Introduction
Definition of Cloud-Based and On-Premises Software
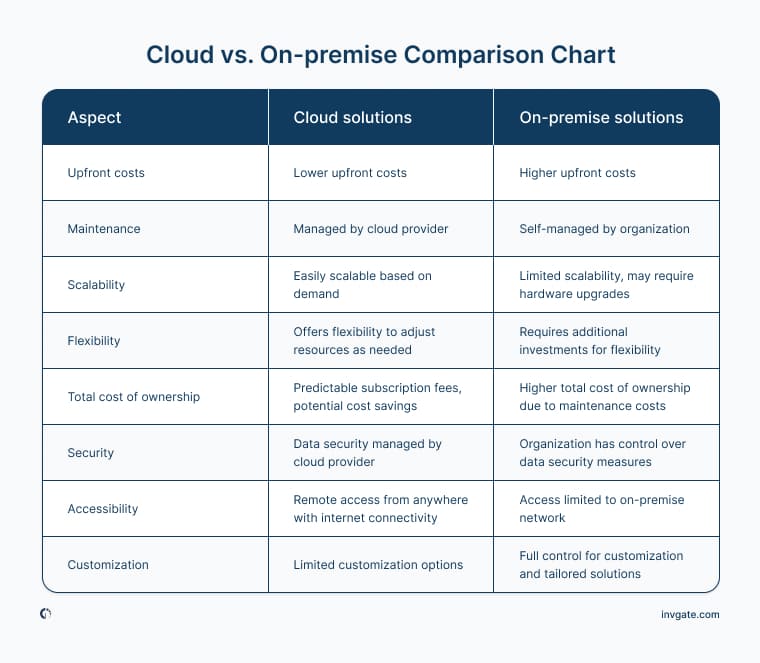
In today’s digital landscape, businesses often find themselves weighing two primary software solutions: cloud-based software and on-premises software.
- Cloud-Based Software operates on the internet, meaning users can access applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This model allows for real-time collaboration and scalability.
- On-Premises Software, on the other hand, is installed locally on a company’s hardware. This often leads to greater control over data and systems, which can be crucial for some organizations.
Understanding these definitions sets the stage for exploring their unique benefits and drawbacks.
Significance of Choosing Between the Two Options
Choosing the right software model goes beyond mere preference; it can significantly affect a business’s efficiency, security, and financial health.
For example, a startup might favor cloud-based software due to its cost-effectiveness and rapid scalability, while an established enterprise might opt for on-premises solutions to maintain stringent data security laws.
Ultimately, this decision shapes how a company operates and interacts with technology—making it a critical consideration for growth and sustainability.

Pros and Cons of Cloud-Based Software
Advantages of Cloud-Based Software
Many organizations are drawn to cloud-based software for its myriad advantages, making it a popular choice across industries. Let’s explore some compelling benefits that could make it the right fit for your business.
Accessibility and Scalability
One of the standout features of cloud-based solutions is their accessibility. Team members can work from anywhere, enabling seamless collaboration.
- Scalability: As your business grows, so can your software needs—allowing you to easily upgrade and expand your services without major disruptions.
Cost-Effectiveness
Financially, cloud solutions can be more budget-friendly. Typically, they operate on a subscription basis, reducing upfront costs.
- Predictable Spending: No more hefty licenses or installation fees.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance
With cloud software, updates and maintenance are handled by providers, ensuring that you always operate on the latest version without lifting a finger—freeing up your IT resources.
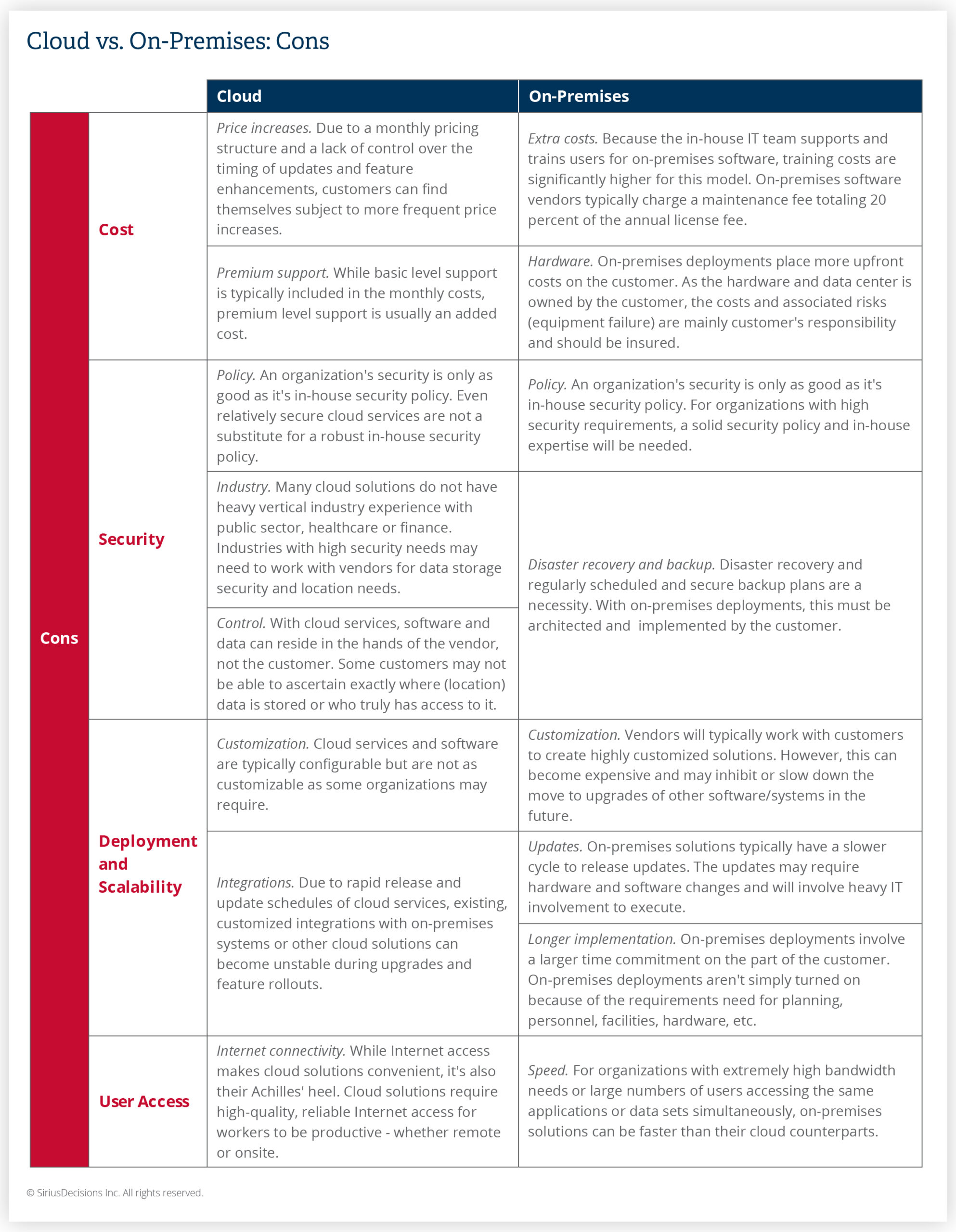
Disadvantages of Cloud-Based Software
However, there are downsides to this model.
Data Security Concerns
Many businesses worry that storing data off-site may expose them to security threats.
- Sensitive Information: Data breaches can lead to significant repercussions.
Dependency on Internet Connection
Lastly, cloud solutions depend on internet connectivity. A weak signal may hinder access, posing challenges especially in remote locations.
Overall, understanding both the merits and drawbacks allows businesses to make informed decisions when considering cloud-based software.
Pros and Cons of On-Premises Software
Advantages of On-Premises Software
While cloud-based solutions have taken the spotlight, on-premises software offers several unique advantages that make it appealing to certain businesses.
Data Control and Security
One of the biggest draws of on-premises software is the heightened control over data security. Organizations can implement their own security measures and protocols, protecting sensitive information from external threats.
- Compliance: This is crucial for industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as finance or healthcare.
Customization and Flexibility
On-premises solutions allow businesses to tailor features to fit specific needs. Unlike cloud software, which often operates on a one-size-fits-all model, on-premises software offers:
- Bespoke functionalities: Companies can create and modify interfaces, workflows, and integrations to suit their operational requirements.
No Reliance on Internet Connectivity
Additionally, with on-premises software, users aren’t dependent on an internet connection. Data access remains consistent and uninterrupted, even during network outages.
Disadvantages of On-Premises Software
However, there are notable downsides to consider.
High Initial Costs
The upfront investment for on-premises software can be substantial. Costs include:
- Licensing fees, hardware purchases, and installation expenses that can take a toll on a budget.
Maintenance and Upgrades
Moreover, managing upgrades and maintenance shifts responsibility to IT teams. This can consume valuable resources and time, detracting from other projects.
Limited Accessibility
Finally, accessibility can be an issue. On-premises software is typically accessible only from the company’s network, limiting remote work options.
By weighing these pros and cons, businesses can better navigate their software selection, ensuring they find the ideal fit for their operational needs.

Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Cloud-Based and On-Premises Software
Choosing between cloud-based and on-premises software is no small task, and various factors can help inform this critical decision. Let’s explore some key considerations that can significantly impact your choice.
Company Size and IT Infrastructure
Understanding your company size is essential. Smaller businesses may benefit more from cloud-based solutions, given their limited IT resources and need for scalability.
- Larger firms, conversely, often have the infrastructure in place to manage on-premises software effectively. Having an established IT team can facilitate the customization and ongoing maintenance of these systems.
Security and Compliance Requirements
Security is a hot topic in today’s data-driven world. Businesses in regulated industries, like healthcare or finance, are often bound by strict compliance requirements.
- For such companies, on-premises software can provide an added layer of data control that may be crucial for meeting compliance standards.
Budget Constraints
Lastly, budget constraints play a pivotal role in this decision-making process.
- Cloud solutions often come with lower initial costs and predictable subscription fees, ideal for startups. On-premises software may require hefty upfront investments but could be more cost-effective in the long run if scaled appropriately.
Considering these factors will enable businesses to make an informed choice that best meets their technological and operational needs.

Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Companies Choosing Cloud-Based or On-Premises Software
To illustrate the choice between cloud-based and on-premises software, let’s look at two real-world examples: one company that embraced the cloud and another that opted for on-premises deployment.
Company A: Adoption of Cloud-Based Software
Company A, a small marketing agency, decided to adopt cloud-based software to enhance collaboration among their remote workforce.
- Benefits Experienced: With applications like Google Workspace and Slack, team members could access files and communicate seamlessly, regardless of their location.
- Scalability: As the agency grew, they easily upgraded their subscription plans without costly hardware installations.
This flexibility allowed them to focus on client projects rather than IT infrastructure, dramatically increasing their productivity.
Company B: Implementation of On-Premises Software
Conversely, Company B, a financial institution, implemented on-premises software to ensure stringent data security and compliance with industry regulations.
- Customization: By tailoring the software to fit their specific processes, they maintained greater control over security measures.
- Challenges Faced: However, they had to invest in robust IT infrastructure and resources to manage regular maintenance and updates.
These case studies highlight how varying business needs can lead to distinct software choices, reinforcing the importance of aligning technology with organizational goals.

Conclusion and Recommendations
As we conclude our exploration of cloud-based versus on-premises software, it’s crucial to recap the key points to ensure clarity in making this important decision.
Recap of Key Points
- Cloud-Based Software offers accessibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, but may raise concerns about data security and internet dependency.
- On-Premises Software provides greater control and customization, though it comes with high initial costs and ongoing maintenance needs.
Understanding these advantages and disadvantages can guide businesses toward the best fit for their unique needs.
Guidance on Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When deciding, consider the following steps:
- Assess Company Size: Startups might lean towards cloud solutions, while larger organizations may prefer on-premises software.
- Evaluate Security Requirements: Prioritize data security and compliance based on your industry.
- Budget Analysis: Compare total costs, including maintenance and potential upgrades.
By carefully analyzing these factors, businesses can make informed choices that align with their goals, helping ensure a successful technological future.

