Overview of Cloud Computing
Definition and Evolution of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has radically transformed how businesses and individuals access computing resources. At its core, cloud computing refers to delivering various computing services—storage, processing, and data management—via the internet. This means you can store or access data from anywhere, eliminating the need for local servers and cumbersome hardware.
The evolution of cloud computing began in the early 2000s with Software as a Service (SaaS) and has progressed rapidly, encompassing Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS). As these services matured, they allowed organizations to innovate faster and reduce costs significantly.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
The advantages of cloud computing are numerous and compelling:
- Cost-Efficiency: Save on hardware and maintenance costs.
- Scalability: Easily adjust resources to meet demand.
- Accessibility: Access applications and files from any location, on any device.
- Disaster Recovery: Simplified backup solutions and enhanced data security.
These benefits are why organizations increasingly gravitate towards cloud solutions, reinforcing the notion that cloud technology is shaping the future of business operations.
Key Players in the Cloud Computing Industry
Within the thriving landscape of cloud computing, several major players are leading the charge:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): A pioneer in cloud services offering robust scalability and an extensive service portfolio.
- Microsoft Azure: Known for seamless integration with enterprise applications and strong developer tools.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Recognized for its data analytics and machine learning capabilities.
These companies continually innovate, offering diverse solutions that benefit businesses of all sizes, laying down the framework for what is undoubtedly the future of cloud computing.
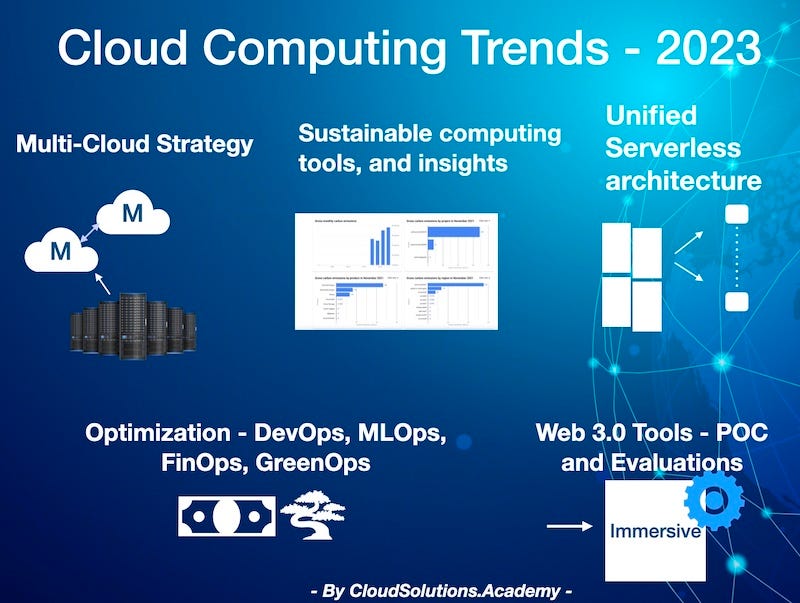
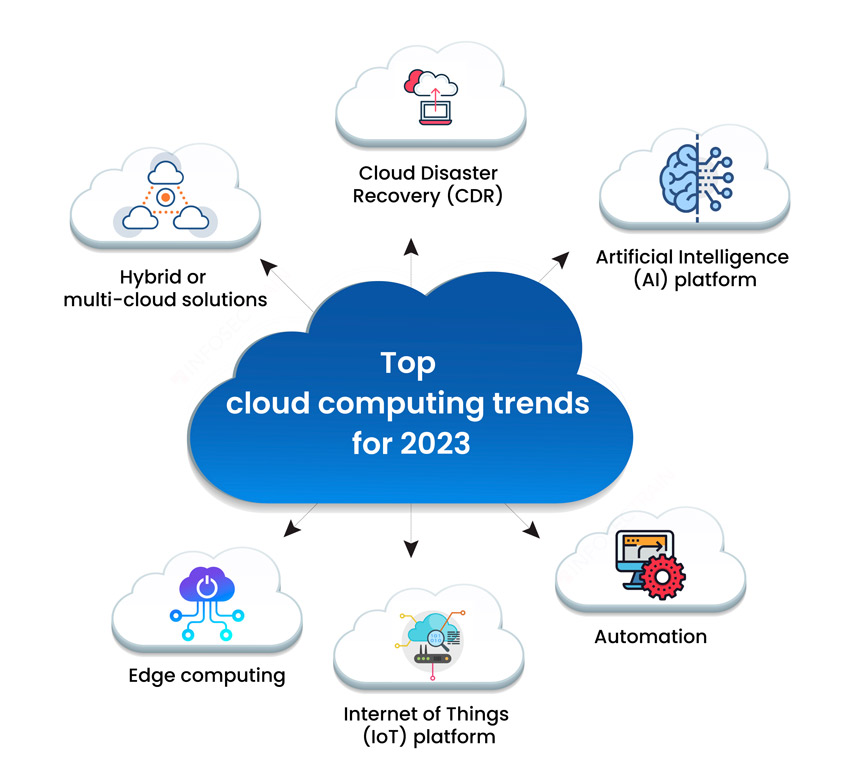
Current Trends in Cloud Computing
Multi-Cloud Adoption
As organizations strive for resilience and flexibility, the trend of multi-cloud adoption has gained momentum. Companies are no longer relying on a single cloud provider; they are leveraging the strengths of multiple services. This approach provides:
- Reduced Vendor Lock-in: Avoiding dependence on one provider.
- Optimized Costs: Selecting services based on pricing and performance.
- Enhanced Redundancy: Ensuring operations can continue seamlessly, even during outages.
This methodology allows businesses to create a tailored cloud environment that best suits their unique needs.
Edge Computing
Closely interwoven with multi-cloud strategies is the rise of edge computing. By processing data closer to its source—think IoT devices—companies can enhance real-time decision-making and reduce latency. An example is smart cities utilizing edge computing to manage traffic lights based on real-time data; this not only optimizes traffic flow but also promotes efficiency in urban planning.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
Lastly, integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into cloud computing is transforming data analysis. Organizations are harnessing cloud capabilities to:
- Analyze Large Datasets: Uncover valuable insights.
- Automate Processes: Streamline operations and improve accuracy.
These technologies enable businesses to make data-driven decisions more efficiently, showcasing how the future of cloud computing is increasingly intelligent and interconnected.

Security and Compliance in Cloud Computing
Data Privacy and Governance
With the rapid growth of cloud computing, ensuring data privacy and governance is paramount. Organizations must navigate a complex landscape of data ownership, usage, and protection. Establishing robust data governance policies is essential to ensure compliance with regulations and maintain customer trust. For example:
- Data Classification: Identify sensitive data and apply appropriate protection measures.
- Access Controls: Implement role-based access to safeguard critical information.
Adopting these practices helps organizations uphold their commitments to data privacy.
Compliance Regulations in Cloud Computing
Compliance regulations are continuously evolving, adding another layer of complexity for businesses. Regulations like GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in the United States mandate strict guidelines for data handling and storage. Companies must be proactive by:
- Conducting regular compliance audits.
- Utilizing certified cloud providers to ensure adherence to standards.
- Training employees on compliance requirements and best practices.
By staying ahead of these regulations, organizations can avoid costly penalties and reputational damage.
Identity and Access Management in the Cloud
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a crucial component of cloud security. Definitive control over user identities ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive systems. Effective IAM strategies include:
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Simplifies user experience while maintaining security.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra security layer against unauthorized access.
Through a comprehensive IAM approach, businesses can significantly fortify their cloud security, paving the way for a trustworthy environment that enhances the future of cloud computing.

Future Innovations in Cloud Computing
Serverless Computing
As we look to the future of cloud computing, serverless computing stands out as a game-changer. This approach allows developers to build and run applications without managing servers, simplifying deployment and scaling. For instance, if a startup launches an app that experiences sudden popularity, serverless computing automatically scales the necessary resources without manual intervention. Key benefits include:
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for the compute resources used.
- Increased Agility: Focus more on coding and less on infrastructure management.
Quantum Computing and its Impact
While still in its infancy, quantum computing promises to revolutionize cloud services. By leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics, this technology could dramatically increase processing power. This means organizations could solve complex problems—such as optimization and encryption—much faster than ever before. Consider companies in finance utilizing quantum algorithms to perform risk assessments in real time. The potential is enormous.
Cloud-Native Technologies
Finally, cloud-native technologies are reshaping application development. They enable organizations to build, scale, and manage applications in dynamic environments. Tools like Kubernetes for container orchestration are gaining traction, allowing deployable units to function together seamlessly. This methodology enhances:
- Resilience: Applications can withstand failures more effectively.
- Speed: Continuous deployment ensures that updates are faster and more reliable.
All these innovations underscore how the future of cloud computing is not just about storage and computing power—it’s about creating an ecosystem where businesses can thrive and innovate without boundaries.

Challenges and Opportunities in Cloud Computing
Scalability Challenges
While cloud computing offers remarkable scalability, it isn’t without its challenges. As businesses grow and their needs change, managing resource consumption can become complex. For instance, a retail company during the holiday season may experience a surge in traffic; if not anticipated, this can lead to performance issues or even downtime. Companies must adopt strategies such as:
- Load Balancing: Distributing workloads across multiple servers.
- Auto-Scaling: Automatically adjusting resources based on traffic demands.
These measures ensure that scalability enhances user experience rather than hindering it.
Cost Management Strategies
Cost management is another critical challenge in cloud computing. Without careful monitoring, cloud expenses can spiral out of control. To navigate this, businesses can implement strategies like:
- Cost Monitoring Tools: Utilize analytics to track cloud usage.
- Budgeting: Set and adhere to budgets for different departments.
By being proactive, organizations can maximize their investment while optimizing their resources.
Skills and Workforce Development in Cloud Computing
Lastly, the rapid evolution of cloud technologies necessitates a skilled workforce. While opportunities are ripe for those with cloud expertise, there remains a significant skills gap. Companies can bridge this by:
- Investing in Training Programs: Facilitate ongoing education and certifications.
- Encouraging Knowledge Sharing: Foster a culture of collaboration through mentoring.
By prioritizing skills development, organizations not only enhance their internal capabilities but also position themselves competitively in a fast-paced market, illustrating that challenges in cloud computing come with opportunities for growth and innovation.

Sustainable Practices in Cloud Computing
Green Cloud Computing
As organizations embrace cloud technology, the importance of sustainable practices in cloud computing has become increasingly clear. Green cloud computing focuses on reducing environmental impact while optimizing energy efficiency. For instance, companies are now opting for energy-efficient data centers equipped with advanced cooling systems and virtualization technologies. Benefits include:
- Lower Energy Consumption: Reducing costs and environmental footprints.
- Sustainable Resource Use: Utilizing eco-friendly materials in production.
By adopting these practices, businesses can contribute to a safer planet while still enjoying the advantages of cloud computing.
Renewable Energy Integration
Integration of renewable energy sources into cloud operations is another pivotal milestone. Major cloud providers are committing to powering their data centers with renewable energy, making substantial strides toward carbon neutrality. Companies like Google and Microsoft are leading this charge, investing in wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. This shift not only minimizes reliance on fossil fuels but also sets an industry standard.
Carbon Footprint Reduction Initiatives
Finally, cloud computing can actively support carbon footprint reduction initiatives. Many organizations are now tracking their carbon emissions and working toward reductions by shifting to hybrid or fully cloud-based models. By utilizing advanced analytics and reporting tools, they can:
- Monitor Emissions: Identify high-impact areas for targeted improvements.
- Set Goals: Implement achievable sustainability objectives.
Through these sustainable practices, the cloud computing industry is not just innovating; it is also reinforcing a commitment to a greener future. With these initiatives, companies are demonstrating that technology can harmonize with environmental stewardship to foster a brighter tomorrow.

