
Introduction
Definition of Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and interact with one another seamlessly. Picture this: you have various islands (blockchains) in an ocean (the digital world), and interoperability serves as the bridges connecting these islands. This connection allows for the transfer of assets, data, and information across distinct blockchain platforms, enabling a more integrated and efficient ecosystem.
In practical terms, interoperability means that a token on Ethereum could be exchanged for another token on Binance Smart Chain without needing a cumbersome process. It opens doors for decentralized applications (dApps) to utilize multiple blockchains’ strengths while mitigating their limitations.
Significance of Blockchain Interoperability
The significance of blockchain interoperability can’t be overstated. In an era where blockchain technology is becoming increasingly prevalent, interconnectedness among various platforms fosters the following benefits:
- Enhanced Collaboration: Different blockchains can pool resources and innovate, much like diverse teams coming together to solve complex problems.
- Increased User Accessibility: Users can engage with multiple platforms without the hassle of navigating through numerous interfaces, streamlining their experience.
- Boosted Market Value: As networks become interconnected, the overall market value of the blockchain ecosystem can flourish.
In essence, embracing blockchain interoperability is akin to building a vibrant, interconnected community where everyone thrives together, which is precisely what the blog TECHFACK aims to foster in its discussions on emerging technologies.

Importance of Blockchain Interoperability
Enhancing Scalability
One of the most significant benefits of blockchain interoperability is its potential to enhance scalability. Imagine you’re hosting a party, and your living room can only fit a handful of guests. If you open up your backyard, suddenly you can accommodate many more friends. Similarly, interoperability allows blockchains to share the workload, which alleviates congestion and makes transactions faster.
- Load Balancing: By distributing transactions across multiple networks, it reduces the strain on any single blockchain.
- Increased Throughput: Interconnected systems can collectively handle a larger volume of transactions without slowing down.
Improving Security
Blockchain interoperability can also improve overall security. When different blockchains work together, they can leverage the security features of each other. Think of it as a team of superheroes; each hero has unique abilities that complement one another.
- Redundancy: If one blockchain faces a threat, the interconnected networks can step in, preventing potential losses.
- Diverse Security Protocols: The variance in security mechanisms provides multiple layers of defense, enhancing overall reliability.
Promoting Innovation
Lastly, interoperability fosters innovation across the blockchain landscape. With different networks collaborating, developers can create exciting new applications that weren’t possible in siloed environments.
- Creative Solutions: Developers can mix and match functionalities from various blockchains, leading to groundbreaking dApps.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Teams can come together from various backgrounds, sending innovation into overdrive.
As we journey further into the world of blockchain technology, bridging these networks continues to unlock new possibilities, driving us toward a more connected digital future.
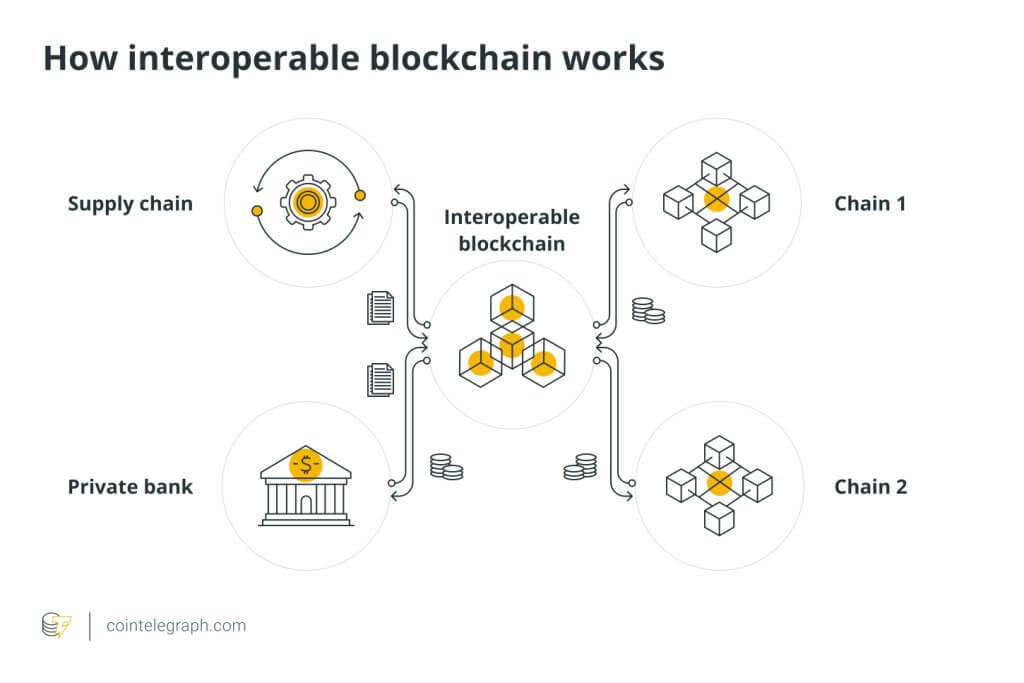
How Blockchain Interoperability Works
Understanding Protocols and Standards
To achieve blockchain interoperability, understanding protocols and standards is paramount. Protocols act as the rules of engagement, ensuring different blockchains can understand one another. It’s like speaking a common language at a multi-national conference.
- Common Protocols: Technologies such as the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol offer a blueprint for blockchains to transmit data.
- Standardization: Adopting standardized methods ensures that participants can access and validate across networks, promoting a harmonious exchange.
Cross-Chain Communication Mechanisms
Cross-chain communication mechanisms serve as the bridges connecting various blockchain platforms. Think of these as highways that allow vehicles (data or assets) to travel between cities (blockchains).
- Message Passing: This approach uses scripts or messages to convey operations and data between different blockchains.
- Atomic Networks: These ensure that transactions happen simultaneously across different platforms, eliminating the risk of incomplete or flawed exchanges.
Smart Contracts and Atomic Swaps
Smart contracts and atomic swaps take blockchain interoperability to the next level. These mechanisms automate agreements and transactions, saving time and reducing human error. Picture it as a vending machine—insert the right coins, and your selected item drops without a hitch.
- Smart Contracts: Automatically execute actions based on pre-set conditions, enabling seamless interactions without intermediaries.
- Atomic Swaps: Allow for the direct exchange of different cryptocurrencies between users, ensuring both parties receive their assets without third-party reliance.
In summary, understanding how these components work together is crucial in paving the way for a future where blockchains can operate fluidly side by side. With each piece working in harmony, the vision for a connected blockchain ecosystem is within reach.

Challenges in Achieving Blockchain Interoperability
Scalability Issues
While the benefits of blockchain interoperability are immense, several challenges must be addressed to realize its full potential. One of the primary hurdles is scalability. Just imagine a user trying to join a popular online game during peak hours; the server may lag or crash due to overwhelming demand.
- Transaction Volume: As more blockchains connect, the overall volume of transactions can skyrocket, straining network capacities.
- Latency: Delays in communication between interconnected blockchains can lead to slower transaction times, which can be frustrating for users.
Security Concerns
Another significant challenge is security. The more interconnected systems become, the more vulnerabilities can arise. Think of your home—every door you open creates a potential risk, and the same applies to blockchain networks.
- Cross-Chain Vulnerabilities: Connecting different blockchains may expose them to various attack vectors that each individual blockchain might not face alone.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring sensitive information remains secure across different platforms is crucial, requiring robust encryption and privacy measures.
Regulatory Compliance
Lastly, navigating the regulatory landscape poses its own set of challenges. Each blockchain may be governed by different laws and regulations—like trying to follow multiple traffic rules when driving through different countries.
- Diverse Legal Frameworks: Creating a cohesive system that adheres to diverse regulatory standards is a complex task.
- Compliance Costs: Ensuring that all transactions comply with legal guidelines can lead to increased operational costs.
In conclusion, while the journey toward blockchain interoperability is promising, it also demands careful navigation through scalability, security, and regulatory challenges. Addressing these issues head-on will be crucial for fostering a reliable and efficient interconnected blockchain ecosystem.

Solutions for Blockchain Interoperability
Interoperability Projects and Initiatives
As we navigate the challenges surrounding blockchain interoperability, numerous projects and initiatives are coming to the forefront, working actively to bridge the gaps. These initiatives help create cohesive ecosystems, much like how community programs bring people together for a common goal.
- Polkadot: This project enables different blockchains to communicate and share information by using a shared security model, similar to a neighborhood watch.
- Cosmos: It offers a framework for different blockchains to interoperate seamlessly, creating an “Internet of Blockchains.”
These projects are paving the way toward a more integrated blockchain future, demonstrating the collective effort in the space.
Role of Bridges and Oracles
In this movement, bridges and oracles play pivotal roles. Think of them as the skilled interpreters who ensure that two people speaking different languages can understand each other.
- Bridges: These are mechanisms that facilitate transferring assets and data between separate blockchains. They function seamlessly, allowing for one-click transactions.
- Oracles: They act as data providers, supplying smart contracts with real-world information—essential for triggering actions across blockchains.
Future Outlook for Interconnected Blockchains
Looking ahead, the outlook for interconnected blockchains is exciting. Imagine a future where various blockchains operate like interconnected highways, each offering a unique journey while providing easy access to every destination.
- Innovative Applications: With multiple blockchains cooperating, innovative applications will emerge, fostering creativity and efficiency.
- Global Adoption: As interoperability becomes standard, we can expect more widespread adoption across industries, from finance to supply chain management.
In summary, with ongoing initiatives, the pivotal role of bridges and oracles, and a bright outlook for the future, the path toward blockchain interoperability is becoming clearer. Embracing these solutions will not only enhance user experiences but also revolutionize how we interact with digital assets and applications.

