
Introduction
Definition of Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Security
The Shared Responsibility Model in cloud security defines the division of responsibilities between cloud service providers (CSPs) and their customers. Essentially, it illustrates that while CSPs are responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure, customers must safeguard their data and applications within this infrastructure. This model ensures clarity on who handles what, leading to a more secure environment for all parties involved.
Significance of Shared Responsibility Model
Understanding the significance of the Shared Responsibility Model is crucial for effective cloud security. This framework mitigates risks and enhances compliance by:
- Allowing clear role definition to avoid security blind spots.
- Reducing the potential for data breaches by ensuring all parties understand their duties.
- Encouraging proactive security measures tailored to unique business needs.
By grasping these responsibilities, organizations can strengthen their security posture and trust their cloud solutions.

Components of Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud Service Provider’s Responsibilities
Continuing from our earlier discussions, it’s essential to delve deeper into the specific responsibilities outlined in the Shared Responsibility Model. For Cloud Service Providers (CSPs), their obligations largely include:
- Physical Security: Protection of data centers and network infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Security: Ensuring that the core cloud services are secured against vulnerabilities and threats.
- Patch Management: Regular updates and patches to systems to mitigate risks.
CSPs aim to create a secure foundation for their customers, allowing them to focus on their unique needs.
Customer’s Responsibilities
On the flip side, customers hold significant responsibilities as well, such as:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
- Access Controls: Managing user permissions to restrict access based on roles.
- Application Security: Ensuring that applications deployed on the cloud are free from vulnerabilities.
By understanding these responsibilities, organizations can actively contribute to safeguarding their assets and minimizing risks in the cloud environment.

Understanding the Division of Responsibilities
Detailed Analysis of CSP’s Responsibilities
Building upon the previous sections, it’s important to explore in greater detail the responsibilities of Cloud Service Providers (CSPs). CSPs ensure the integrity and availability of the cloud infrastructure. Their key responsibilities include:
- Network Security: Implementing measures to protect the cloud network from threats.
- Data Center Management: Maintaining physical security and environmental controls at data centers.
- Compliance Support: Offering compliance certifications and adhering to regulatory requirements.
These responsibilities create a safe environment for organizations to operate.
Breakdown of Customer’s Responsibilities
Conversely, customers are tasked with several critical responsibilities to maintain security. These include:
- User Management: Regularly updating user access levels and monitoring activities.
- Data Backup: Implementing robust backup solutions to prevent data loss.
- Incident Response: Developing a plan for responding to security incidents promptly.
By clearly understanding these divisions, organizations can take proactive steps to enhance their overall cloud security.
Navigating Security Challenges Within the Model
Risks Associated with Shared Responsibility
As organizations embrace the Shared Responsibility Model, they must also recognize the security challenges it presents. Some key risks include:
- Misunderstandings of Responsibilities: Gaps in knowledge can lead to weakened security postures.
- Data Breaches: Customers may fail to adequately secure their data, leading to vulnerabilities.
- Shared Cloud Risks: Attacks on the cloud provider can affect all customers reliant on the service.
These challenges highlight the importance of clear communication.
Mitigation Strategies for Enhanced Security
To navigate these challenges, organizations can adopt several strategies:
- Regular Training: Educate teams about their responsibilities within the model.
- Robust Security Policies: Implement clear policies for data management and access control.
- Continuous Monitoring: Use tools to monitor system activity and detect suspicious behavior.
By proactively addressing these risks, organizations can bolster their cloud security and ensure a safer digital journey.

Ensuring Compliance and Accountability
Regulatory Compliance Within the Model
Continuing from the discussion of security challenges, compliance with regulations is a significant aspect of the Shared Responsibility Model. Organizations must ensure they adhere to industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. This compliance can be challenging because:
- Data Location: Knowing where data is stored can affect compliance with local laws.
- Understanding Regulations: Awareness of specific regulations can be complex and varies by industry.
Therefore, collaborating closely with CSPs is essential to ensure compliance is met consistently.
Accountability Measures for Both Parties
To maintain accountability within this model, both CSPs and customers must:
- Establish Clear Contracts: Define roles and responsibilities in service agreements.
- Document Security Protocols: Keep records of security practices and compliance measures.
- Regular Audits: Conduct audits to ensure adherence to standards and improve processes.
By integrating these accountability measures, both parties can foster a culture of transparency and security, ultimately strengthening their partnership.

Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Application of Shared Responsibility Model
To grasp the true impact of the Shared Responsibility Model, examining real-world applications can be quite enlightening. For instance, a major cloud provider partnered with a large retail company:
- CSP’s Role: Ensured secure infrastructure and offered compliance certifications.
- Customer’s Role: Managed customer data and enforced access controls.
This collaboration not only strengthened security but also enhanced customer trust.
Lessons Learned from Past Incidents
Reflecting on past security incidents reveals vital lessons. Take the high-profile data breach of a cloud application:
- Over-Focused on CSP: The customer assumed the CSP was solely responsible for data security.
- Outcome: The incident exposed sensitive customer data due to poor access management by the customer.
The key takeaway? Both parties must actively engage and understand their security roles to prevent vulnerabilities, highlighting the importance of proactive communication and vigilance in the cloud environment.

Future Trends and Evolving Practices
Emerging Trends in Cloud Security
As we look ahead, it’s essential to recognize some key emerging trends in cloud security that are shaping the landscape. For instance, organizations are increasingly adopting:
- Zero Trust Architectures: This strategy ensures that no user, whether inside or outside the organization, is automatically trusted.
- AI-Driven Security Solutions: Artificial intelligence is being used to detect anomalies and automate responses to potential threats.
- Cloud-Native Security: As more services migrate to the cloud, security tools are being developed specifically for cloud environments.
These trends reflect the increased sophistication of cyber threats and the need for proactive security measures.
Evolution of Shared Responsibility Models
Alongside these trends, the Shared Responsibility Model itself is evolving. As customers demand more from their CSPs, the model is adapting to include:
- Greater Clarity on Responsibilities: More detailed agreements that specify security tasks.
- Enhanced Compliance Features: Tools that help customers maintain regulatory compliance seamlessly.
- Collaboration Enhancements: Improved communication channels between CSPs and customers to address emerging security challenges.
In embracing these evolving practices, organizations can better navigate the complexities of cloud security and ensure a robust defense against future threats.
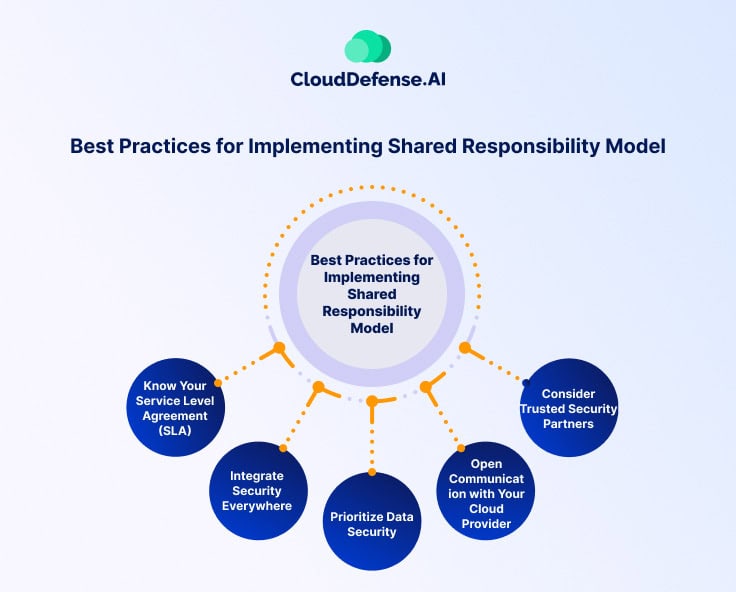
Conclusion
Recap of Key Takeaways
Wrapping up, it’s clear that understanding the Shared Responsibility Model is essential for effective cloud security. Key takeaways include:
- Defined Roles: Both CSPs and customers play crucial roles in maintaining security.
- Ongoing Education: Regular training and awareness are vital for staying ahead of threats.
- Compliance Matters: Keeping up with regulatory requirements ensures a secure environment.
These insights highlight the importance of collaboration and clarity in responsibilities.
Final Considerations for Effective Cloud Security
As organizations navigate their cloud journeys, they should consider:
- Adaptability: Be prepared to adjust security strategies in response to emerging threats.
- Proactive Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with CSPs regarding security issues.
- Investing in Security Tools: Leverage the latest technologies to strengthen defenses.
By implementing these considerations, businesses can foster a secure cloud environment, ultimately leading to greater trust and success in their digital operations.

