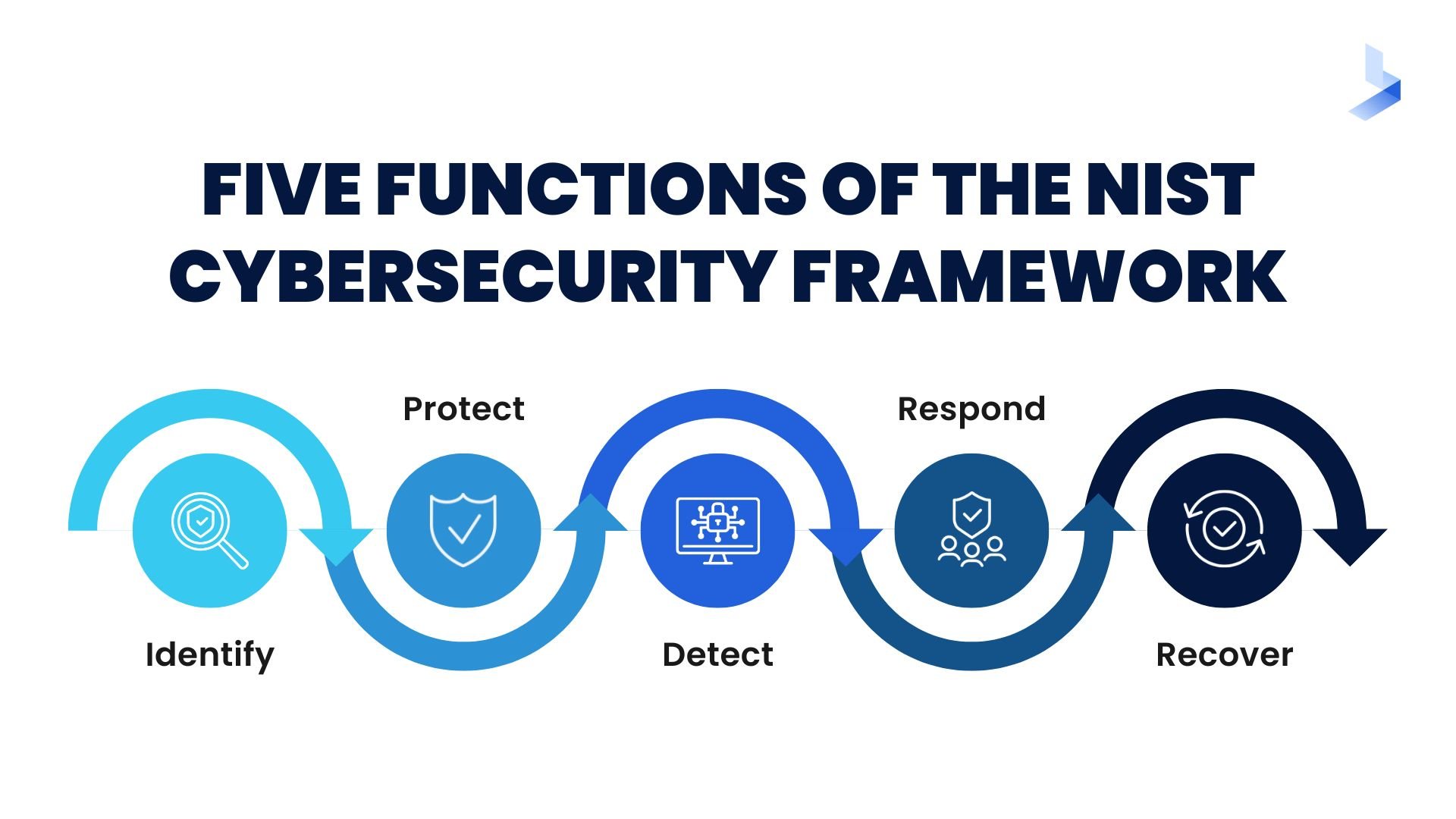
Importance of Cybersecurity
Understanding the Risks
In today’s digital landscape, understanding the risks associated with cyber threats is paramount for both individuals and organizations. With the rise of technology, vulnerabilities have evolved, making it essential to remain vigilant. Cyber threats can come in various forms such as:
- Phishing: Deceptive emails designed to steal sensitive information.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts data and demands payment for restoration.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access leading to personal or sensitive information exposure.
Each of these risks poses significant challenges that can lead to severe consequences. An organization that might think “it won’t happen to us” often finds itself in a precarious situation due to such oversight.
Impact of Cyber Attacks
The impact of cyber attacks can be devastating. An organization I once consulted for did not prioritize cybersecurity until they faced a ransomware attack, which halted operations for a week. The aftermath included:
- Financial Loss: Recovery costs and potential ransom payments.
- Reputation Damage: Losing customers’ trust can alter brand perception.
- Legal Consequences: Non-compliance with data protection regulations can lead to hefty fines.
In summary, underestimating cyber risks can lead to unforeseen and long-lasting repercussions. It is critical to assess and bolster cybersecurity measures proactively to safeguard against these threats.
Assessing Your Current State
Conducting a Security Audit
Once the importance of cybersecurity is crystal clear, assessing your current state becomes an essential next step. Conducting a security audit is a thorough examination of your existing security measures. Think of it as a health check-up for your organization’s digital environment. During my experience with a mid-sized firm, they uncovered numerous lapses that had gone unnoticed, such as:
- Outdated software: Not installing regular updates that leave systems vulnerable.
- Weak access controls: Employees having overly broad access to sensitive data.
A complete security audit should ideally cover areas such as policies, procedures, and technology. It’s about understanding where you stand so you can effectively prioritize your cybersecurity efforts.
Identifying Vulnerabilities
The next step after the audit is identifying vulnerabilities. This might sound daunting, but it can be quite straightforward.
Consider using vulnerability assessment tools that provide detailed reports of weaknesses in your network.
Common vulnerabilities include:
- Unpatched software: Leaving doors open to cyber attackers.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi networks: Overlooking basic security measures.
Once identified, these vulnerabilities can guide your security enhancements. During my consulting career, a simple update to firewalls mitigated risks significantly, improving the organization’s overall security posture. In essence, assessing your current state effectively sets the groundwork for a robust cybersecurity strategy.

Developing a Robust Security Policy
Creating Strong Password Policies
With a clear understanding of your cybersecurity landscape, the next crucial step is developing a robust security policy. One of the foundational elements of this policy is creating strong password guidelines. In my experience, I’ve witnessed how a simple password mishap can lead to significant breaches. To avoid this, consider implementing the following practices in your organization:
- Length and Complexity: Require a minimum of 12 characters that include a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Password Expiration: Mandate regular password changes, perhaps every 90 days.
- Password Managers: Encourage the use of reliable password management tools to store and generate secure passwords.
These strategies not only bolster security but also cultivate a security-conscious culture within your team.
Implementing Multi-factor Authentication
Immediately following strong password policies, the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) can significantly enhance your security framework. By requiring two or more verification methods, MFA adds an additional layer of protection.
Consider these examples:
- Something You Know: A password or PIN.
- Something You Have: A smartphone app or hardware token generating time-based codes.
- Something You Are: Biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition.
The investment in MFA pays off. For instance, a client I advised saw a drastic reduction in unauthorized access attempts after deploying MFA. By developing a robust security policy that includes strong password practices and MFA, organizations can immensely strengthen their defenses against potential cyber threats.

Employee Training and Awareness
Educating Staff on Cyber Risks
With a robust security policy in place, the next vital aspect to focus on is employee training and awareness. Your employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats, making it crucial that they understand the various risks involved. During a training session I conducted at a local company, it became evident that many staff members were unaware of the common types of cyber threats, including:
- Phishing Scams: Deceptive emails aiming to extract personal and financial information.
- Social Engineering: Manipulative tactics used to trick individuals into divulging confidential information.
By providing comprehensive training sessions that cover these topics, organizations not only empower their staff but also foster a culture of cybersecurity mindfulness. Regular workshops and online courses can be instrumental in this educational journey.
Simulating Phishing Attacks
To reinforce this training, simulating phishing attacks can be an effective strategy. By creating controlled scenarios where employees must identify and report phishing attempts, organizations can gauge their staff’s responses and knowledge of cybersecurity practices.
For example, I once organized a mock phishing campaign that revealed a 30% click rate on fraudulent links, highlighting areas that needed improvement. This not only raised awareness but also prompted a series of follow-up training sessions targeted at those specific vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, combining educational initiatives with real-world simulations equips employees with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate and combat potential cyber risks effectively. This proactive training approach establishes a more secure digital environment for everyone involved.

Investing in Reliable Security Solutions
Firewalls and Antivirus Software
Having established a solid foundation of employee training and awareness, it is crucial to complement these efforts with robust security technologies. Investing in reliable security solutions, like firewalls and antivirus software, forms the backbone of any cybersecurity strategy. Firewalls act as a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, diligently monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic.
In my practice, I’ve seen the difference a well-configured firewall can make. For instance, during a client engagement, we implemented a next-generation firewall that significantly reduced unauthorized access attempts by over 70%. Alongside firewalls, antivirus software plays a vital role in detecting and mitigating malware threats.
When choosing antivirus software, consider:
- Regular updates: To counter evolving threats.
- Comprehensive scanning: Catching potential risks in real-time.
- User-friendly interfaces: To make it easier for staff to interact with.
Encryption Technologies and Secure Backups
In addition to firewalls and antivirus software, leveraging encryption technologies and establishing secure backups is essential. Encryption protects sensitive data by converting it into unreadable formats, ensuring that even if data falls into the wrong hands, it remains secure. Implementing full-disk encryption on devices where sensitive information is stored can prevent unauthorized access effectively.
Moreover, a reliable backup solution is vital. Often overlooked, regular backups can save the day in the event of data loss or ransomware attacks. I recall working with a company that had suffered a ransomware attack; fortunately, their recent backups allowed them to restore operations with minimal disruption.
In conclusion, investing in these reliable security solutions—firewalls, antivirus software, encryption technologies, and secure backups—creates a multi-layered defense that protects an organization from imminent cyber threats, safeguarding its digital assets effectively.

