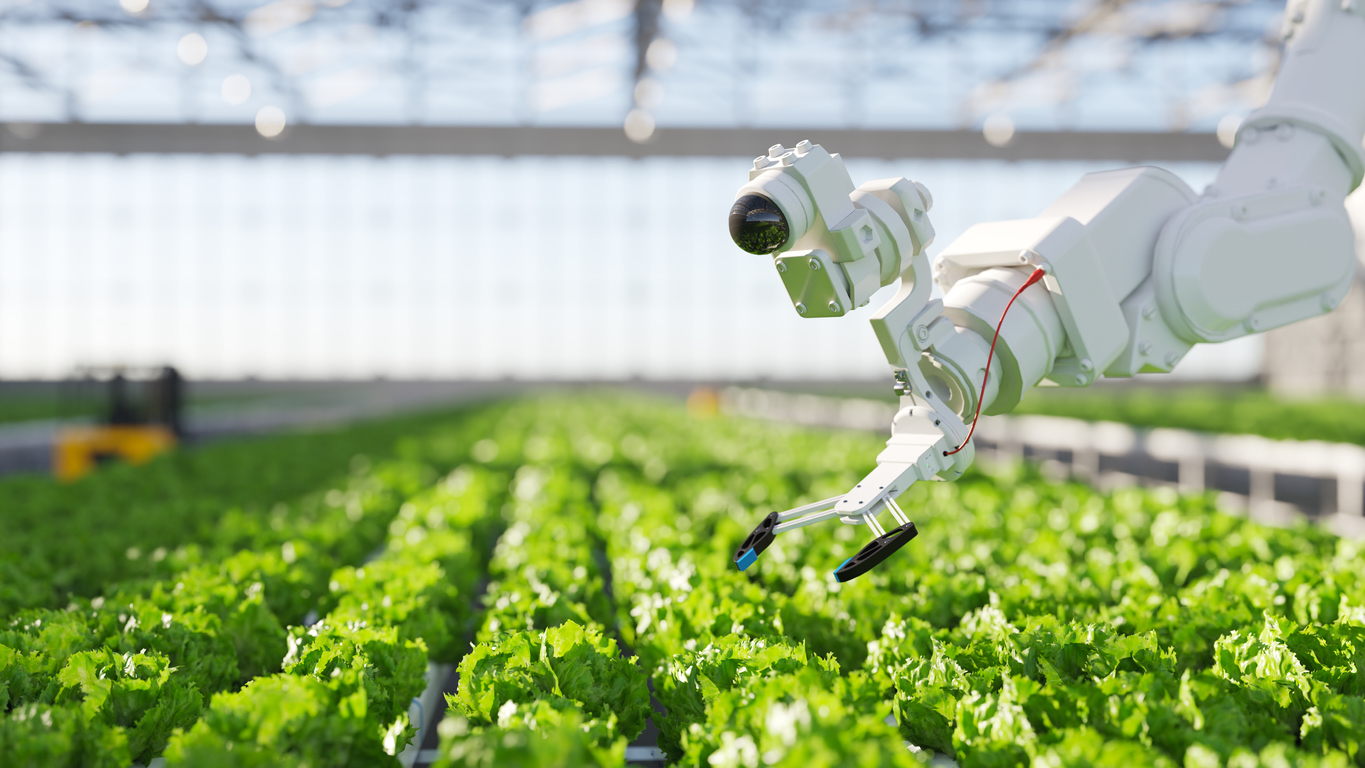

Robotics and Automation in Agriculture
Types of Agricultural Robots
As we explore the realm of robotics in agriculture, it’s clear that these machines are revolutionizing how farmers operate. Agricultural robots come in various forms, each designed to address specific challenges faced in the fields. Think of them as your farming allies, tirelessly working to improve efficiency and productivity.
Some notable types of agricultural robots include:
- Autonomous Tractors: These self-driving machines can plow, plant, and even fertilize fields without human intervention.
- Weeding Robots: Equipped with advanced sensors, these robots identify and remove weeds, reducing the need for chemical herbicides.
- Harvesting Robots: Designed to pick ripe fruits and vegetables with precision, ensuring minimal damage to crops.
Automation in Planting and Harvesting
The integration of robotics in planting and harvesting processes is a game-changer. For instance, automated planting systems can ensure seeds are sown at the optimal depth and spacing, which directly influences yield.
- Benefits of Automated Systems:
- Precision: Enhanced accuracy in planting contributes to uniform crop growth.
- Labor Savings: Reduces manual labor requirements, allowing farmers to focus on other essential tasks.
- Efficiency: Speeds up the harvesting process, especially during peak seasons.
As agricultural robots continue to evolve, they promise not only to make farming more efficient but also to ensure the sustainable management of our precious resources.

Drones and Satellite Technology in Farm Management
Role of Drones in Precision Agriculture
Continuing the journey through smart farming, drones have emerged as invaluable tools in precision agriculture. Picture a farmer using a drone to survey vast fields, gaining insights that were once unattainable. Drones offer a bird’s-eye view, enabling farmers to monitor crop health and detect issues before they escalate.
Key roles of drones in agriculture include:
- Field Mapping: Drones capture high-resolution images to create detailed maps, helping farmers assess the health of their crops.
- Crop Spraying: Equipped with advanced spraying systems, drones can apply fertilizers and pesticides with pinpoint accuracy, reducing waste.
- Monitoring Irrigation: Drones can identify areas in need of water, ensuring efficient use of irrigation resources.
Satellite Imaging for Crop Monitoring
In tandem with drones, satellite technology plays a crucial role in crop monitoring. Satellites can provide extensive data on weather patterns, soil moisture, and overall landscape conditions.
- Benefits of Satellite Imaging:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Unlike drones, satellites can monitor large areas over time, offering a broader perspective.
- Long-Term Analysis: Enables farmers to track changes over seasons, aiding in strategic planning.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces costs related to ground monitoring.
By integrating drones and satellite imaging, farmers can cultivate their land with unparalleled precision, leading to improved crop yields and sustainable practices.

Data Analytics and Farm Management Software
Importance of Data Analytics
As we tread further into the world of smart farming, the role of data analytics becomes increasingly pivotal. Imagine having the capability to turn mountains of data from sensors, drones, and weather forecasts into actionable insights. This transformation allows farmers to make informed decisions that can significantly boost productivity and sustainability.
The importance of data analytics in agriculture includes:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Data-driven insights enable farmers to optimize resource usage, leading to cost savings.
- Risk Management: Predictive analytics helps mitigate risks related to weather conditions and pest infestations.
- Performance Tracking: Real-time data allows for continuous assessment of crop health and overall farm performance.
Farm Management Platforms for Decision Making
To harness the power of data, farmers increasingly rely on farm management platforms. These software solutions provide users with a comprehensive overview of their operations, merging various data sources into a single interface.
Key features of farm management platforms include:
- Centralized Data Access: Farmers can track everything from planting schedules to financials in one place.
- Collaboration Tools: Facilitate communication between farm staff, enhancing teamwork in achieving common goals.
- Customizable Reporting: Generate tailored reports for easy analysis of farm performance.
Utilizing data analytics and these sophisticated platforms empowers farmers to navigate the complexities of modern agriculture confidently, ensuring better outcomes for their crops and the environment.
Sustainable Practices in Smart Farming
Advantages of Sustainable Agriculture
Transitioning toward sustainable practices in smart farming is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for preserving our planet’s health. The advantages of sustainable agriculture extend beyond the immediate benefits to crop yields; they influence long-term ecological balance and economic viability.
Some key advantages include:
- Environmental Preservation: Sustainable techniques help protect biodiversity, reduce pollution, and conserve water resources.
- Improved Soil Health: Practices such as cover cropping and reduced tillage enhance soil structure and microbiome, leading to healthier plants.
- Economic Resilience: By optimizing resources and reducing input costs, farmers can improve their bottom line while contributing to environmental stewardship.
Implementing Sustainable Techniques
Implementing sustainable techniques requires a shift in mindset and practices, but the outcomes can be transformative. Here are some effective methods farmers can adopt:
- Crop Rotation: Diversifying crops helps break pest and disease cycles and improves soil fertility.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Combining biological, cultural, and chemical practices ensures pest control with minimal environmental impact.
- Precision Agriculture: Utilizing data analytics and technology allows for efficient resource application, minimizing waste.
Embracing sustainable practices in smart farming ultimately leads to a healthier planet and more resilient agricultural systems—proving that careful stewardship of the land can be harmoniously blended with technological advancement.

Challenges and Future Trends in Smart Farming
Challenges Faced by Smart Farming
As we look at smart farming, it’s essential to acknowledge the challenges that accompany this technological revolution. While the potential is vast, several issues can hinder progress, and farmers must navigate through them.
Some notable challenges include:
- High Initial Costs: The investment required for advanced technologies can deter many farmers, especially those operating on a smaller scale.
- Technical Skills Gap: Not all farmers are well-versed in the latest technologies, leading to difficulties in implementation and management.
- Data Privacy Concerns: With increased data collection comes the responsibility of safeguarding sensitive information, which can be a daunting task.
Future Innovations in Agriculture Technology
Despite the challenges, the future of smart farming is promising, with innovative technologies on the horizon that could transform agriculture even further.
- Blockchain in Supply Chain: Enhancing transparency and traceability in food supply chains can build consumer trust.
- More Advanced AI Algorithms: These can provide deeper insights and predictive capabilities for farmers, streamlining operations.
- Robotics Evolution: Emerging robotics technologies will further automate planting and harvesting, making farming more efficient.
As we delve into these exciting future trends, our blog, TECHFACK, is here to keep you informed and updated with the latest innovations shaping the agriculture landscape. The journey into smart farming holds great promise, and staying ahead of these challenges could lead to sustainable and efficient farming solutions for all.

