
Introduction
Overview of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals access and utilize technology resources. By allowing users to store and process data over the internet, rather than relying on local servers or personal computers, it provides unmatched flexibility and scalability. Imagine having the ability to scale your resources up or down with just a few clicks, or accessing your applications and data from anywhere in the world—this is the power of cloud computing.
Here are some key characteristics of cloud computing:
- On-Demand Self-Service: Users can automatically provision resources without human intervention.
- Broad Network Access: Resources are available over the network and can be accessed through standard mechanisms, promoting use across various platforms.
- Resource Pooling: Providers’ computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers, enhancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
These features make cloud computing an essential component of modern IT infrastructure, enabling businesses to focus on growth without the burden of managing physical hardware.
Importance of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
As we delve deeper into cloud computing, three main service models emerge: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each of these models addresses different business needs and plays a crucial role in a comprehensive cloud strategy.
To highlight their importance:
- IaaS provides essential computing resources, allowing businesses to avoid the costs of physical hardware.
- PaaS alleviates the complexities of building and maintaining applications, letting developers focus on coding without worrying about infrastructure management.
- SaaS offers ready-to-use applications, accessible via any device, which enhances collaboration, productivity, and scalability.
In summary, these models form the backbone of cloud computing, enabling businesses to operate more efficiently, innovate swiftly, and respond to market demands effectively. The adaptability and cost-effectiveness of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS reflect the cloud computing landscape’s inherent value, which TECHFACK continues to explore in detail.

Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Definition and Characteristics
Building on our understanding of cloud computing, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) stands out as a vital offering in this realm. But what exactly is IaaS? In essence, IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, allowing businesses to rent servers, storage, networks, and operating systems as needed. This model significantly reduces the need for physical hardware and enables companies to scale resources up or down based on real-time demand.
Key characteristics of IaaS include:
- Virtualization: Resources are abstracted and delivered as virtual machines, allowing for efficient resource allocation.
- Self-Service Provisioning: Users can independently configure and manage their infrastructure without requiring direct provider intervention.
- Pay-as-You-Go: This model allows companies to pay only for the resources they use, enhancing managing overhead costs.
Key Players in IaaS Market
The IaaS market is competitive and populated by several notable providers. Some of the key players include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Often considered the leader in the cloud space, AWS offers a diverse range of services to cater to various business needs.
- Microsoft Azure: With its seamless integration into Microsoft products, Azure is a popular choice for enterprises already utilizing Microsoft solutions.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Known for its data analytics and machine learning features, GCP attracts businesses focused on innovation.
Benefits and Challenges
While IaaS delivers numerous benefits, it also comes with its unique challenges.
Benefits:
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the capital expense associated with purchasing and maintaining physical servers.
- Scalability: Easily scalable resources allow businesses to adapt to growth without interruption.
- Focus on Core Activities: Frees up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine hardware maintenance.
Challenges:
- Security Concerns: Data security is a significant concern for businesses leveraging IaaS, as sensitive information is stored off-site.
- Downtime Risks: Dependency on cloud service providers can lead to downtime issues, potentially impacting business operations.
As organizations navigate these benefits and challenges, understanding IaaS becomes critical for making informed decisions about their cloud infrastructure, a topic we will continue to explore as we delve deeper into PaaS and SaaS.
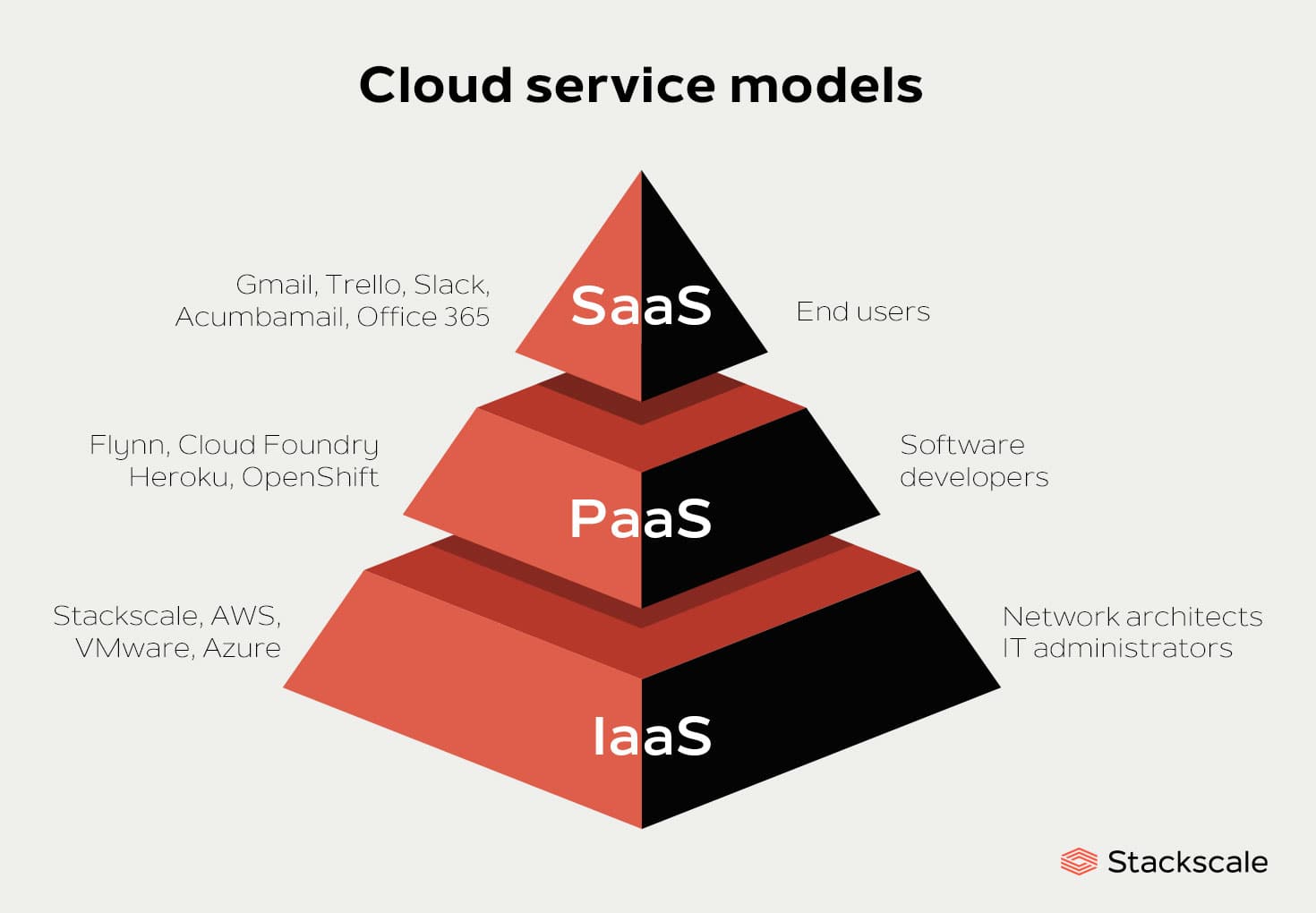
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Understanding PaaS
Transitioning from Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), we come to Platform as a Service (PaaS), which serves as the next layer of the cloud computing stack. PaaS provides an environment where developers can build, test, and deploy applications without the complexity of managing underlying infrastructure. This service model streamlines the development process by offering pre-configured software components, enabling developers to focus on writing code rather than worrying about hardware and networking issues.
Key features of PaaS include:
- Development Tools: Integrated development environments (IDEs) make coding more accessible and efficient.
- Middleware Services: Supports applications with essential services, such as messaging, database management, and workflow tools.
- Built-in Scalability: Automatically adjusts resources based on application demand, facilitating seamless growth.
Comparison with IaaS and SaaS
When distinguishing between IaaS, PaaS, and Software as a Service (SaaS), it helps to visualize them along a spectrum of management and control:
- IaaS: Users manage the operating systems, applications, and runtime while the provider handles the underlying hardware.
- PaaS: The provider manages the underlying infrastructure and operating systems, offering tools for developers to create applications.
- SaaS: The provider delivers fully functional software applications, removing the need for users to manage anything aside from access.
This layered approach highlights PaaS as a middle ground, ideal for organizations that prioritize development without deep infrastructure management.
Use Cases and Examples
PaaS is particularly beneficial for a variety of scenarios. Here are some common use cases:
- Application Development: Organizations can rapidly develop and deploy applications using built-in tools and frameworks. For example, Google App Engine is a popular PaaS for building scalable web apps.
- API Development and Management: Businesses can create APIs to connect multiple applications. A notable example is Microsoft Azure API Management, which simplifies API consumption.
- Collaboration: Teams can collaborate on development projects in real-time, regardless of location. Salesforce platform, also a PaaS, allows development and customization of applications shared amongst teams.
These examples illustrate how PaaS enhances productivity and innovation in software development. As we delve deeper, the exploration of Software as a Service (SaaS) will continue to reveal the broader impacts of these cloud concepts on modern business landscapes.

Software as a Service (SaaS)
What is SaaS?
Continuing along the cloud computing spectrum, we arrive at Software as a Service (SaaS). This model provides software applications over the internet, removing the need for organizations to install, manage, or maintain software locally. With SaaS, users can access applications through a web browser, making it incredibly convenient and accessible from any location.
In this model, the software provider manages the entire infrastructure, platform, and application, enabling businesses to focus on their core operations rather than IT management. Popular examples of SaaS applications include email services like Gmail, customer relationship management (CRM) tools like Salesforce, and productivity suites like Microsoft 365.
Popular SaaS Applications
SaaS applications have proliferated across various industries and have transformed how businesses operate. Some of the most popular SaaS applications include:
- Salesforce: A leading CRM platform that helps manage customer relationships and automate sales processes.
- Slack: A collaboration tool that streamlines communication within teams, enhancing productivity.
- Zoom: A video conferencing tool that gained immense popularity, especially during the shift to remote work.
- Dropbox: A cloud storage service that allows users to access their files from any device, making file sharing and collaboration easy.
These applications illustrate the versatility and convenience of the SaaS model, appealing to organizations of all sizes.
Pros and Cons
As with any technology, SaaS comes with its own set of advantages and challenges.
Pros:
- Cost-effective: Typically, SaaS operates on a subscription basis, allowing businesses to manage expenses more efficiently without significant upfront costs.
- Automatic Updates: Users benefit from regular updates and new features without having to worry about manual installations or system management.
- Scalability: SaaS providers often offer flexible subscription plans that can be adjusted according to business demands.
Cons:
- Data Security: Storing sensitive data off-site can raise security concerns, necessitating robust provider vetting.
- Limited Customization: Unlike traditional software, SaaS applications might not allow extensive customization, which can hinder specific business requirements.
- Dependence on Internet Connectivity: Since SaaS relies heavily on internet access, disruptions can impact user accessibility and productivity.
These factors provide a deeper understanding of SaaS’s place within the broader cloud landscape. As we continue to explore the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, we will consider their implications for organizations navigating their digital transformations.

Differences and Comparisons
Contrasting IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Now that we’ve explored IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, it’s crucial to highlight how these models differ from one another. Understanding these differences can help businesses make informed decisions when selecting a cloud service provider.
- Control and Management:
- IaaS: Offers maximum control over the infrastructure but requires businesses to manage operating systems and applications.
- PaaS: Provides a balanced approach by managing the underlying infrastructure while granting developers the freedom to build applications.
- SaaS: Places the least burden on users, as everything is managed by the service provider, from infrastructure to applications.
- Use Cases:
- IaaS is ideal for companies needing extensive computing resources or those with unpredictable workloads.
- PaaS is best suited for development teams aiming to quickly create applications without worrying about hardware or system maintenance.
- SaaS fits organizations looking for ready-to-use software solutions with minimal setup.
This clear distinction allows organizations to choose the model that best aligns with their operational requirements and technical capabilities.
Decision Factors for Choosing Between Them
When selecting between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, several decision factors come into play:
- Business Needs: Identify the specific needs of your organization—whether it’s robust infrastructure for large-scale applications (IaaS), rapid development capabilities (PaaS), or user-friendly applications for daily tasks (SaaS).
- Technical Skills: Assess the technical expertise of your team. If your staff has strong development skills, PaaS might be more beneficial. Conversely, if they prefer straightforward solutions, SaaS could be the answer.
- Budget Considerations: Determine your budget. IaaS may come with higher initial costs due to infrastructure requirements, while SaaS often operates on a subscription model that can be more financially manageable.
- Scalability Requirements: Consider your growth projections. IaaS offers flexibility in scaling resources, PaaS supports scaling applications, and SaaS typically provides scaling through subscription levels.
These decision factors pave the way for organizations to navigate their cloud computing strategies efficiently. The depth of understanding between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS empowers businesses to leverage the right solution for their unique needs as they embrace digital transformation. With each service offering promising distinct advantages, careful consideration is key to success in today’s cloud-centric landscape.
Adoption and Trends
Growth of Cloud Computing
As we explore the landscape of cloud computing, one cannot overlook its remarkable growth in recent years. Businesses across various sectors have swiftly adopted cloud technologies to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and foster innovation. According to recent studies, the cloud computing market is expected to grow at an annual rate of over 20%, reflecting an ongoing shift towards digital solutions.
Some contributing factors to this growth include:
- Remote Work Revolution: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of cloud services as companies transitioned to remote work, making it imperative to access data and applications from anywhere.
- Advancements in Technology: Innovations in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics are increasingly being integrated into cloud services, making them more attractive to businesses.
Impact on Industries
Cloud computing is transforming various industries, reshaping operations and enhancing service delivery. For instance:
- Retail: E-commerce platforms leverage cloud computing to provide personalized shopping experiences, manage inventory, and streamline logistics.
- Healthcare: Cloud services facilitate telemedicine, enabling healthcare providers to manage patient records securely and enhance remote care capabilities.
- Finance: Financial institutions use cloud computing for risk assessment, compliance, and managing large volumes of transactions seamlessly.
These examples illustrate the diverse applications of cloud computing, offering businesses the flexibility and responsiveness required in a dynamic marketplace.
Future Projections
Looking ahead, the future of cloud computing seems exceptionally bright. Several trends are on the horizon:
- Increased Focus on Security: With growing concerns about data privacy and cybersecurity, businesses will prioritize investing in secure cloud solutions and compliance measures.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Companies are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance flexibility.
- Edge Computing: As Internet of Things (IoT) devices proliferate, edge computing will gain traction, allowing data processing closer to the source for quicker response times.
As organizations navigate these trends, leveraging cloud computing will be pivotal in shaping their digital transformation journeys. The insights gained from understanding growth patterns, industry impact, and future projections empower businesses to strategically position themselves in the ever-evolving world of technology, ensuring they remain competitive and resilient. Such adaptability is crucial as they embrace the potential of cloud computing, ultimately contributing to innovation and success in their respective fields.
Security and Compliance
Concerns in Cloud Computing
As cloud computing continues to grow, security and compliance have emerged as critical considerations for organizations. Many businesses remain hesitant to fully embrace cloud technologies due to concerns about data privacy and regulatory compliance. After all, sensitive information stored off-premises can feel vulnerable, leading to apprehensions about cloud security.
Some prevalent concerns include:
- Data Breaches: Cyberattacks are increasingly sophisticated, and cloud environments can present attractive targets for hackers.
- Data Loss: Accidental deletions, corruption, or failure of the cloud provider can lead to irreversible data loss if proper backups aren’t maintained.
- Compliance Risks: Many industries train significant detail to regulatory compliance, such as GDPR for data protection or HIPAA for healthcare, and non-compliance can result in hefty fines.
These concerns highlight the need for organizations to take proactive measures to safeguard sensitive data.
Strategies for Ensuring Security
To address security concerns in cloud computing effectively, businesses can implement several strategies:
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Regularly evaluate potential vulnerabilities within the cloud environment, identifying areas that may require additional security measures.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit can significantly mitigate the risk of unauthorized access, ensuring that data remains secure even if breached.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access to cloud resources adds an additional layer of security beyond just passwords.
- Regular Audits and Compliance Checks: Conducting audits ensures that the organization adheres to regulatory requirements and helps identify any remaining lapses in security protocols.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can not only build a safer cloud infrastructure but also improve their confidence in utilizing cloud solutions. As we explore the vast benefits of cloud computing, effectively addressing security and compliance must remain a priority. After all, a secure cloud environment will empower businesses to expand their digital operations confidently while safeguarding against potential threats and ensuring regulatory adherence. This proactive approach fosters trust and security, reinforcing the value of cloud technologies in today’s data-driven world.
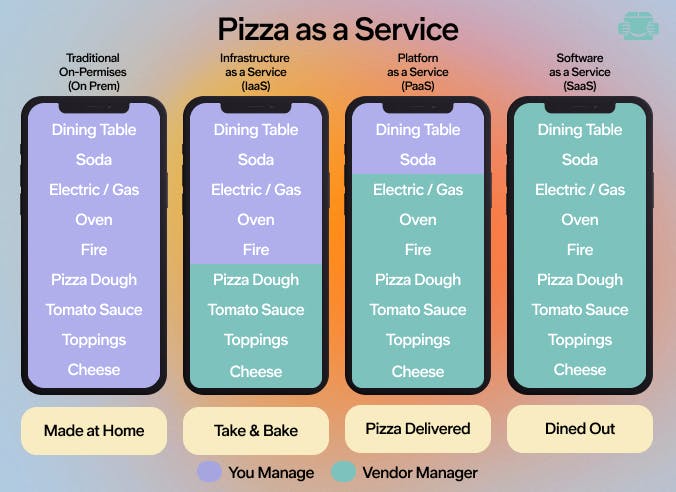
Best Practices for Cloud Deployment
Tips for Successful Implementation
As organizations venture into cloud computing, following best practices for deployment is essential to ensure a smooth transition and maximize benefits. Transitioning to the cloud can be complex, but with the right approach, businesses can streamline the process and enhance their overall cloud experience.
Here are some tips for successful implementation:
- Define Clear Objectives: Before migrating to the cloud, organizations should identify their goals, be it improving scalability, enhancing performance, or reducing costs.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders early in the process. Understanding their needs and concerns can facilitate smoother transitions and help ensure that the cloud solution aligns with organizational goals.
- Choose the Right Cloud Model: Assess whether IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS best fits your needs. This choice can drastically affect performance, control, and flexibility.
- Implement a Comprehensive Migration Plan: A well-structured migration strategy that includes timelines, resources, and risk mitigation strategies can provide better control over the deployment.
Cost Management Strategies
While the cloud can lead to cost savings, it’s vital to proactively manage those costs to avoid unexpected expenses. Here are effective cost management strategies to consider:
- Monitor Usage Regularly: Utilize cloud management tools to keep tabs on resource consumption and identify underused resources that can be downsized or eliminated.
- Set Budgets and Alerts: Establish clear budgets for departmental cloud usage, and set up alerts that notify stakeholders when approaching those limits.
- Leverage Reserved Instances: For predictable workloads, consider reserved instances for services like compute power, which can offer significant cost reductions compared to on-demand pricing.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Regularly review your resource allocation and adjust as necessary to ensure that you are not paying for more than you need.
Implementing these best practices will enable organizations to enjoy the plethora of benefits that cloud computing offers while ensuring a cost-effective and efficient deployment. With a well-planned strategy and vigilant management, businesses can navigate their cloud journeys successfully, leading to increased agility and innovation in their operations. Ultimately, a thoughtful approach to cloud deployment not only accelerates the transition but also lays the groundwork for long-term growth and success in the digital landscape.

Case Studies
Real-world Examples of Cloud Adoption
As organizations increasingly turn to cloud computing, there are numerous inspiring case studies that highlight the transformative effects of cloud adoption. One remarkable example is Netflix, a pioneer in embracing cloud technology. By migrating its entire infrastructure to Amazon Web Services (AWS), Netflix achieved unparalleled scalability and reliability. This move allowed them to stream content seamlessly to millions of viewers worldwide, even during peak usage times.
Another notable case is General Electric (GE), which implemented PaaS solutions for its industrial applications through the Predix platform. By leveraging cloud computing, GE was able to analyze vast amounts of machine data in real-time, leading to improved operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Lessons Learned and Success Stories
These case studies illustrate several important lessons for organizations considering cloud adoption:
- Embrace Flexibility: Companies should remember that cloud platforms offer flexibility in scaling resources based on demand. Netflix’s ability to handle viewer spikes during popular show releases exemplifies this advantage.
- Focus on Collaboration: Successful cloud adoption often hinges on fostering collaboration between IT and business teams. GE’s integration of industrial data into its cloud infrastructure illustrates how cross-functional teamwork can drive significant innovation.
- Prioritize Security and Compliance: While the benefits are substantial, organizations must remain vigilant about security and compliance. With sensitive data stored in the cloud, it’s essential to adopt best practices and protocols, as both Netflix and GE did to protect their assets.
These success stories and lessons learned serve as a valuable guide for businesses embarking on their cloud journey. They showcase how strategic cloud adoption can lead to enhanced efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantages. Leveraging the experiences of industry leaders not only inspires confidence but also paves the way for organizations to navigate their own transitions effectively, ensuring that they maximize the potential of cloud technologies. Embracing the cloud is not just about technology—it’s about transforming business strategies to thrive in an ever-evolving digital landscape.

Conclusion
Recap of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
As we wrap up our exploration of cloud computing, it’s essential to recap the three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each model addresses different business needs:
- IaaS provides businesses with virtualized computing resources, allowing them to rent infrastructure. This flexibility enables organizations to scale their IT needs without significant capital investment.
- PaaS offers a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications without managing the underlying hardware or software. It simplifies the development process, encouraging faster innovation.
- SaaS delivers fully functional software applications over the internet, ensuring users have access to software without installation or management concerns. This model enhances collaboration and productivity across various teams.
These service models transform the traditional IT landscape, offering dynamic solutions to enhance business operations.
Final Thoughts on Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become an integral part of modern business strategy. With its ability to promote agility, reduce costs, and foster innovation, it’s no wonder that companies are increasingly seeking cloud solutions to gain a competitive edge.
However, successful cloud adoption requires continuous evaluation and strategic planning. Companies must prioritize security and compliance while also keeping an eye on costs using effective management practices.
As technology evolves, so will the tools and capabilities available within the cloud. Organizations that embrace change and adopt cloud strategies will find themselves better positioned to respond to market demands, enhance operational efficiency, and drive growth.
In conclusion, the journey to cloud computing is not just a technological transition—it’s an opportunity for businesses to redefine their strategies for the future. By leveraging IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS effectively, organizations can unlock their full potential and navigate the complexities of the digital age with confidence. As we look ahead, the possibilities within cloud computing are limitless, and the success stories continue to unfold.

