
Understanding Cloud Disaster Recovery
Definition and Importance
Cloud Disaster Recovery (CDR) is a strategy that businesses employ to safeguard their data and systems in the event of a disaster. This can range from natural calamities like floods or earthquakes to cyberattacks and hardware failures. Essentially, CDR utilizes cloud computing to provide backup and recovery solutions that are accessible from anywhere at any time.
The importance of CDR cannot be overstated. In today’s digital age, data is critical to a company’s operations, and losing it can result in significant disruptions or even complete business failure. Here’s why CDR is vital:
- Minimizes Downtime: Quick recovery processes help ensure that business operations can resume faster.
- Improves Data Security: Leveraging cloud technology can offer robust security measures that protect sensitive information.
- Enhances Business Continuity: CDR contributes to a comprehensive business continuity plan, ensuring that companies are prepared for unforeseen events.
Difference from Traditional Disaster Recovery
When comparing Cloud Disaster Recovery to traditional disaster recovery methods, several significant differences emerge. Traditional approaches typically involve on-premises solutions, making them less flexible and often more expensive due to hardware and maintenance needs.
- Cost:
- Traditional: Requires upfront investment in hardware.
- Cloud: Often operates on a pay-as-you-go model, reducing initial costs.
- Accessibility:
- Traditional: Can be restricted to physical locations.
- Cloud: Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Scalability:
- Traditional: Scaling requires purchasing and setting up additional hardware.
- Cloud: Easily adjustable resources based on business needs at any time.
As organizations increasingly adopt digital transformations, understanding these differences is crucial for effective data management. By choosing to leverage Cloud Disaster Recovery, businesses can ensure a more agile, cost-effective, and resilient approach to safeguarding their operations.
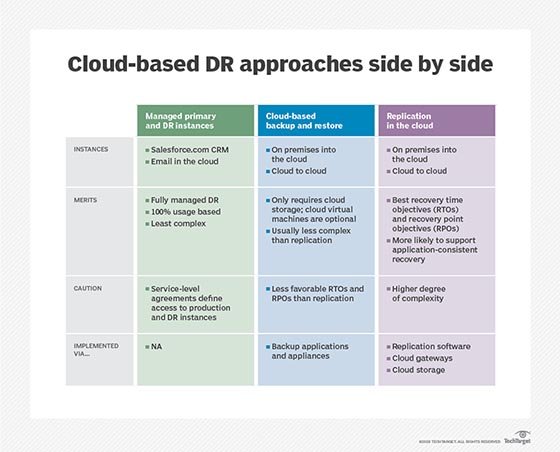
Benefits of Cloud Disaster Recovery
Cost-effectiveness
One of the standout benefits of Cloud Disaster Recovery is its cost-effectiveness. Traditional disaster recovery methods can often require hefty investments in hardware, software, and maintenance. In contrast, cloud-based solutions operate on a subscription model, meaning businesses only pay for the resources they use.
- No Upfront Costs: With cloud services, there’s no need for substantial initial expenditures. This allows businesses, especially startups or smaller enterprises, to allocate funds more effectively.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: The cloud provider manages infrastructure and updates, which significantly reduces maintenance overhead on the organization’s side.
This financial approach can relieve some pressure from IT budgets and free up resources for other critical projects.
Scalability and Flexibility
Another vital advantage of Cloud Disaster Recovery is the inherent scalability and flexibility it offers. As businesses evolve, their data needs change, and CDR can accommodate those changes seamlessly.
- On-Demand Resources: With cloud services, businesses can easily increase or decrease their storage and processing power based on real-time needs. This means no more wasted resources on underused systems.
- Support for Growth: For example, a budding e-commerce platform experiencing a surge in traffic during the holiday season can quickly scale up its disaster recovery resources to handle increased data load, ensuring their systems and information stay protected.
This level of adaptability is particularly useful in a fast-paced business environment.
Automation and Simplification
Cloud Disaster Recovery solutions also streamline backup and recovery processes through automation. This simplification of tasks allows IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance.
- Scheduled Backups: Automating backups ensures that data is consistently protected without manual intervention.
- Simplified Recovery: In case of a failure, the recovery process can often be initiated with just a few clicks, significantly reducing the time and effort involved.
By embracing cloud solutions, organizations can transform their disaster recovery plans into a straightforward process that minimizes human error and maximizes efficiency. Overall, these benefits not only enhance operational resilience but also contribute to a more robust approach to safeguarding critical data.

Key Components of Cloud Disaster Recovery
Data Backup and Storage
As we delve deeper into the world of Cloud Disaster Recovery (CDR), it’s essential to highlight its key components—starting with data backup and storage. This is essentially the backbone of any robust disaster recovery strategy.
- Automated Backups: With cloud solutions, organizations can automatically schedule backups, ensuring that the most critical data is captured without the risk of human error. This can be invaluable during peak business times when distractions abound.
- Cloud Storage Options: Different cloud providers offer various storage options, such as block storage and object storage. Each solution caters to different use cases, allowing businesses to optimize their storage according to needs.
I remember a particular case where a retail company faced a data loss right before Black Friday. Thanks to their automated backup solution, they quickly restored everything without a hitch, allowing them to focus on maximizing sales rather than scrambling to recover lost data.
Failover and Redundancy
Failover and redundancy mechanisms are also critical in cloud disaster recovery. These systems ensure that businesses can swiftly switch to a backup system if the primary one fails.
- Redundant Systems: Implementing redundancy means that if one server goes down, another instantly takes over to keep operations running without interruption.
- Geographical Diversity: Many cloud providers set up data centers in different locations, allowing companies to protect their data against location-specific disasters.
For instance, a financial institution might use geo-redundancy where one data center is in New York and another in California. Hence, if a natural disaster affects one, operations can seamlessly shift to the unaffected center.
Disaster Recovery Plan
Lastly, a well-defined disaster recovery plan is crucial for effective CDR. This plan outlines processes to be followed in the event of a failure, ensuring that everyone knows their role and responsibilities.
- Documentation: A good disaster recovery plan should encompass detailed documentation, including recovery objectives (RTO and RPO), contact lists, and procedures.
- Regular Updates: It’s vital to keep this plan updated and conduct regular audits to reflect any changes in business processes or technology.
Without a comprehensive disaster recovery plan, organizations risk making critical errors during a crisis. Personal experience shows that having a plan in place, routinely reviewed and practiced, can make all the difference when the unexpected strikes.
By understanding and implementing these key components, businesses can bolster their cloud disaster recovery strategies, ensuring resilience in the face of adversity.

Cloud Disaster Recovery Strategies
Data Replication
Continuing our exploration of Cloud Disaster Recovery, one of the most effective strategies is data replication. This process involves duplicating critical data across multiple locations or systems to ensure accessibility even during a disaster.
- Continuous Data Protection: With real-time data replication, changes made to primary data are mirrored instantly to a secondary site. This minimizes data loss—essential for businesses that cannot afford to lose even a few hours’ worth of transactions.
- Geographical Distribution: Replicating data across different geographical regions means that, even if one location faces an outage, another can provide seamless access.
For instance, I once worked with a healthcare provider who implemented data replication between facilities. This ensured patient records were always up-to-date and accessible, crucial for emergencies.
Virtualization
Another robust strategy is virtualization. This technology allows businesses to create virtual versions of their servers, storage, and networking resources rather than relying solely on physical hardware.
- Quick Recovery Times: Virtualized environments enable faster recovery processes. When a server fails, an organization can spin up a virtual server in minutes, often with no data loss.
- Resource Optimization: Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, maximizing resource use and reducing hardware costs.
A memorable implementation was with a tech startup that scaled rapidly. By virtualizing their data center, they not only improved recovery times but also optimized their resource allocation, which was especially beneficial during peak product releases.
Cloud-based Backup Solutions
Finally, cloud-based backup solutions provide another necessary pillar in the disaster recovery landscape. These solutions allow organizations to back up their data to cloud storage, offering a scalable and secure method of data preservation.
- Flexible Storage Options: Businesses can choose from various backup options, including full, incremental, or differential backups, depending on their specific needs.
- Automated Scheduling: Many cloud backup solutions come with automation features, allowing companies to set up regular backups effortlessly.
A small business I consulted once struggled with managing backups manually. By switching to a cloud-based solution, they transformed their data management approach—streamlining operations and providing peace of mind knowing their data was secure.
In summary, adopting these cloud disaster recovery strategies—data replication, virtualization, and cloud-based backup solutions—enables organizations to create a more resilient and responsive disaster recovery plan, safeguarding their critical operations against unforeseen events.

Implementing Cloud Disaster Recovery
Assessment and Planning
As we shift to the practical aspect of Cloud Disaster Recovery (CDR), the first step in this journey is thorough assessment and planning. Before diving into solutions, understanding your organization’s unique needs is crucial.
- Identify Critical Data: Begin by assessing what data and applications are essential for business continuity. This will help prioritize what needs to be backed up first.
- Define Recovery Objectives: Establish your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO). These metrics will guide your strategy, determining how quickly systems should be restored and how much data loss is acceptable.
In my experience, working with a regional bank on their CDR plan highlighted the need for careful assessment. We identified various departments with differing needs, ultimately leading to a finely tuned plan that catered to their specific requirements.
Choosing the Right Provider
Once you have a clear plan, the next step is selecting the right cloud provider. This can feel overwhelming given the plethora of options available, but focusing on a few key factors can simplify your decision-making process.
- Reputation and Reliability: Look for providers with a solid track record in disaster recovery services. Customer testimonials and case studies can give valuable insights.
- Compliance Standards: Ensure the provider meets industry regulations and compliance standards, especially regarding sensitive data.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Carefully review SLAs to understand responsibilities, uptime guarantees, and support availability.
A client I worked with chose a cloud provider based solely on price, which backfired when they required immediate support but faced delays. This experience underscores the importance of thorough evaluation.
Testing and Maintenance
Even the best disaster recovery plans can falter without proper testing and maintenance, making this a vital phase in implementation. Regular testing ensures that your disaster recovery solutions work as intended.
- Conduct Regular Drills: Schedule simulations of disaster scenarios to evaluate how quickly your organization can recover. This helps identify weaknesses in your plan.
- Update Your Plan: Changes in business operations, technology, or personnel may necessitate updates to your disaster recovery strategy. Make it a point to review your plan at least annually.
One memorable scenario involved a large retail chain running a disaster recovery drill. They identified a critical communication gap between departments, which, once fixed, drastically improved their overall response plan.
By focusing on assessment and planning, selecting the right provider, and ensuring ongoing testing and maintenance, businesses can effectively implement a Cloud Disaster Recovery strategy that stands the test of time and unforeseen challenges. This proactive approach leads to enhanced resilience and peace of mind in an ever-changing digital landscape.
Challenges and Considerations
Security Concerns
Building on the importance of implementing Cloud Disaster Recovery (CDR), it’s crucial to also address the challenges and considerations that companies must navigate. First and foremost are security concerns. As businesses migrate data to the cloud, the responsibility for safeguarding sensitive information partially shifts to the cloud provider.
- Data Encryption: Ensure that data is encrypted both during transmission and at rest. This adds a layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Implement robust user access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to critical data.
I recall a situation where a retail company neglected to secure its data adequately. They faced a breach, leading to significant reputational damage and loss of customer trust. A strong security strategy is paramount for avoiding such pitfalls.
Compliance and Regulations
Next, compliance and regulatory issues can pose significant challenges when implementing CDR. Depending on the industry, there may be specific regulations regarding data protection, retention, and privacy.
- Industry Standards: Familiarize yourself with relevant standards such as GDPR for businesses operating within the EU or HIPAA for healthcare organizations in the U.S.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular compliance audits to ensure adherence to regulations, which can prevent legal penalties and safeguard your organization’s reputation.
For example, an international corporation learned the hard way that their initial cloud setup did not comply with GDPR, resulting in hefty fines and costly reconfigurations.
Vendor Lock-in
Lastly, vendor lock-in is a concern that many organizations grapple with when embracing cloud solutions. This happens when businesses become overly dependent on a single cloud provider, making it difficult and costly to switch to another provider in the future.
- Multi-Cloud Strategies: To mitigate this risk, consider a multi-cloud strategy that spreads your data and applications across multiple providers. This approach can enhance flexibility and reduce the threat of vendor lock-in.
- Open Standards: Choose providers that adhere to open standards to facilitate easier data migration in the future.
In my work with a startup, they faced challenges when trying to migrate their services to another cloud provider. The switching costs were astronomical, leading them to reconsider how they approached their initial cloud strategy.
By being aware of these challenges—security concerns, compliance issues, and the risk of vendor lock-in—organizations can take proactive steps to ensure that their Cloud Disaster Recovery plans are not only effective but also resilient in the face of potential obstacles. A well-rounded approach sets the foundation for a secure and adaptable digital future.

Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-world Examples of Effective Cloud DR
As we explore the tangible aspects of Cloud Disaster Recovery (CDR), case studies and success stories provide compelling evidence of its effectiveness. One notable example is a renowned online retailer that faced a significant service outage during peak holiday shopping days.
- Challenge: The retailer’s on-premises servers were overwhelmed, leading to downtime that risked losing millions in sales.
- Solution: They quickly transitioned to a cloud-based disaster recovery solution that involved data replication and automatic failover to the cloud during peak times.
As a result, they managed to maintain uptime even during traffic surges, ultimately increasing their holiday sales by 30%. This experience solidified their commitment to cloud solutions as part of their ongoing business strategy.
Business Continuity Achievements
Another striking example comes from a healthcare organization that recognized the critical need for robust disaster recovery. When a natural disaster threatened the primary data center housing patient records, the organization had to act rapidly.
- Forethought: They had previously implemented a cloud disaster recovery strategy that included regular backups and automated failovers.
- Outcome: The transition to the cloud facilitated real-time access to patient data from remote locations, ensuring continuity of care during a stressful timeframe.
The results were impressive—no patient care was disrupted, and operational efficiencies improved significantly post-implementation. Their commitment to planning and investing in cloud solutions not only helped safeguard sensitive information but also reinforced their reputation as a reliable healthcare provider.
These real-world examples illustrate that effective Cloud Disaster Recovery strategies not only protect businesses from catastrophic failures but also empower them to seize new opportunities for growth. Embracing cloud solutions leads to heightened business continuity achievements and can ultimately define a company’s resilience in today’s competitive landscape.

Future Trends and Innovations
AI and Machine Learning in Disaster Recovery
As we look ahead, it’s exciting to see how advancements in technology are shaping the future of Cloud Disaster Recovery (CDR). One of the most significant trends is the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into disaster recovery strategies.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze historical data patterns to predict potential system failures or vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to preemptively address issues before they escalate.
- Automated Responses: Machine learning algorithms can streamline the disaster recovery process by automating recovery actions, minimizing the need for manual intervention, and dramatically reducing recovery times.
In my experience working with a tech company that adopted AI for their disaster recovery, the results were astonishing. They were able to predict and resolve potential failures with remarkable accuracy, ultimately boosting their operational reliability.
Hybrid Cloud DR Solutions
Another vital trend is the rise of hybrid cloud disaster recovery solutions. These approaches combine both public and private cloud infrastructures, offering businesses greater flexibility and control over their data.
- Balanced Solutions: Organizations can keep sensitive data in a private cloud while utilizing the scalability of public cloud services for less sensitive applications.
- Cost Efficiency: By leveraging both environments, companies can optimize costs while maintaining the security and efficiency their operations require.
For example, a financial services firm I worked with found that this hybrid model allowed them to balance compliance and flexibility, enabling them to adapt their disaster recovery strategies swiftly in response to changing regulations.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Lastly, the concept of continuous improvement in disaster recovery strategies is gaining traction. This proactive mindset involves regularly analyzing and refining recovery processes.
- Feedback Loops: Organizations can implement feedback mechanisms to learn from recovery exercises and real-world incidents, using these insights to enhance future strategies.
- Adaptation and Growth: As new technologies emerge and business landscapes change, continuous improvement ensures that disaster recovery plans evolve accordingly.
An educational institution I collaborated with implemented continuous improvement strategies following several simulated disasters. By regularly revisiting and enhancing their plans, they not only increased their resilience but also fostered a culture of preparedness among staff.
Embracing these future trends—AI and ML’s potential, the flexibility of hybrid solutions, and ongoing improvement—will ensure that Cloud Disaster Recovery strategies remain robust and relevant in an increasingly unpredictable world. Creating a forward-thinking approach lays the foundation for lasting resilience and operational excellence.

