
Understanding Cloud Compliance
Definition of Cloud Compliance
Cloud compliance refers to the process of ensuring that cloud computing services adhere to relevant regulations, laws, and standards concerning data security and privacy. This encompasses a wide array of guidelines depending on the industry and geographical location, including specific frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Organizations utilizing cloud services must continually assess and adjust their practices to meet these compliance requirements to safeguard sensitive information.
Significance for Businesses
For businesses navigating the complexities of cloud compliance, the stakes are high. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, legal ramifications, and damaging reputational issues. Key reasons businesses prioritize cloud compliance include:
- Risk Mitigation: Protects against data breaches and legal penalties.
- Operational Integrity: Ensures reliable cloud operations with minimal disruptions.
- Competitive Advantage: Demonstrates commitment to data security, enhancing brand reputation.
For instance, a financial services company that complies with SOC 2 standards not only safeguards customer data but also builds trust with clients, directly impacting their bottom line. Thus, understanding the nuances of cloud compliance is essential for any organization in today’s digital landscape.

Common Cloud Compliance Standards
Overview of GDPR
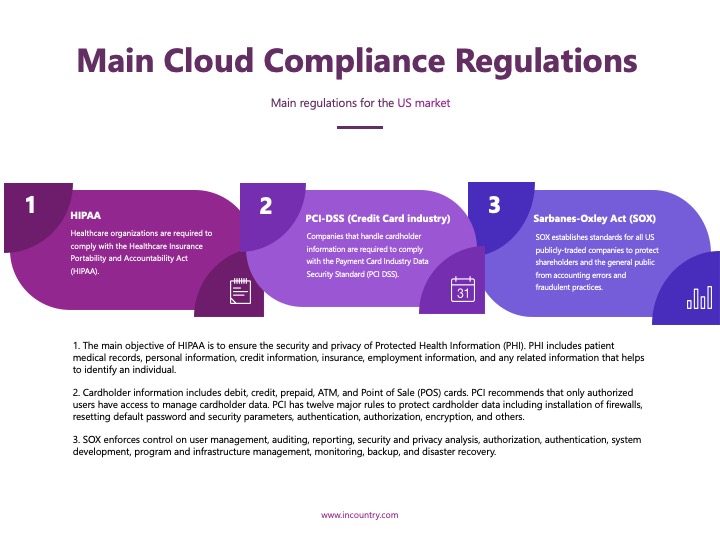
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection law in the European Union designed to enhance citizens’ control over their personal data. It mandates that organizations obtain explicit consent from individuals before processing their data.
- Key Principles:
- Data minimization: Only collect data that is necessary.
- Transparency: Inform individuals about data usage.
- Right to access: Allow individuals to see their data upon request.
For example, if a company collects user data without consent, it could face significant fines under GDPR.
Explaining HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a U.S. regulation aiming to protect sensitive patient health information. Healthcare providers and their business associates must comply with HIPAA to ensure confidentiality and security.
- Core Requirements:
- Administrative safeguards: Implement policies and procedures.
- Physical safeguards: Protect against unauthorized access to facilities.
- Technical safeguards: Encrypt patient data to prevent breaches.
A healthcare app, for instance, that fails to encrypt patient records could not only compromise patient trust but also face heavy fines.
Understanding SOC 2
System and Organization Controls (SOC) 2 focuses on non-financial reporting controls related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. It’s especially relevant for technology and cloud computing companies.
- Trust Services Criteria:
- Security: Protecting the system against unauthorized access.
- Availability: Ensuring the system is operational and accessible.
A tech company seeking to demonstrate its reliability might leverage SOC 2 compliance to reassure clients about their data handling practices.
With these standards, businesses can navigate the complex landscape of cloud compliance and build a solid foundation for trust with stakeholders.

Challenges in Cloud Compliance
Data Security Concerns
Navigating cloud compliance is not without its challenges, particularly regarding data security. Companies often store sensitive information in cloud environments, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. For instance, a breach could expose customer data, leading to financial loss and tarnished reputations.
- Common Data Security Issues:
- Lack of encryption: Failing to encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest can leave it vulnerable.
- Insider threats: Employees with access to sensitive information can intentionally or unintentionally compromise it.
- Inadequate third-party security controls: Reliance on third-party providers without thorough assessments can introduce vulnerabilities.
To illustrate, a retail company that does not encrypt its customer payment information risks exposing that data during a breach, leading to severe consequences.
Compliance Monitoring Issues
Monitoring compliance effectively can be another daunting task. Regulations are evolving constantly, and keeping up can feel like chasing a moving target.
- Key Monitoring Challenges:
- Resource-intensive audits: Regular compliance audits can consume significant time and resources.
- Lack of automated tools: Many businesses struggle with manual compliance tracking, leading to errors and oversights.
- Misunderstanding regulations: Organizations may misinterpret compliance requirements, resulting in inadvertent violations.
For example, a small start-up might miss critical changes in GDPR due to limited resources, potentially leading to costly penalties. Addressing these monitoring issues is crucial for maintaining compliance in an ever-changing cloud landscape.

Essential Guidelines for Cloud Compliance
Data Encryption Best Practices
To enhance cloud compliance and secure sensitive data, implementing robust encryption practices is vital. Encryption is like a digital lock, ensuring that unauthorized users cannot access critical information.
- Best Practices Include:
- Use Strong Algorithms: Employ AES-256 encryption for data at rest and TLS for data in transit to ensure top-notch security.
- Regular Key Management: Rotate encryption keys periodically to minimize the risks of exposure.
- End-to-End Encryption: Encrypt data before it even leaves your systems, ensuring it remains protected throughout its lifecycle.
Consider a healthcare provider that securely encrypts patient records, ensuring compliance with HIPAA, while also protecting patient information against breaches.
Access Control Policies
Access control is another cornerstone of cloud compliance. Limiting data access only to authorized personnel significantly mitigates risks.
- Implement Effective Policies:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on user roles to streamline access management.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Incorporate MFA to enhance security for accessing critical information.
- Regular Review of Access Rights: Continuously assess who has access to what, ensuring that unnecessary permissions are revoked.
For example, a financial institution using RBAC ensures that only its accounting team can access sensitive transaction data, reducing the chance of unauthorized access.
Regular Compliance Audits
Lastly, conducting regular compliance audits is crucial for maintaining cloud compliance over time. These audits help identify potential weaknesses and ensure adherence to regulations.
- Audit Guidelines:
- Establish a Routine Schedule: Regular audits, whether quarterly or semi-annually, keep compliance top of mind.
- Involve Third-Party Experts: Engaging external auditors can provide objective insights and help spot issues you may overlook.
- Document Findings and Action Plans: Always keep thorough records of audits and follow up on corrective actions.
With these essential guidelines, businesses can solidify their cloud compliance efforts, fostering trust and security in an increasingly digital world.
Implementing Cloud Compliance Framework
Selecting the Right Cloud Service Provider
Choosing the right cloud service provider (CSP) is a fundamental step in establishing robust cloud compliance. Not all providers are created equal, and it’s essential to ensure they align with your compliance requirements.
- Key Considerations:
- Reputation and Experience: Look for providers with a proven track record in complying with industry standards (e.g., ISO 27001, HIPAA).
- Transparency: Providers should openly share their compliance certifications and audit results.
- Security Features: Ensure they offer advanced security services like encryption, firewalls, and robust access controls.
For instance, a global e-commerce company might select a CSP that meets international compliance standards, ensuring they can operate seamlessly in multiple regions.
Training Employees on Compliance Measures
Once the right CSP is in place, educating employees about compliance measures is crucial. Employees are often the first line of defense against compliance risks.
- Effective Training Strategies:
- Regular Workshops: Host quarterly workshops that cover compliance policies, security practices, and industry regulations.
- Accessible Resources: Create a centralized repository of compliance guidelines that employees can refer to at any time.
- Simulations and Drills: Conduct security drills or phishing simulations to prepare employees for potential threats.
For example, a tech start-up might implement monthly training sessions, boosting employee awareness and ensuring everyone understands the importance of compliance as part of the company culture. By focusing on these critical areas, businesses can lay a solid foundation for a successful cloud compliance framework.

Benefits of Cloud Compliance for Businesses
Improved Data Security
One of the significant advantages of cloud compliance is the noticeable enhancement of data security. In an age where data breaches are increasingly common, compliance frameworks ensure that businesses adopt best practices for protecting sensitive information.
- Key Security Improvements:
- Stronger Encryption: Compliance requirements often push companies to implement advanced encryption protocols for data both in transit and at rest.
- Regular Security Audits: Frequent assessments help identify vulnerabilities, allowing companies to address them proactively.
- Access Controls: Implementing strict access management ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data, minimizing potential leaks.
For example, a manufacturing company that meets ISO/IEC standards can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to their operational data.
Enhanced Customer Trust
Beyond data security, ensuring compliance can dramatically boost customer trust. In an environment where consumers are increasingly aware of data privacy issues, compliance demonstrates a commitment to protecting their information.
- How Compliance Builds Trust:
- Transparency: Compliance initiatives involve clear communication about how customer data is handled and secured.
- Certifications: Displaying compliance certifications can reassure customers that their data is managed according to industry standards.
- Better Customer Engagement: Trust leads to stronger customer relationships, resulting in increased loyalty and repeat business.
For instance, an online retailer that showcases its adherence to GDPR not only complies with regulations but also fosters confidence among its European customers. Overall, cloud compliance serves as a powerful asset for businesses, reinforcing their security posture and cultivating lasting relationships with their clients.

Case Studies: Successful Cloud Compliance Implementations
Company A: Compliance Journey
Company A, a mid-sized healthcare provider, recently embarked on a journey to achieve compliance with HIPAA regulations. Recognizing the critical importance of protecting patient data, they implemented a multi-step plan.
- Steps Taken:
- Vendor Assessment: They carefully evaluated their cloud service provider, ensuring it offered robust security features aligned with HIPAA’s requirements.
- Employee Training: The organization conducted extensive training sessions to educate staff on data privacy and security protocols.
- Regular Audits: They scheduled bi-annual audits to assess their compliance status and make necessary adjustments.
As a result, Company A not only became compliant but also experienced a notable reduction in data breaches, reinforcing their reputation as a trustworthy healthcare provider.
Company B: Lessons Learned
Company B, a financial services company, faced significant challenges during its compliance journey. Initially, they rushed through implementing security measures without a comprehensive strategy.
- Challenges Faced:
- Insufficient Training: Employees were not adequately trained on compliance, leading to accidental data exposure.
- Weak Security Policies: They relied on outdated protocols, putting customer data at risk.
Realizing these missteps, Company B revamped their approach by focusing on thorough training and engaging compliance experts. Their journey highlights the importance of thorough preparation and adaptation in achieving effective cloud compliance, providing valuable lessons for other businesses in the process.

Future Trends in Cloud Compliance
Automation in Compliance Processes
As organizations strive for greater efficiency, one of the most promising trends in cloud compliance is automation. Automation tools can streamline compliance processes, allowing businesses to focus on strategic initiatives rather than administrative tasks.
- Benefits of Automation:
- Reduced Human Error: Automated systems help mitigate the risk of mistakes in compliance documentation and reporting.
- Real-time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring tools can immediately flag compliance issues, enabling quicker resolution.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, automated processes can easily adapt to increasing compliance demands without the need for extensive manpower.
For instance, a large enterprise might implement automated compliance software to track adherence to industry standards across multiple departments, thus improving overall efficiency.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
Another significant trend is the increasingly dynamic regulatory landscape. As technologies advance, regulations are continually evolving to address new challenges.
- Key Considerations:
- Cross-Border Compliance: Businesses must navigate varying regulations in different jurisdictions, requiring a flexible compliance framework.
- Focus on Privacy: With a global shift towards more stringent data privacy laws, organizations need to prioritize regulatory updates.
- Adaptable Strategies: Companies will need to develop agile compliance strategies that can quickly adjust to regulatory changes.
For example, a tech start-up operating internationally will need to stay ahead of emerging data protection laws like GDPR while adapting to local regulations. Staying informed and proactive in these areas will be paramount for organizations looking to thrive in the future cloud landscape.

Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
In this journey through cloud compliance, we’ve uncovered the fundamental aspects that organizations must navigate to ensure the protection of sensitive data and adherence to regulatory requirements. Key takeaways include:
- Understanding essential compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
- Recognizing the importance of data encryption, access control, and regular audits for maintaining compliance.
- Learning from real-world examples, as seen in the journeys of Company A and Company B, which highlight both successful strategies and valuable lessons.
These insights emphasize that cloud compliance is not merely a checkbox, but a critical element in today’s data-centric world.
Final Recommendations
As you move forward, consider these recommendations to enhance your cloud compliance efforts:
- Invest in Technology: Utilize automation tools to simplify compliance processes and facilitate better data management.
- Prioritize Employee Training: Ensure your team is well-informed about compliance policies and practices.
- Stay Vigilant: Regularly review and adapt your compliance strategies to keep pace with the evolving regulatory landscape.
By taking proactive measures, businesses can not only protect sensitive data but also build lasting trust with their customers, laying the groundwork for future success.

